Abstract
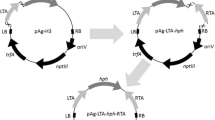
TheAgrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated transformation procedure was developed by using the hygromycin B phosphotransferase gene (hph) as a selective marker for the oil-producing fungusUmbelopsis isabellina. Different conditions were combined to increase the transformation efficiency. The highest efficiency was obtained by usingA. rhizogenes strain R105 and a vector with zygomycete promoter. Southern blot analysis demonstrated that 71 % of transformants contained random integrations of T-DNA sequences under optimal conditions. We randomly selected 115 positive transformants resistant to hygromycin to analyze the amount of total fatty acid and gamma-linolenic acid (GLA). Six transformants produced a higher amount of total fatty acids than the wild strain, and one transformant also produced a higher level of GLA than the wild strain in gas chromatography analysis. This is the first report about usingA. rhizogenes strain R105 and germinated conidia to transform successfully the recalcitrant zygomycetes and to obtain transformants with a stable phenotype.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando A, Sumida Y, Negoro H, Suroto DA, Ogawa J, Sakuradani E, Shimizu S, 2009. Establishment ofAgrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of an oleaginous fungus Mortierella alpina 1S-4 and its application for eicosapentaenoic acid-producer breeding. Appl Environ Microbiol (in press), Doi: 10.1128/AEM.00648-09.
Bundock P, Dulk-Ras A, Beij ersbergen A, Hooykaas P J, 1995. Trans-kingdom T-DNA transfer fromAgrobacterium tumefaciens toSaccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J 14: 3206–3214.
Combier JP, Melayah D, Raffier C, Gay G, Marmeisse R, 2003.Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation as a tool for insertional mutagenesis in the symbiotic ectomycorrhizal fungusHebeloma cylindrosporum. FEMS Microbiol Lett 220: 141–148.
Czapek F, 1902. Untersuchungen über die Stickstoffgewinnung und Eiweißbildung der Pflanzen. Beitr Chem Physiol u Pahtol 1: 540–560.
De Groot MJA, Bundock P, Hooykaas PJJ, Beijersbergen AGM, 1998.Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of filamentous fungi. Nat Biotechnol 16: 839–842.
Dox AW, 1910. The intracellular enzymes ofPenicillium and Aspergillus with special references to those ofP. camenberti. US Dept Agr Bur Anim Ind Bull 120: 170.
Fang G, Hammar S, Grumet R, 1992. A quick and inexpensive method for removing polysaccharides from plant genomic DNA. BioTechniques 13: 52–57.
Fang W-G, Zhang Y-J, Yang X-Y, Zheng X-L, Duan H, Li Y, Pei Y, 2004.Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation ofBeauveria bassiana using an herbicide resistance gene as a selection marker. J Invertebr Pathol 85: 18–24.
Gardiner DM, Jarvis RS. Howlett BJ, 2005. The ABC transporter gene in the sirodesmin biosynthetic gene cluster ofLeptosphaeria maculans is not essential for sirodesmin production but facilitates self-protection. Fungal Genet Biol 42: 257–263.
Gill I, Valivety R, 1997. Polyunsaturated fatty acids, part 1: Occurrence, biological activities and application. Trends Biotechnol 15: 401–409.
Hoekema A, Hirsch PR, Hooyka PK, Schilperoort RA, 1983. A binary plant vector strategy based on separation of vir- and T-region of theAgrobacterium tumefaciens Ti-plasmid. Nature 303: 179–180.
Hood EE, Gelvin SB, Melchers LS, Hoekema A, 1993. NewAgrobacterium helper plasmids for gene transfer to plants. Transgenic Res 2: 208–218.
Horrobin DF, 1992. Nutritional and medical importance of gamma-linolenic acid. Prog Lipid Res 31: 163–194.
Leclerque A, Wan H, Abschütz A, Chen S, Mitina GV, Zimmermann G, Schairer HU, 2004.Agrobacterium-mediated insertional mutagenesis (AIM) of the entomopathogenic fungusBeauveria bassiana. Curr Genet 45: 111–119.
Li W, Guo G-Q, Zheng G-Ch, 2000. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation: state of the art and future prospect. Chin. Science Bull 45: 1537–1546.
Mackenzie DA, Wongwathanarat P, Carter AT, Archer DB, 2000. Isolation and use of a homologous histone H4 promoter and a ribosomal DNA region in a transformation vector for the oil-producing fungusMortierella alpina. Appl Environ Microbiol 66: 4655–4661.
