Abstract
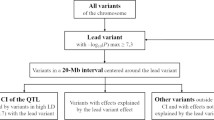
The progress in molecular genetics in animal breeding is moderately effective as compared to traditional animal breeding using quantitative genetic approaches. There is an extensive disparity between the number of reported quantitative trait loci (QTLs) and their linked genetic variations in cattle, pig, and chicken. The identification of causative mutations affecting quantitative traits is still very challenging and hampered by the cloudy relationship between genotype and phenotype. There are relatively few reports in which a successful identification of a causative mutation for an animal production trait was demonstrated. The examples that have attracted considerable attention from the animal breeding community are briefly summarized and presented in a table. In this mini-review, the recent progress in mapping quantitative trait nucleotides (QTNs) are reviewed, including theABCG2 gene mutation that underlies a QTL for fat and protein content and the ovineMSTN gene mutation that causes muscular hypertrophy in Texel sheep. It is concluded that the progress in molecular genetics might facilitate the elucidation of the genetic architecture of QTLs, so that also the high-hanging fruits can be harvested in order to contribute to efficient and sustainable animal production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson L, Georges M, 2004. Domestic-animal genomics: deciphering the genetics of complex traits. Nat Rev Genet 5: 202–212.
Bellinge RHS, Liberles DA, Iaschi SPA, O’Brien A, Tay GK, 2005. Myostatin and its implications on animal breeding. Anim Genet 36: 1–6.
Boman IA, Klemetsdal G, Blichfeldt T, Nafstad O, Víge DI, 2009. A frameshift mutation in the coding region of the myostatin gene (MSTN) affects carcass conformation and fatness in Norwegian White Sheep (Ovis aries). Anim Genet 40: 41–422.
Boman IA, Klemetsdal G, Nafstad O, Blichfeldt T, Víge DI, 2010. Impact of two myostatin (MSTN) mutations on weight gain and lamb carcass classification in Norwegian White Sheep (Ovis aries). Genet Sel Evol 42: 4.
Braunschweig MH, Van Laere A-S, Buys N, Andersson L, Andersson G, 2004.IGF2 antisense transcript expression in porcine postnatal muscle is affected by a quantitative trait nucleotide in intron 3. Genomics 84: 1021–1029.
Carlborg O, and Haley CS, 2004. Epistasis: too often neglected in complex trait studies? Nat Rev Genet 5: 618–625.
Carlborg O, Jacobsson L, Ahgren P, Siegel P, Andersson L, 2006. Epistasis and the release of genetic variation during long-term selection. Nat Genet 38: 418–420.
Charlier C, Coppieters W, Rollin F, Desmecht D, Agerholm JS, Cambisano N, et al. 2008. Highly effective SNP-based association mapping and management of recessive defects in livestock. Nat Genet 40: 449–454.
Clop A, Marcq F, Takeda H, Pirottin D, Tordoir X, Bibé B, et al. 2006. A mutation creating a potential illegitimate microRNA target site in the myostatin gene affects muscularity in sheep. Nat Genet 38: 813–818.
Cohen-Zinder M, Seroussi E, Larkin DM, Loor JJ, Everts-van der Wind A, Lee JH, Drackley JK, et al. 2005. Identification of a missense mutation in the bovineABCG2 gene with a major effect on the QTL on chromosome 6 affecting milk yield and composition in Holstein cattle. Genome Res 15: 936–944.
Cole JB, VanRaden PM, O’Connell JR, Van Tassell CP, Sonstegard TS, Schnabel RD, et al. 2009 Distribution and location of genetic effects for dairy traits. J Dairy Sci 92: 2931–2946 Erratum in: J Dairy Sci 2009 92: 3542.
Denhardt DT, Guo X, 1993. Osteopontin: a protein with diverse functions. FASEB J 7: 1475–1482.
de Koning DJ, 2006. Conflicting candidates for cattle QTLs. Trends Genet 22: 301–305.
Farnir F, Coppieters W, Arranz JJ, Berzi P, Cambisano N, Grisart B, et al. 2000. Extensive genome-wide linkage disequilibrium in cattle. Genome Res 10: 220–227.
Freking BA, Murphy SK, Wylie AA, Rhodes SJ, Keele JW, Leymaster KA, et al. 2002. Identification of the single base change causing the callipyge muscle hypertrophy phenotype, the only known example of polar overdominance in mammals. Genome Res 12: 1496–1506.
Fujii J, Otsu K, Zorzato F, de Leon S, Khanna VK, Weiler JE, et al. 1991. Identification of a mutation in porcine ryanodine receptor associated with malignant hyperthermia. Science 253: 448–451.
Georges M, 1999. Towards marker assisted selection in livestock. Reprod Nutr Dev 39: 555–561.
Georges M, 2007. Mapping, fine mapping, and molecular dissection of quantitative trait loci in domestic animals. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 8: 131–62.
