Abstract
Background
This study aimed to investigate the effects of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors on the pharmacokinetics of nifedipine in rats.
Methods: We determined the pharmacokinetic parameters of nifedipine and dehydronifedipine in rats after oral and intravenous administration of nifedipine without and with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors.
We evaluated the effect of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors on the activity of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and cytochrome P450 (CYP)3A4.
Results
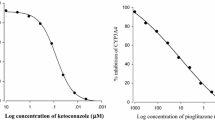
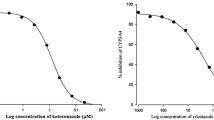
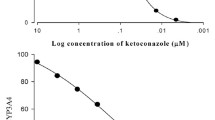
Atorvastatin, fluvastatin, pravastatin and simvastatin inhibited CYP3A4 activities; inhibitory concentration (IC50) values were 47.0, 5.2, 15.0 and 3.3 μM, respectively. Simvastatin and fluvastatin increased the cellular uptake of rhodamine-123.
The area under the plasma concentration–time curve (AUC0–∞) and the peak plasma concentration (Cmax) of oral nifedipine were significantly increased by fluvastatin and simvastatin, respectively, compared to control group. The total body clearance (CL/F) of nifedipine after oral administration with fluvastatin and simvastatin were significantly decreased compared to those of control. The metabolite–parent AUC ratio (MR) of nifedipine with fluvastatin and simvastatin were significantly decreased, which suggested that fluvastatin and simvastatin inhibited metabolism of nifedipine, respectively. The AUC0–∞ of intravenouse nifedipine with fluvastatin and simvastatin was significantly higher than that of the control group.
Conclusion
The increased bioavailability of nifedipine may be mainly due to inhibition of both P-gp in the small intestine and CYP3A subfamily-mediated metabolism of nifedipine in the small intestine and/or in the liver and to the reduction of the CL/F of nifedipine by fluvastatin and simvastatin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koh KK, Quon MJ, Waclawiw MA. Are statins effective for simultaneously treating dyslipidemias and hypertension? Atherosclerosis 2008;196:1–8.
Milionis HJ, Liberopoulos EN, Elisaf MS, Mikhailidis DP. Analysis of antihypertensive effects of statins. Curr Hypertens Rep 2007;9:175–83.
Prueksaritanont T, Gorham LM, Ma B. In vitro metabolism of simvastatin in humans: identification of metabolizing enzymes and effect of the drug on hepatic P450s. Drug Metab Dispos 1997;25:1191–9.
Deslypere JP. Clinical implications of the biopharmaceutical properties of fluvastatin. Am J Cardiol 1994;73:12–7.
Transon C, Leemann T, Dayer P. In vitro comparative inhibition profiles of major human drug metabolising cytochrome P450 isozymes (CYP2C9, CYP2D6 and CYP3A4) by HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1996;50:209–15.
Lea AP, McTavish D. Atrovastatin: a review of its pharmacology and therapeutic potential in the management of hyperlipidaemias. Drug 1997;53:828–47.
Holtzman CW, Wiggins BS, Spinler SA. Role of P-glycoprotein in statin drug interaction. Pharmacotherapy 2006;26:1601–7.
Sorkin EM, Clissold SP, Brogden RN. Nifedipine: a review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic efficacy, in ischaemic heart disease, hypertension and related cardiovascular disorders. Drugs 1985;30:182–274.
Blackshear JL, Orlandi C, Williams GH, Hollenberg NK. The renal response to diltiazem and nifedipine: comparison with nitroprusside. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1986;8:37–43.
Hamann SR, Piascik MT, McAllister RGJ. Aspects of the clinical pharmacology of nifedipine, a dihydropyridine calcium-entry antagonist. Biopharm Drug Dispos 1986;7:1–10.
Funaki T, Soons PA, Guengerich FP, Breimer DD. In vivo oxidative cleavage of a pyridine-carboxylic acid ester metabolite of nifedipine. Biochem Pharmacol 1989;38:4213–6.
Watkins PB. Noninvasive tests of CYP3A enzymes. Pharmacogenetics 1994;4:171–84.
