Abstract
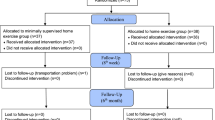
Background and aims: Falls are particularly common among older people living in residential care facilities. The aim of this randomized controlled trial was to evaluate the effectiveness of a high-intensify functional exercise program in reducing falls in residential care facilities. Methods: Participants comprised 191 older people, 139 women and 52 men, who were dependent in activities of daily) living. Their mean±SD score on the Mini-Mental State Examination was 17.8±5.1 (range 10–30). Participants were randomized to a high-intensity functional exercise program or a control activity, consisting of 29 sessions over 3 months. The fall rate and proportion of participants sustaining a fall were the outcome measures, subsequently analysed using negative binominal analysis and logistic regression analysis, respectively. Results: During the 6-month follow-up period, when all participants were compared, no statistically significant differences between groups were found for fall rate (exercise group 3.6 falls per person years [PY], control group 4.6 falls per PY), incidence rate ratio (95% CI) 0.82 (0.49−1.39), p=0.46, or the proportion of participants sustaining a fall (exercise 53%, control 51%), odds ratio (95% CI) 0.95 (0.52−1.74), p=0.86. A subgroup interaction analysis revealed that, among participants who improved their balance during the intervention period, the exercise group had a lower fall rate than the control group (exercise 2.7 falls per PY, control 5.9 falls per PY), incidence rate ratio (95% CI) 0.44 (0.21−0.91), p=0.03. Conclusions: In older people living in residential care facilities, a high-intensity functional exercise program may prevent falls among those who improve their balance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tinetti ME, Speechley M, Ginter SF. Risk factors for falls among elderly persons living in the community. N Engl J Med 1988; 319: 1701–7.
Luukinen H, Koski K, Hiltunen L, Kivelä SL. Incidence rate of falls in an aged population in northern Finland. J Clin Epidemiol 1994; 47: 843–50.
O’Loughlin JL, Robitaille Y, Boivin JF, Suissa S. Incidence of and risk factors for falls and injurious falls among the community-dwelling elderly. Am J Epidemiol 1993; 137: 342–54.
Nevitt MC, Cummings SR, Kidd S, Black D. Risk factors for recurrent nonsyncopal falls. A prospective study. JAMA 1989; 261: 2663–8.
Sattin RW. Mullins RJ. Geriatric trauma: the continuing epidemic. J Am Geriatr Soc 2002; 50: 394–5.
Vellas BJ, Wayne SJ, Romero LJ, Baumgartner RN, Garry PJ. Fear of falling and restriction of mobility in elderly fallers. Age Ageing 1997; 26: 189–93.
Cumming RG, Salkeld G, Thomas M, Szonyi G. Prospective study of the impact of fear of falling on activities of daily living, SF-36 scores, and nursing home admission. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2000; 55: M299–305.
Delbaere K, Crombez G, Vanderstraeten G, Willems T, Cambier D. Fear-related avoidance of activities, falls and physical frailty. A prospective community-based cohort study. Age Ageing 2004; 33: 368–73.
Kallin K, Jensen J, Lundin-Olsson L, Nyberg L, Gustafson Y. Why the elderly fall in residential care facilities, and suggested remedies. J Fam Pract 2004; 53: 41–52.
Luukinen H, Koski K, Honkanen R, Kivelä SL. Incidence of injurycausing falls among older adults by place of residence: a population-based study. J Am Geriatr Soc 1995; 43: 871–6.
Masud T, Morris RO. Epidemiology of falls. Age Ageing 2001; 30 (Suppl 4): 3–7.
Tinetti ME. Clinical practice. Preventing falls in elderly persons. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 42–9.
Chang JT, Morton SC, Rubenstein LZ, et al. Interventions for the prevention of falls in older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. BMJ 2004; 328: 680–3.
Gillespie LD, Gillespie WJ, Robertson MC, Lamb SE, Cumming RG, Rowe BH. Interventions for preventing falls in elderly people. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003: CD000340.
Rubenstein LZ, Robbins AS, Josephson KR, Schulman BL, Os-terweil D. The value of assessing falls in an elderly population. A randomized clinical trial. Ann Intern Med 1990; 113: 308–16.
Becker C, Kron M, Lindemann U, et al. Effectiveness of a multifaceted intervention on falls in nursing home residents. J Am Geriatr Soc 2003; 51: 306–13.
Kerse N, Butler M, Robinson E, Todd M. Fall prevention in residential care: a cluster, randomized, controlled trial. J Am Geriatr Soc 2004; 52: 524–31.
Dyer CA, Taylor GJ, Reed M, Robertson DR, Harrington R. Falls prevention in residential care homes: a randomised controlled trial. Age Ageing 2004; 33: 596–602.
Jensen J, Lundin-Olsson L, Nyberg L, Gustafson Y. Fall and injury prevention in older people living in residential care facilities. A cluster randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 2002; 136: 733–41.
McMurdo ME, Millar AM, Daly F. A randomized controlled trial of fall prevention strategies in old peoples’ homes. Gerontology 2000; 46: 83–7.
Schnelle JF, Kapur K, Alessi C, et al. Does an exercise and incontinence intervention save healthcare costs in a nursing home population? J Am Geriatr Soc 2003; 51: 161–8.
