Summary
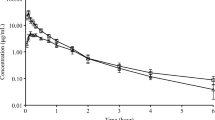
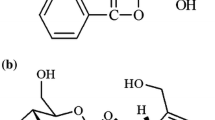
The objective of the present study was to firstly investigate the in vivo pharmacokinetics of phillyrin and forsythiaside in beagle dog. On I.V. administration, a rapid distribution was observed and followed by a slower elimination for phillyrin and forsythiaside. The mean t1/2z was 49.99, 34.87 and 43.81 min for 0.19, 0.70 and 1.43 mg/kg of phillyrin, and 60.90, 64.30, 57.99 min for 0.62, 1.39 and 5.52 mg/kg of forsythiaside respectively. And the AUC0-t increased linearly from 36.51 to 160.22 μg·min/ml of phillyrin and from 50.63 to 681.08 μsdmin/ml after the three dosage administrated. In the range of the dose examined, the pharmacokinetics of phillyrin and forsythiaside in beagle dog was based on first order kinetics. Although both drugs were widely distributed to various tissues in the dog, no concerns about extensive binding to tissues that may be consumed by the public should a dog be exposed to phillyrin and forsythiaside according to the rapid elimination.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yoshida T., Sakane N., Wakabayashi Y., et al. (1995): Thermogenic anti-obesity effects of bofu-tsusho-san in MSG-obese mice. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord., 19, 717–722.
Sato Y., Kumazawa N., Suzuki M., et al. (1991): Studies on chemical protectors against radiation. XXXIII. Protective mechanisms of various compounds against skin injury induced by radiation. Yakugaku Zasshi, 111, 51 -58.
Schinella G.R., Tournier H.A., Prieto J.M., et al. (2002): Synthesis and opioid activity of new fentanyl analogs. Life Sei., 9, 1023–1033.
Bing Qing, Wei Qi, Xing Hong, et al. (1999): study on the anti-inflammatory and analgesia function of fructus forsythia extraction. Zhong Cao Yao, 30, 43–45.
Yang Tiang-ming, Zhang Zhi-hai, Zhang-hong, et al. (2003): study on the anti-bacteria function of Water extraction fructus forsythia. J. Lanzhou Med. Coll., 9, 40–42.
Liu Ying-juan, Yang Zhan-qiu, Xiao Hong, et al. (2004) effective component in vitro anti-fever blisters virus’s experimental study on the Chinese medicine fructus forsythia. J. Hubei Coll. TCM, 6, 36–37
Liu J., Zhang L.W., (2006): Functions of Forsythiaside on the Damage of DNA Induced by Hydroxyl Radical. J. Shanxi Med. Univ., 7, 23–24.
Ishizuka O., Kumazawa N., Ohta S., et al. (1992): Effects of various methanol extracts of crude drugs on experimental subacute and chronic hepatic injury. Yakugaku Zasshi, 112, 174–182.
Kumazawa N., Ohta S., Ishizuka O., et al. (1990): Protective effects of various methanol extracts of crude drugs on experimental hepatic injury induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats. Yakugaku Zasshi, 110, 950–957.
Jin H., Zuo J.F., Li J.S. (2006): Study on the pharmacology of phenylethanoid glycosides. Lishizhen Med. Materia Med. Res., 17, 440–444.
Diaz Lanza A.M., Abad Martinez M.J., Fernandez Matellano L. (2001): Lignan and phenylpropanoid glycosides from Phillyrea latifolia and their in vitro anti-inflammatory activ ity. Planta Med., 67, 219–223.
Chen X., Zhang J., Xue C., et al. (2004): Simultaneous determination of some active ingredients in anti-viral preparations of traditional Chinese medicine by micellar electrokinetic chromatography. Biomed. Chromatogr., 18, 673–680.
Shi Y., Shi R.B., Liu B., et al. (2003): Isolation and elucidation of chemical constituents with antiviral action from yinqiaosan on influenza virus. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi., 28, 43–47.
Zhao Yong-mei, Li Fa-rong (2005): Study on the reducing blood lipid and antioxidition effects of phillyrin. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev., 17, 157–159.
Zhao Y., Li F., Yang J., et al. (2005): Effect of phillyrin on the anti-obesity in nutritive obesity mice. Zhong Yao Cai, 28, 123–124.
Tamotsu Nikaido, Taichi Ohamoto and Takeshi Kinoshita. (1981): Inhibition of Cyclic AMP Phosphodiesterase by Lignans. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 29, 3586–3606.
Kuang H.X., Zhang N and Lu Z.B. (1988) Antibacterial constituents of the unripe fruit of Forsythia suspensa (Thunb.) Vahl. Zhong Yao Tong Bao, 13, 32–34, 62–63.
Hu J.K., Xu K.J., Wang Y.H. et al. (2001): Study on the in vitro antiviral effect of forsythiaside. J. Chin. Tra. Med. Sei. Tech., 8, 89–91.
Zhang L.W., Zhao C.G., Yang P. (2003): Study on the antioxidant activity and structure-activity relationship of forsythiaside. Chin. Pharmac. J., 38, 334–336.
Hu J.K., Qu F.J., Sun K.X. et al. (2004): Experiment study on the induction of a-rnterferon of human leucocyte in vitro by forsythiaside. J. Chin. Tra. Med. Sei. Tech., 11, 355–356.
Li Yunxia, Jiang Xuehua, Huang Liang et al. (2006): Determination of phillyrin in rat plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography and its application to pharmacokinetic studies, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 41, 628- 632.
Li Y.X., Jiang X.H., Liang H.Y., et al. (2008) Determination of forsythiaside in rat plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography and its application to pharmacokinetic studies. Biomed. Chromatogr., 22, 361–6.
Chiou, W. L. (1978) Critical evaluation of potential error in pharmacokinetic studies using the linear trapezoidal rule method for the calculation of the area under the plasma level-time curve. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm., 6, 539–546.
Gibaldi M., Perrier D. (1982): Pharmacokinetics. New York.
Chiou, W.L. (1980): New calculation method of mean total body clearance of drugs and its application to dosage regi-mens. J. Pharm. Sei., 69, 90–91.
Chiou, W.L. (1979): New calculation method for mean apparent drug volume of distribution and application to rational dosage regimen. J. Pharm. Sei., 68, 1068–1069.
Eatman, F.B., Colburn, W.A., Boxenbaum, H.G., et al. (1977): Pharmacokinetics of diazepam following multiple dose oral administration to healthy human subjects. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm., 5, 481–494.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, YX., Peng, C., Zhang, RQ. et al. Pharmacokinetics of phillyrin and forsythiaside followingiv administration to Beagle dog. Eur. J. Drug Metabol. Pharmacokinet. 34, 79–83 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03191155
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03191155