He F, Bi HC, Xie ZY, Zuo Z, Li JK, Li X, et al. Rapid determination of six metabolites from multiple cytochrome P450 probe substrates in human liver microsome by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry: application to high-throughput inhibition screening of terpenoids. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 2007;21:635–43.
Shimada T, Yamazaki H, Mimura M, Inui Y, Guengerich FP. Interindividual variations in human liver cytochrome P-450 enzymes involved in the oxidation of drugs, carcinogens and toxic chemicals: studies with liver microsomes of 30 Japanese and 30 Caucasians. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1994;270:414–23.
Rendic S, Di Carlo FJ. Human cytochrome P450 enzymes: a status report summarizing their reactions, substrates, inducers, and inhibitors. Drug Metab Rev 1997;29:413–580.
Lin JH, Chiba M, Baillie TA. Is the role of the small intestine in first-pass metabolism overemphasized? Pharmacol Rev 1999;51:135–58.
Dresser GK, Spence JD, Bailey DG. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic consequences and clinical relevance of cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibition. Clin Pharmacokinet 2000;38:41–57.
Doherty MM, Charman WN. The mucosa of the small intestine: how clinically relevant as an organ of drug metabolism? Clin Pharmacokinet 2002;41:235–53.
Thiebaut F, Tsuruo T, Hamada H, Gottesman MM, Pastan I, Willingham MC. Cellular localization of the multidrug-resistance gene product P-glycoprotein in normal human tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1987;84:7735–8.
Sugawara I, Kataoka I, Morishita Y, Hamada H, Tsuruo T, Itoyama S, et al. Tissue distribution of P-glycoprotein encoded by a multidrugresistant gene as revealed by a monoclonal antibody, MRK 16. Cancer Res 1988;48:1926–9.
Thiebaut F, Tsuruo T, Hamada H, Gottesman MM, Pastan I, Willingham MC. Immunohistochemical localization in normal tissues of different epitopes in the multidrug transport protein P170: evidence for localization in brain capillaries and crossreactivity of one antibody with a muscle protein. J Histochem Cytochem 1989;37:159–64.
Cordon-Cardo C, O’Brien JP, Casals D, Rittman-Grauer L, Biedler JL, Melamed MR, et al. Multidrug-resistance gene (P-glycoprotein) is expressed by endothelial cells at bloodebrain barrier sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1989;86: 695–8.
Leveque D, Jehl F. P-glycoprotein and pharmacokinetics. Anticancer Res 1995;15:231–336.
Relling MV. Are the major effects of P-glycoprotein modulators due to altered pharmacokinetics of anticancer drugs? Ther Drug Monit 1996;18:350–6.
Wacher VJ, Wu CY, Benet LZ. Overlapping substrate specificites and tissues distribution of cytochrome P450 3A and P-glycoprotein: implications for drug delivery and activity in cancer chemotherapy. Mol Carcinog 1995;13:129–34.
Dorababu M, Nishimura A, Prabha T, Naruhashi K, Sugioka N, Takada K, et al. Effect of cyclosporine on drug transport and pharmacokinetics of nifedipine. Biomed Pharmacother 2009;63:697–702.
Mousa O, Brater DC, Sunblad KJ, Hall SD. The interaction of diltiazem with simvastatin. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2000;67:267–74.
Azie NE, Brater DC, Becker PA, Jones DR, Hall SD. The interaction of diltiazem with lovastatin and pravastatin. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1998;64:369–77.
Choi DH, Chang KS, Hong SP, Choi JS, Han HK. Effects of atorvastatin on the intravenous and oral pharmacokinetics of verapamil in rats. Biopharm Drug Dispos 2008;29:45–50.
Choi DH, Shin WG, Choi JS. Drug interaction between oral atorvastatin and verapamil in healthy subjects; effects of atorvastatin on the pharmacokinetics of verapamil and norverapamil. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2008;64:445–9.
Hong SP, Chang KS, Koh YY, Choi DH, Choi JS. Effects of lovastatin on the pharmacokinetics of verapamil and its active metabolite, norverapamil, in rats: possible role of P-glycoprotein inhibition by lovastatin. Arch Pharm Res 2009;32:1447–52.