Meyer V, Mueller D, Strowig T, Stahl U, 2003. Comparison of different transformation methods forAspergillus giganteus. Curr Genet 43: 371–377.
Miao X-L, Wu Q-Y, 2006. Biodiesel production from heterotrophic microalgal oil. Bioresour Technol 97: 841–846.
Michielse CB, Hooykaas PJJ, van den Hondel CAMJJ, Ram AFJ, 2005.Agrobacterium-mediated transformation as a tool for functional genomics in fungi. Curr Genet 48: 1–17.
Michielse CB, Salim K, Ragas P, Ram AFJ, Kudla B, Jarry B, et al. 2004. Development of a system for integrative and stable transformation of the zygomyceteRhizopus oryzae byAgrobacterium-mediated DNA transfer. Mol Genet Genomics 271: 499–510.
Monfort A, Cordero L, Maicas S, Polaina J, 2003. Transformation ofMucor miehei results in plasmid deletion and phenotypic instability. FEMS Microbiol Lett 224: 101–106.
Mullaney EJ, Hamer JE, Roberti KA, Yelton MM, Timberlake WE, 1985. Primary structure of the trpC gene fromAspergillus nidulans. Mol Gen Genet 199: 37–45.
Mullins ED, Chen X, Romaine P, Raina R, Geiser DM, Kang S, 2001.Agrobacterium-mediated transformation ofFusarium oxysporum: an efficient tool for insertional mutagenesis and gene transfer. Phytopathology 91: 173–180.
Mullins ED, Kang S, 2001. Transformation: a tool for studying fungal pathogens of plants. Cell Mol Life Sci 58: 2043–2052.
Nyilasi I, Papp T, Csernetics Á, Vágvölgyi C, 2008.Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of the zygomycete fungusBackusella lamprospora. J Basic Microbiol 48: 59–64.
Pahl G, McKibben B, 2005. Biodiesel: growing a new energy economy. White River Junction, Vermont: Chelsea Green.
Papanikolaou S, Sarantou S, Komaitis M, 2004. Repression of reserve lipid turnover inCunninghamella echinulata andMortierella isabellina cultivated in multiple limited media. J Appl Microbiol 97: 867–75.
Rho H, Kang S, Lee Y, 2001.Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of the plant pathogenic fungusMagnaporthe grisea. Mol cells 12: 407–411.
Stafford HA, 2000. Crown gall disease andAgrobacterium tumefaciens: a study of the history, present knowledge, missing information and impact on molecular genetics. Bot Rev 66: 101–118.
Sugui JA, Chang YC, Kwon-Chung KJ, 2005.Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation ofAspergillus fumigatus: an efficient tool for insertional mutagenesis and targeted gene disruption. Appl Environ Microbiol 71: 1798–1802.
Takahara H, Tsuji G, Kubo Y, Yamamoto M, Toyoda K, Inagaki Y, et al. 2004.Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation as a tool for random mutagenesis of Colletotrichum trifolii. J Gen Plant Pathol 70: 93–96.
Yang X-H, Sun Zh-H, Tong R-J, 2006. Optimizing culture system of Ri T-DNA transformed roots forCitrus grandis cv. Changshou Shatian You. Agric Sci China 5: 90–97.
Yan Z, Chen J, 2003. Research advance on microbial oils and their exploitation and utilization. Journal of Cereals & Oils 7: 13–15.
Zhang P-Y, Xu B, Wang Y-Zh, Li Y-Q, Qian Zh, Tang Sh-R, et al. 2008a.Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation as a tool for insertional mutagenesis in the fungusPenicillium marneffei. Mycol Res 112: 943–949.
Zhang X-W, Li M-Ch, Wei D-Sh, Wang X-M, Chen X, Xing L-J, 2007. Disruption of the fatty acid delta6-desaturase gene in the oil-producing fungusMortierella isabellina by homologous recombination. Curr Microbiol 55: 128–134.
Zhang Y-H, Wei D-Sh, Xing L-J, Li M-Ch, 2008b. A modified method for isolating DNA from fungus. Microbiology 35: 466–469 (In Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, D.S., Zhang, Y.H., Xing, L.J. et al. Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated transformation of a high oil-producing fil a m en to us fungusUmbelopsis isabellina. J Appl Genet 51, 225–232 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03195734
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03195734