Gilad Y, Rifkin SA, Pritchard JK, 2008. Revealing the architecture of gene regulation: the promise of eQTL studies. Trends Genet 24: 408–415.
Glazier AM, Nadeau JH, Aitman TJ, 2002. Finding genes that underlie complex traits. Science 298: 2345–2349.
Grisart B, Coppieters W, Farnir F, Karim L, Ford C, Berzi P, et al. 2002. Positional candidate cloning of a QTL in dairy cattle: identification of a missense mutation in the bovineDGAT1 gene with major effect on milk yield and composition. Genome Res 12: 222–231.
Grobet L, Martin LJ, Poncelet D, Pirottin D, Brouwers B, Riquet J, et al. 1997. A deletion in the bovine myostatin gene causes the double-muscled phenotype in cattle. Nat Genet 17: 71–74.
Hadjipavlou G, Matika O, Clop A, Bishop SC, 2008. Two single nucleotide polymorphisms in the myostatin (GDF8) gene have significant association with muscle depth of commercial Charollais sheep. Anim Genet 39: 346–353.
Harmegnies N, Farnir F, Davin F, Buys N, Georges M, Coppieters W, 2006. Measuring the extent of linkage disequilibrium in commercial pig populations. Anim Genet 37: 225–231.
Hayes B, 2008. Course notes ‘QTL mapping, MAS, and genomic selection’. Animal Breeding and Genomics Centre, Animal Sciences Group, Wageningen University and Research Centre, Lelystad, The Netherlands.
Hayes BJ, Bowman PJ, Chamberlain AJ, Goddard ME, 2009. Genomic selection in dairy cattle: progress and challenges. J Dairy Sci 92: 433–443.
Hickford JG, Forrest RH, Zhou H, Fang Q, Han J, Frampton CM, Horrell AL, 2010. Polymorphisms in the ovine myostatin gene (MSTN) and their association with growth and carcass traits in New Zealand Romney sheep. Anim Genet 41: 64–72.
Ibeagha-Awemu ME, Kgwatalala P, Zhao X, 2008. A critical analysis of production-associated DNA polymorphisms in the genes of cattle, goat, sheep, and pig. Mamm Genome 19: 591–617.
Johnson PL, Dodds KG, Bain WE, Greer GJ, McLean NJ, McLaren RJ, et al. 2009. Investigations into theGDF8 g+6723G-A polymorphism in New Zealand Texel sheep. J Anim Sci 87: 1856–1864.
Jonker JW, Merino G, Musters S, van Herwaarden AE, Bolscher E, Wagenaar E, et al. 2005. The breast cancer resistance protein BCRP (ABCG2) concentrates drugs and carcinogenic xenotoxins into milk. Nat Med 11: 127–129.
Karlskov-Mortensen P, Bruun CS, Braunschweig MH, Sawera M, Markljung E, Enfält AC, et al. 2006. Genome-wide identification of quantitative trait loci in a cross between Hampshire and Landrace I: carcass traits. Anim Genet 37: 156–162.
Khatkar MS, Thomson PC, Tammen I, Raadsma HW, 2004. Quantitative trait loci mapping in dairy cattle: review and meta-analysis. Genet Sel Evol 36: 163–190.
Kijas JW, McCulloch R, Edwards JE, Oddy VH, Lee SH, van der Werf J, 2007. Evidence for multiple alleles effecting muscling and fatness at the ovineGDF8 locus. BMC Genet 8: 80.
Mackay TFC, 2001. Quantitative trait loci inDrosophila. Nat Rev Genet 2: 11–20.
Marcq F, Larzul C, Marot V, Bouix J, Eychenne F, Laville E, et al. 2002. Preliminary results of a whole-genome scan targeting QTL for carcass traits in Texel × Romanov intercross. Proc 7th World Cong on Genetic Appl Livest Prod, Montpellier, France: 323–326.
Markljung E, Braunschweig MH, Karlskov-Mortensen P, Bruun CS, Sawera M, Cho IC, et al. 2008. Genome-wide identification of quantitative trait loci in a cross between Hampshire and Landrace II: meat quality traits. BMC Genet 9: 22.
Markljung E, Jiang L, Jaffe JD, Mikkelsen TS, Wallerman O, Larhammar M, et al2009. ZBED6, a novel transcription factor derived from a domesticated DNA transposon regulates IGF2 expression and muscle growth. PLoS Biol 7.
Milan D, Jeon JT, Looft C, Amarger V, Robic A, Thelander M, et al. 2000. A mutation in PRKAG3, associated with excess glycogen content in pig skeletal muscle. Science 288: 1248–1251.
Mulsant P, Lecerf F, Fabre S, Schibler L, Monget P, Lanneluc I, et al. 2001. Mutation in bone morphogenetic protein receptor-IB is associated with increased ovulation rate in Booroola Mérino ewes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98: 5104–5109.