Latham NK, Bennett DA, Stretton CM, Anderson CS. Systematic review of progressive resistance strength training in older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2004; 59: 48–61.
Day L, Fildes B, Gordon I, Fitzharris M, Ramer H, Lord S. Randomised factorial trial of falls prevention among older people living in their own homes. BMJ 2002; 325: 128–31.
Robertson MC, Devlin N, Gardner MM, Campbell AJ. Effectiveness and economic evaluation of a nurse delivered home exercise programme to prevent falls. 1: Randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2001; 322: 697–701.
Campbell AJ, Robertson MC, Gardner MM, Norton RN, Tilyard MW, Buchner DM. Randomised controlled trial of a general practice programme of home based exercise to prevent falls in elderly women. BMJ 1997; 315: 1065–9.
Skelton D, Dinan S, Campbell M, Rutherford O. Tailored group exercise (Falls Management Exercise — FaME) reduces falls in community-dwelling older frequent fallers (an RCT). Age Ageing 2005; 34: 636–9.
Barnett A, Smith B, Lord SR, Williams M, Baumand A. Community-based group exercise improves balance and reduces falls in at-risk older people: a randomised controlled trial. Age Ageing 2003; 32: 407–14.
Lord SR, Castell S, Corcoran J, et al. The effect of group exercise on physical functioning and falls in frail older people living in retirement villages: a randomized, controlled trial. J Am Geriatr Soc 2003; 51: 1685–92.
Mulrow CD, Gerety MB, Kanten D, et al. A randomized trial of physical rehabilitation for very frail nursing home residents. JAMA 1994; 271: 519–24.
Nowalk MP, Prendergast JM, Bayles CM, D’Amico FJ, Colvin GC. A randomized trial of exercise programs among older individuals living in two long-term care facilities: the FallsFREE program. J Am Geriatr Soc 2001; 49: 859–65.
Sihvonen SE, Sipilä S, Era PA. Changes in postural balance in frail elderly women during a 4-week visual feedback training: a randomized controlled trial. Gerontology 2004; 50: 87–95.
Sihvonen S, Sipilä S, Taskinen S, Era P. Fall incidence in frail older women after individualized visual feedback-based balance training. Gerontology 2004; 50: 411–6.
Rosendahl E, Lindelöf N, Littbrand H, et al. A high-intensity functional exercise program and a protein-enriched energy supplement for older persons dependent in ADL: a randomised controlled trial. Aust J Physiother 2006; 52: 105–13.
Katz S, Ford AB, Moskowitz RW, Jackson BA, Jaffe MW. Studies of Illness in the Aged. The index of ADL: a standardized measure of biological and psychosocial function. JAMA 1963; 185: 914–9.
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. Mini-Mental State. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of the patient for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 1975; 12: 189–98.
Littbrand H, Rosendahl E, Lindelöf N, Lundin-Olsson L, Gustafson Y, Nyberg L. A high-intensity functional weight-bearing exercise program for older people dependent in activities of daily living and living in residential care facilities: evaluation of the applicability with focus on cognitive function. Phys Ther 2006; 86: 489–98.
DeLorme TL. Restoration of muscle power by heavy-resistance exercises. J Bone Joint Surg 1945; 27: 645–67.
Mahoney FI, Barthel DW. Functional evaluation: the Barthel Index. Maryland State Med J 1965; 14: 61–5.
Wade DT. Measurement in neurological rehabilitation. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1992.
Guralnik JM, Simonsick EM, Ferrucci L, et al. A short physical performance battery assessing lower extremity function: association with self-reported disability and prediction of mortality and nursing home admission. J Gerontol 1994; 49: M85–94.
Berg KO, Wood-Dauphinee SL, Williams JI, Maki B. Measuring balance in the elderly: validation of an instrument. Can J Public Health 1992; 83 (Suppl 2): S7–11.
Berg K, Wood-Dauphinee S, Williams JI. The Balance Scale: reliability assessment with elderly residents and patients with an acute stroke. Scand J Rehabil Med 1995; 27: 27–36.
Sheikh JI, Yesavage JA. Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS): recent evidence and development of a shorter version. Clin Gerontol 1986; 5: 165–72.
Guigoz Y, Vellas B, Garry PJ. Mini Nutritional Assessment: a practical assessment tool for grading the nutritional state of elderly patients. Facts and Research in Gerontology 1994; (Suppl 2): 15–59.
Robertson MC, Campbell AJ, Herbison P. Statistical analysis of efficacy in falls prevention trials. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2005; 60: 530–4.
Kerry SM, Bland JM. The intracluster correlation coefficient in cluster randomisation. BMJ 1998; 316: 1455.
Campbell MK, Elbourne DR, Altman DG. CONSORT statement: extension to cluster randomised trials. BMJ 2004; 328: 702–8.
Lavery LL, Studenski SA. Tai chi, falls, and the heritage of JAGS. J Am Geriatr Soc 2003; 51: 1804–5.
Shaw FE, Bond J, Richardson DA, et al. Multifactorial intervention after a fall in older people with cognitive impairment and dementia presenting to the accident and emergency department: randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2003; 326: 73–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosendahl, E., Gustafson, Y., Nordin, E. et al. A randomized controlled trial of fall prevention by a high-intensity functional exercise program for older people living in residential care facilities. Aging Clin Exp Res 20, 67–75 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03324750
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03324750