Abstract
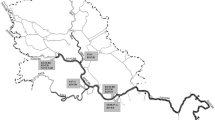
A method using the solid phase extraction (SPE) and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) to analyse atrazine and its degradation products at levels of low nanograms per liter in water has been developed. The environmental water samples were filtered and then extracted by SPE with a new sulfonation of poly(divinylbenzene-co-N-vinylpyrrolidone) sorbents MCX. HPLC/APCIMS was used for the analysis of atrazine and its degradation products, desethylatrazine (DEA), deisopropylatrazine (DIA), dideal-kylatrazine (DEDIA), and hydroxyatrazine (HYA). The detection limits ranged from 10–50 ng/L in water samples. Samples were collected from deep wells and a reservoir near a plant that produced atrazine. Atrazine concentration levels in most surface samples were above the limit of the China Surface Water Regulation (3 μg/L). In ground water, the levels of degradation product were more than 0.1 μg/L and 5 –10 times greater than those of atrazine. The highest DEA concentration in the groundwater sample taken at the 130 m depth was 7.2 μg/L.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Donson, S. L., Merritt, C. M., Shannahan, J. P., Low exposure concentrations of atrazine increase male production in Daphnia, Environ. Toxicol. & Chemistry, 1999, 18(7): 1568.
Van Leeuwen, J. A., Walnter-Toews, D., Abernathy, T., Associations between stomach cancer incidence and drinking water contamination with atrazine and nitrate in Ontario (Canada) agroecosystems, 1987–1991, International Journal of Epidemiology, 1999, 28(5): 836.
Nalina, S., Elizabeth, D., A review of epidemiologic studies of triazine herbicides and cancer, Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 1997, 27(6): 599.
Ciba-Geigy Corporation, Summary of toxicologic data of atrazine and its chlorotriazine metabolites, Attachment 12, 56FR3526, Ciba-Geigy, 1993.
Ren Jin, Jiang Ke, Progress in research of endocrine disrupting chemical, Progress in Chemistry (in Chinese), 2000, 13(2): 135.
Ren Jin, Huang Cuiling, Zhao Guodong et al., Determination of herbicides in drinking water by SPE-HPLC-APCIMS, Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry (in Chinese), 2001, 29(8): 876.
Ren Jin, Jiang Ke, The determination of concentration and research of source of atrazine residue in water of guanting reservoir, Environmental Science (in Chinese), 2002, 23(1): 126.
Nouri, B., Toussaint, G., Chambon, P., Application of a new polymeric adsorbent to isolate chlorotriazines and their dealkylated degradation products from water samples, Analyst, 1995, 120(12): 2683.
Hassan, S., Roger, J., Bernard, R., Multiresidue methods using solid-phase extraction techniques for monitoring priority pesticides, including triazines and degradation products, in ground and surface waters, Journal of Chromatography A, 2000, 885: 217.
Antonio, D. C., Carlo, C., Ettore, G. et al., Ultratrace determination of atrazine and its six major degradation products in water by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-electrospray/ mass spectrometry, Environ. Sci. Technol., 1997, 31(6): 1658.
Imma, F., Marie-Claire, H., Damia, B., Immunosorbents coupled on-line with, liquid chromatography/atmospheric pressure chemical ionization/mass spectrometry for the part per trillion level determination of pesticides in sediments and natural waters using low preconcentration volumes, Anal. Chem., 1997, 69(22): 4508.
Ren, J., Jiang, K., The adverse impact of atrazine disposal on the water resources of Yang River in Zhangjiakou Area in China, Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2002, 68(6): 893.
Robert, N. L., William, W. D., Li Yongxi et al., Hydroxylated atrazine degradation products in a small missouri stream, Environ. Sci. Technol., 1995, 29(11): 2759.
Sylvie, N., Maciej, S., Jacques, E., Tandam solid-phase extraction of atrazine ozonation products in water, Journal of Chromatography A, 2000, 866: 195.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, J., Jiang, K. Atrazine and its degradation products in surface and ground waters in Zhangjiakou District, China. Chin.Sci.Bull. 47, 1612–1616 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03184108
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03184108