Naveau, J, Pommeret P, Lechaux P, 1985. Proposition d’une méthode de mesure du rendement technologique “la méthode Napole”. Institut Technique du Porc 8: 7–13.
Nemir M, Bhattacharyya D, Li X, Singh K, Mukherjee AB, Mukherjee BB, 2000. Targeted inhibition of osteopontin expression in the mammary gland causes abnormal morphogenesis and lactation deficiency. J Biol Chem 275: 969–976.
Nezer C, Collette C, Moreau L, Brouwers B, Kim JJ, Giuffra E, et al. 2003. Haplotype sharing refines the location of an imprinted quantitative trait locus with major effect on muscle mass to a 250-kb chromosome segment containing the porcineIGF2 gene. Genetics 165: 277–285.
Nsengimana J, Baret P, Haley CS, Visscher PM, 2004. Linkage disequilibrium in the domesticated pig. Genetics 166: 1395–1404.
Olsen HG, Lien S, Svendsen M, Nilsen H, Roseth A, Aasland Opsal M, et al. 2004. Fine mapping of milk production QTL on BTA6 by combined linkage and linkage disequilibrium analysis. J Dairy Sci 87: 690–698.
Olsen HG, Lien S, Gautier M, Nilsen H, Roseth A, Berg PR, et al. 2005. Mapping of a milk production quantitative trait locus to a 420-kb region on bovine chromosome 6. Genetics 169: 275–283.
Olsen HG, Nilsen H, Hayes B, Berg PR, Svendsen M, Lien S, Meuwissen T, 2007. Genetic support for a quantitative trait nucleotide in theABCG2 gene affecting milk composition of dairy cattle. BMC Genet 8: 32.
Phillips PC, 2008. Epistasis the essential role of gene interactions in the structure and evolution of genetic systems. Nat Rev Genet 9: 855–867.
Richards EJ, 2006. Inherited epigenetic variation revisiting soft inheritance. Nat Rev Genet 7: 395–401.
Riquet J, Coppieters W, Cambisano N, Arranz JJ, Berzi P, Davis SK, et al. 1999. Fine-mapping of quantitative trait loci by identity by descent in outbred populations: application to milk production in dairy cattle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 96: 9252–9257.
Ron M, Kliger D, Feldmesser E, Seroussi E, Ezra E, Weller JI, 2001. Multiple quantitative trait locus analysis of bovine chromosome 6 in the Israeli Holstein population by a daughter design. Genetics 159: 727–735.
Ron M, Weller JI, 2007. From QTL to QTN identification in livestock winning by points rather than knock-out: a review. Anim Genet 38: 429–439.
Schnabel RD, Kim JJ, Ashwell MS, Sonstegard TS, Van Tassell CP, Connor EE et al. 2005. Fine-mapping milk production quantitative trait loci on BTA6: analysis of the bovine osteopontin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102: 6896–6901.
Seroussi E, 2009. The concordance test emerges as a powerful tool for identifying quantitative trait nucleotides: lessons from BTA6 milk yield QTL. Anim Genet 40: 230–234.
Van Herwaarden AE, Wagenaar E, Merino G, Jonker JW, Rosing H, Beijnen JH, Schinkel AH, 2007. Multidrug transporter ABCG2/breast cancer resistance protein secretes riboflavin (vitamin B2) into milk. Mol Cell Biol 27: 1247–53.
Van Laere A-S, Nguyen M, Braunschweig M, Nezer C, Collette C, Moreau L, et al. 2003. A regulatory mutation in IGF2 causes a major QTL effect on muscle growth in the pig. Nature 425: 832–836.
Van Raden PM, Van Tassell CP, Wiggans GR, Sonstegard TS, Schnabel RD, Taylor JF, et al. 2009. Reliability of genomic predictions for North American Holstein bulls. J Dairy Sci 92: 16–24.
Visscher PM, Hill WG, Wray NR, 2008. Heritability in the genomics era — concepts and misconceptions. Nat Rev Genet 9: 255–266.
Wilson T, Wu XY, Juengel JL, Ross IK, Lumsden JM, et al. 2001. Highly prolific Booroola sheep have a mutation in the intracellular kinase domain of bone morphogenetic protein IB receptor (ALK-6) that is expressed in both oocytes and granulosa cells. Biol Reprod 64: 1225–1235.
Winter A, Krämer W, Werner FA, Kollers S, Kata S, Durstewitz G, et al. 2002. Association of a lysine-232/alanine polymorphism in a bovine gene encoding acyl-CoA:diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT1) with variation at a quantitative trait locus for milk fat content. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99: 9300–9305.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Braunschweig, M.H. Mutations in the bovineABCG2 and the ovineMSTN gene added to the few quantitative trait nucleotides identified in farm animals: a mini-review. J Appl Genet 51, 289–297 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03208858
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03208858