SUMMARY
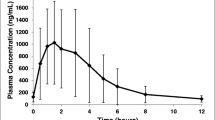
A pharmacokinetic study with mianserin.HC1 was performed in six healthy male subjects. The subjects were treated on different occasions intravenously with a constant-rate infusion of 5 mg mianserin. HC1 in 1 h, orally with a single dose of 60 mg as two tablets of 30 mg each and with 60 mg as an oral solution. The wash-out period between treatments was I month. Blood samples were taken at predetermined times over a period of 120 h following dosing. The mianserin concentration in the plasma samples was determined and the results were pharmacokinetically analyzed. The intravenous data could be adequately described by a 3-compartment model and the oral data by a 2-compartment model, both with first-order transfer and elimination rate constants. The mean plasma clearance of mianserin was found to be 19± 2 1 h−1 (mean± SEM), the kinetic volume of distribution 444± 250 I, the steady-state volume of distribution 242± 171 1 and the elimination half-life 33± 5 h. The absolute bioavailability in terms of extent of absorption was 22± 3% for the solution and 20± 3% for the tablets. The mean peak level for the solution was 79± ng · ml−1 and for the tablets 54± 5 ng · ml−1 ; mean peak time for the solution was 1.1± 0.2 h and for the tablets 1.4± 0.2 h. The mean absorption half-life for the solution was 0.43± 0.13 h and for the tablets 0.39± 0.11 h. The maximum anticipated oral availability determined by hepatic first-pass elimination and taking into account absorption losses was calculated to be in the range of 34–49%.The relatively low extent of absorption can be partially accounted for by firstly an incomplete absorption from the gastro-intestinal tract, which accounts for a loss not exceeding 28% of the dose and secondly a hepatic first-pass effect, which causes approximately 32% of the amount passing through the intestinal wall to be lost before reaching the systemic circulation. The 30 mg tablets were found to be bioequivalent to the oral solution with respect to the extent of absorption as well as the rate of absorption characterized by peak concentration, peak time and absorption half-life.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brogden R.N., Heel R.C., Speight T.M. and Avery G.S. (1978): Mianserin : a review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy in depressive illness. Drugs16, 273–301.
Van Riezen H., Pinder R.M., Nickolson V.J., Hobbelen P., Zayed I. and Van der Veen F. (1981): Mianserin. In: Goldberg M.E. (ed.) Pharmacological and biochemical properties of drug substances, vol. 3. American Pharmaceutical Association, Washington, 56–93.
Jansen H. (1978): Contribution to workshop on the clinical pharmacology and efficacy of mianserin. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol.,5, 91S-99S.
Vink J. and Van Hal H.J.M. (1980): Simplified method for determination of the tetracyclic antidepressant mianserin in human plasma using gas chromatography with nitrogen detection. J. Chromatogr.,181, 25–31.
Rowland M. and Tucker G. (1980): Symbols in pharmacokinetics. J. Pharm. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm.,8, 497–507.
Wijnand H.P. and Timmer C.J. (1979): Curve-fitting and modeling in pharmacokinetics: all programs are equal, but some programs are more equal than others. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm.,7, 681–684.
Boxenbaum H.G., Riegelman S. and Elashoff R.M. (1974): Statistical estimation in pharmacokinetics. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm.,2, 123–147.
Wijnand H.P. and Timmer C.J., (1983): Mini-computer programs for bioequivalence testing of pharmaceutical drug formulations in two-way cross-over studies. Comput. Programs. Biomed.,17, 73–88.
Westlake W.J. (1972): Use of confidence intervals in analysis of comparative bioavailability trials. J. Pharm. Sci,61, 1340–1341.
Rodda B.E. and Davis R.L. (1980): Determining the probability of an important difference in bioavailability. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.,28, 247–252.
Fluehler H., Hirtz J. and Moser H.A. (1981): An aid to decision-making in bioequivalence assessment. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm.,9, 235–243.
Maguire K.P., Norman T.R., Burrows G.D. and Scoggins B.A. (1982): A pharmacokinetic study of mianserin. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol.,21, 517–520.
Hrdina P.O., Lapierre Y.D., McIntosh R. and Oyewumi L.K. (1983): Pharmacokinetic profile of mianserin in depressed patients. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.,33, 757–762.
Tozer T.N. (1981): Concepts basic to pharmacokinetics. Pharmacol. Ther.,12, 109–132.
Gibaldi M., Boyes R.N. and Feldman S. (1971): Influence of first-pass effect on availability of drugs on oral administration. J. Pharm. Sci.,60, 1338–1340.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Timmer, C.J., Pourbaix, S., Desager, J.P. et al. Absolute bioavailability of mianserin tablets and solution in healthy humans. European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics 10, 315–323 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03189759
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03189759