Choi DH, Chung JH, Choi JS. Pharmacokinetic interaction between oral lovastatin and verapamil in healthy subjects: role of P-glycoprotein inhibition by lovastatin. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2010;66:285–90.
Grundy JS, Kherani R, Foster RT. Sensitive high-performance liquid chromatographic assay for nifedipine in human plasma utilizing ultraviolet detection. J Chromatogr B Biomed Appl 1994;654:146–51.
Crespi CL, Miller VP, Penman BW. Microtiter plate assays for inhibition of human, drug-metabolizing cytochromes P450. Anal Biochem 1997;248: 188–90.
Han CY, Cho KB, Choi HS, Han HK, Kang KW. Role of FoxO1 activation in MDR1 expression in adriamycin-resistant breast cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2008;29:1837–44.
Chiou WL. Critical evaluation of potential error in pharmacokinetic studies using the linear trapezoidal rule method for the calculation of the area under the plasma level–time curve. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 1978;6:539–46.
Cummins CL, Jacobsen W, Benet LZ. Unmasking the dynamic interplay between intestinal P-glycoprotein and CYP3A4. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2002;300: 1036–45.
Wolozin B, Kellman W, Ruosseau P, Celesia GG, Siegel G. Decreased prevalence of Alzheimer disease associated with 3-hydroxy-3-methyglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors. Arch Neurol 2000;10:1439–43.
Mason RP. A rationale for combined therapy with a calcium channel blocker and a statin: evaluation of basic and clinical evidence. Curr Drug Targets Cardiovasc Haematol Disord 2005;5:489–501.
Halpin RA, Ulm EH, Till AE, Kari PH, Vyas Kp, Hunninghake DB, Duggan DE. Biotransformation of lovastatin. V, Species differences in in vivo metabolite profiles of mouse, rat, dog, and human. Drug Metab Dispos 1993;21:1003–11.
Wang E, Casciano CN, Clement RP, Johnson WW. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) characterized as direct inhibitors of P-glycoprotein. Pharm Res 2001;18:800–6.
Kelly PA, Wang H, Napoli KL, Kahan BD, Strobel HW. Metabolism of cyclosporine by cytochromes P450 3A9 and 3A4. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 1999;24:321–8.
Choi DH, Choi JS, Li C, Choi JS. Effects of simvastatin on the pharmacokinetics of diltiazem and its main metabolite, desacetyldiltiazem, after oral and intravenous administration in rats: possible role of P-gp and CYP3A4 inhibition by simvastatin. Pharmacol Rep 2011;63:1574–82.
Bogaards JJ, Bertrand M, Jackson P, Oudshoorn MJ, Weaver RJ, van Bladeren PJ, et al. Determining the best animal model for human cytochrome P450 activities: a comparison of mouse, rat, rabbit, dog, micropig, monkey and man. Xenobiotica 2000;30:1131–52.
Lewis DFV. Cytochrome P450. Substrate specificity and metabolism. In: Cytochromes P450. Structure, Function, and Mechanism. Bristol: Taylor & Francis; 1996. p. 122–3.
Wang Y, Zou MJ, Zhao N, Ren JG, Zhou H, Cheng G. Effect of diallyl trisulfide on the pharmacokinetics of nifedipine in rats. J Food Sci 2011;76:30–4.
Kuroha M, Kayaba H, Kishimoto S, Khalil WF, Shimoda M, Kokue E. Effect of oral ketoconazole on first-pass effect of nifedipine after oral administration in dogs. J Pharm Sci 2002;91:868–73.
Nishimura A, Fugimura M, Hasegawa F, Shibata N. Pharmacokinetic interaction between nifedipine and Coenzyme Q10 in rats: a new type of drug-supplement interaction. J Health Sci 2010;56:310–20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, CK., Choi, JS. & Choi, DH. Effects of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors on the pharmacokinetics of nifedipine in rats: Possible role of P-gp and CYP3A4 inhibition by HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Pharmacol. Rep 67, 44–51 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2014.08.005
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2014.08.005