Summary
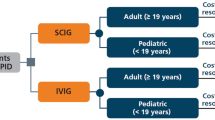
The aim of this study was to assess the costs of immunoglobulin treatment in patients with antibody deficiencies from the perspective of the Tuscany Health Service. We conducted a Cost-Minimization Analysis (CMA) to compare the annual costs of subcutaneous immunoglobulins (SCIG) vs. intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIG). We built a model in which two cohorts of patients received SCIG or IVIG. The model observed the patients for 12 months and was populated using data from Careggi’s Immunoallergology Centre. The model considered only direct medical costs (immunoglobulin, premedication, infusion pump, infusion materials, medical staff, ambulatory). Sensitivity analysis on key economic parameters were performed. SCIG showed the best expected cost versus IVIG of € 15,195.91 and € 17,408.89, respectively. The difference in favour of SCIG (€ 2,212.98) is made by lower costs both for medical staff and ambulatory. This economic evaluation showed that SCIG is a cost-saving strategy compared with IVIG in the treatment of patients with antibody deficiencies from the perspective of the Tuscany Health Service.
Similar content being viewed by others
Bibliografia
Smith CIE, Ochs HD, Puck JM. Genetically determined immunodeficiency diseases: a perspective. In: Ochs HD, Smith CIE, Puck JM (Eds.). Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases, a Molecular and Genetic Approach. 2nd ed. New York: Oxford University Press, 2007: pp. 3–15
Chapel HM. Consensus Panel for the Diagnosis and Management of Primary Antibody Deficiencies. Consensus on diagnosis and management of primary antibody deficiencies. BMJ 1994; 308: 581–5
Rosen FS, Eibl M, Roifman C, et al. Primary immunodeficiency diseases. Report of an IUIS Scientific Committee. Clin Exp Immunol 1999; 118 (Suppl. 1): 1–28
Notarangelo L, Cassanova JL, Fischer A, et al. Primary immunodeficiency diseases: an update. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2004; 114: 667–87
Chapel HM, Spickett GP, Ericson D, et al. The comparison of the efficacy and safety of intravenous versus subcutaneous immunoglobulin replacement therapy. J Clin. Immunol 2000; 20: 94–100
Gardulf A, Nicolay U, Asensio O, et al. Rapid subcutaneous IgG replacement therapy is effective and safe in children and adults with primary immunodeficiencies: a prospective, multi-national study. J Clin Immunol 2006; 26: 177–85
Ochs HD, Gupta S, Kiessling P, et al. Safety and efficacy of self-administered subcutaneous immunoglobulin in patients with primary immunodeficiency diseases. J Clin Immunol 2006; 26: 265–73
Toubi E, Etzioni A. Intravenous immunoglobulin in immunodeficiency states: state of the art. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 2005; 29: 167–72
Berger M. Subcutaneous immunoglobulin replacement in primary immuno-eficiencies, Clin Immunol 2004; 112: 1–7
Gardulf A, Björvell H, Andersen V, et al. Lifelong treatment with gammaglobulin for primary antibody deficiencies: the patients’ experiences of subcutaneous self-infusions and home therapy. J Adv Nurs 1995; 21: 917–27
Hansen S, Gustafson R, Smith CIE, et al. Express subcutaneous IgG infusions: decreased time of delivery with maintained safety. Clin Immunol 2002; 14: 237–41
Drummond MF, O’Brien BJ, Stoddart GL, Torrance GW. (Edizione italiana a cura di Fattore G, Garattini L, Lucioni C). Metodi per la valutazione economica dei programmi sanitari. Roma: Il Pensiero Scientifico Editore, 2000
Gardulf A, Andersen V, Björkander J, et al. Subcutaneous immunoglobulin replacement in patients with primary antibody deficiencies: safety and costs. Lancet 1995; 345: 365–9
Högy B, Keinecke HO, Borte M. Pharmacoeconomic evaluation of immunoglobulin treatment in patients with antibody deficiencies from the perspective of the German statutory health insurance. Eur J Health Econ 2005; 6: 24–9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matucci, A., Ravasio, R., Vultaggio, A. et al. Analisi di minimizzazione dei costi della terapia con immunoglobuline (Ig) per il trattamento di pazienti con immunodeficienza primaria: confronto tra terapia con Ig sottocute vs endovena. G. Ital. Health Technol. Assess 1, 31–37 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03320711
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03320711