Summary
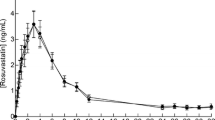
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of simvastatin on the pharmacokinetics of verapamil and its major metabolite, norverapamil, in rats. The pharmacokinetic parameters of verapamil and norverapamil in rats were determined after the oral administration of verapamil (9 mg/kg) in the presence or absence of simvastatin (0.3 and 1.0 mg/kg). The pharmacokinetics of verapamil were significantly altered by the coadministration of simvastatin compared with those in the control group (given verapamil alone). The area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) and the peak plasma concentration (Cmax) of verapamil were significantly increased (P < 0.05 at 0.3 mg/kg;P < 0.01 at 1.0 mg/kg) by simvastatin. Consequently, the absolute bioavailability (A.B.) of verapamil with simvastatin (7.3 % at 0.3 mg/kg, 9.3 % at 1.0 mg/kg) were significantly higher than those in the control group (P < 0.05, 5.2 %). The AUC and Cmax of norverapamil were not significantly increased in the rats coadministered with simvastatin compared with those in the control group. Moreover, the metabolite-parent ratio (M.R.) of norverapamil were significantly decreased in rats coadministered with simvastatin. These results implied that simvastatin significantly enhanced the oral bioavailability of verapamil by inhibiting the CYP3A-mediated metabolism in small intestine or in the liver and P-glycoprotein (P-gp) efflux pump in small intestine. Therefor, concurrent use of verapamil and simvastatin should be monitored closely to potential drug interactions for safe therapy of cardiovascular diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fleckenstein A., (1977): Specific pharmacology of calcium in myocardium, cardiac pacemakers, and vascular smooth muscle. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol., 17, 149–166.
Gould B.A., Mann S., Kieso H., Bala Subramanian V., Raftery E.B. (1982): The 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure profile with verapamil. Circulation, 56, 22–27.
Lewis G.R., Morley K.D., Lewis B.M., Bones P.J. (1978): The treatment of hypertension with verapamil. NZ. Medical J., 87, 351–354.
Schomerus M., Spiegelhaider B., Stieren B., Eichelbaum M., (1976): Physiologic disposition of verapamil in man. Cardiovasc. Res., 10, 605–612.
Eichelbaum, M., Remberg, E. G., Schomerus, M., Dengler, H. J. (1979): The metabolism of D,L(14C) verapamil in man. Drug Metab. Dispos., 7, 145–148.
Eichelbaum M., Mikus G., Vogelgesang B. (1984): Pharmacokinetics of (+)-, (−)- and (±)-verapamil after intravenous administration. Brit. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 17, 453–458.
Adachi Y., Suzuki H., Sugiyama Y., (2001): Comparative studies on in vitro methods for evaluating in vivo function of MDR1 P-glycoprotein. Pharm. Res., 18, 1660–1668.
Doppenschmitt S., Spahn-Langguth H., Regardh C.G., Langguth P., (1999): Role of P-glycoprotein-mediated secretion in absorptive drug permeability: An approach using passive membrane permeability and affinity to P-glycoprotein. J. Pharm. Sci., 88, 1067–1072.
Gottesman M.M., Pastan I., (1993): Biochemistry of multidrug resistance mediated by the multidrug transporter. Annu. Rev. Biochem., 62, 385–427.
Prueksaritanont T., Gorham L.M., Ma B., (1997): In vitro metabolism of simvastatin in humans: identification of metabolizing enzymes and effect of the drug on hepatic P450s. Drug Metab. Dispos., 25, 1191–1199.
FDA Guidance for industry: In vivo drug metabolism/drug interaction studies-study design, data analysis, and recommendations for dosing and labeling, [cited November 24, 1999] http://www.fda.gov/cder/guidance/index.htm
Wang E., Casciano C.N., Clement R.P., Johnson W.W., (2001): HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) characterized as direct inhibitors of P-glycoprotein. Pharm. Res., 18, 800–806.
Bogman K., Peyer A.K., Torok M., Kusters E., Drewe J., (2001): HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and P-glycoprotein modulation. Br. J. Pharmacol., 132, 1183–1192.
Wacher V.J., Salphati L., Benet L.Z., (1996): Active secretion and enterocytic drug metabolism barriers to drug absorption. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev., 20, 99–112.
Benet L.Z., Cummins C.L., Wu C.Y., (2003): Transporterenzyme interactions: implications for predicting drug-drug interactions from in vitro data. Curr. Drug Metab., 4, 393–398.
Cummins C.L., Jacobsen W., Benet L.Z., (2002): Unmasking the dynamic interplay between intestinal P-glycoprotein and CYP3A4. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 300, 1036–1045.
Marumo H., Satoh K., Yamamoto A., Kaneta S., Ichihara K., (2001): Simvastatin and atorvastatin enhance hypotensive effect of diltiazem in rats. Yakugaku Zasshi., 121, 761–764.
Bottorff M.B., (2006): Statin safety and drug interactions: clinical implications. Am. J. Cardiol., 17, 27–31.
Choi J.S., Han H.K., (2004): The effect of quercetin on the pharmacokinetics of verapamil and its major metabolite, norverapamil, in rabbits. J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 56, 1537–1542.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, DH., Li, C. & Choi, JS. Effects of simvastatinon the pharmacokinetics of verapamil and its main metabolite, norverapamil, in rats. Eur. J. Drug Metabol. Pharmacokinet. 34, 163–168 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03191168
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03191168