Summary
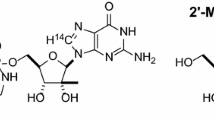
The pharmacokinetics of 3-deazaneplanocin A (c3Nep), a competitive inhibitor of S-adenosyl-l-homocysteine (AdoHcy) hydrolase and novel antiviral agent, was investigated in female BALB/c mice. Animals were given a single intravenous dose of [3H]-c3Nep (0.1 mg/kg: 10 μCi), and blood and selected tissues were collected at various intervals thereafter for up to 72 h. The plasma concentration versus time data for c3Nep was best approximated by a two-compartment open model with first order elimination. The elimination half-life was 12.8 min, the area-under curve (AUC) was 3.38 μg.min.ml−1. The distribution of c3Nep into tissues was not extensive. Following 30, 120 min, and 24 h after dosing, the kidneys and the liver contained the highest amount of drug, but this amount did not exceed 1 μg/g tissue. At these time periods, the majority of activity in the tissues represented labeled derivatives of c3Nep indicating that this compound was converted to stable metabolites. The presence of labeled conversion products in the blood confirmed that this drug is metabolized in vivo. The fact that c3Nep bound to plasma proteins in vitro may explain this drug’s limited tissue distribution. The half-life and tissue distribution of c3Nep were different from those of carbocyclic 3-deazaadenosine, a related adenosine nucleoside antiviral drug and AdoHcy hydrolase inhibitor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Glazer R.I., Hartman K.D., Knode M.C., et al. (1986): 3-deazaneplanocin A: a new and potent inhibitor of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase and its effects on human promyelocytic leukemia cell line HL-60. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 135, 688–694.
Glazer R.I., Knode M.C., Tseng C.K.H., Haines D.R., Marquez V.E. (1986): 3-deazaneplanocin A: a new inhibitor of S-adenosylhomocysteine synthesis and its effects in human colon carcinoma cells. Biochem. Pharmacol., 35, 4523–4527.
Chiang P.K., Richards H.H., Cantoni G.L. (1977): S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolase: analogues of S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine as potential inhibitors. Mol. Pharmacol., 13, 939–947.
De Clercq E. (1987): S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase inhibitors as broad-spectrum antiviral agents. Biochem. Pharmacol., 36, 2657–2575.
Montgomery J.A., Clayton S.J., Thomas H.J., et al. (1982): Carbocyclic analogue of 3-deazaadenosine: a novel antiviral agent using S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase as a pharmacological target. J. Med. Chem., 25, 626–629.
Cools M., De Clercq E. (1989): Correlation between the antiviral activity of acyclic and carbocyclic adenosine analogues in murine L929 cells and their inhibitory effect on L929 cell S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase. Biochem. Pharmacol., 38, 1061–1067.
De Clercq E., Cools M., Balzarini J., et al. (1989): Broad-spectrum antiviral activities of neplanocin A and 3-deazaneplanocin A, and their 5′-nor derivatives. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 33, 1291–1297.
Oxenrider K.A., Bu G., Sitz T.O. (1993): Adenosine analogs inhibit the guanine-7-methylation of mRNA cap structures. FEBS Lett., 316, 273–277.
Chiang P.K., Burbelo P.D., Brugh S.A., Gordon R.K., Fukuda K., Yamada Y. (1992): Activation of collagen IV gene expression of F9 teratocarcinoma cells by 3-deazaadenosine analogs. J. Biol. Chem., 267, 4988–4991.
Tseng C.K.H., Marquez V.E., Fuller F.W., et al. (1989): Synthesis of 3-deazaneplanocin A, a powerful inhibitor of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase with potent and selective in vitro and in vivo antiviral activities. J. Med. Chem., 32, 1442–1446.
Coulombe Jr R.A., Huie J.M., Sharma R.P., Huggins J.W. (1993): Pharmacokinetics of the antiviral agent carbocyclic 3-deazadenosine. Drug Metab. Dispos., 21, 555–559.
El Dareer S.M., Tillery K.F., Rose L.M., Struck R.F., Hill D.L. (1990): Disposition and metabolism of carbovir in mice dosed intravenously or orally. Drug Metab. Dispos., 18, 842–845.
Ibrahim S.S., Boudinot F.D. (1991): Pharmacokinetics of 2′,3′-dideoxycytidine after high dose administration to rats. J. Pharm. Sci., 80, 36–38.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coulombe, R.A., Sharma, R.P. & Huggins, J.W. Pharmacokinetics of the antiviral agent 3-deazaneplanocin A. European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics 20, 197–202 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03189670
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03189670