Abstract
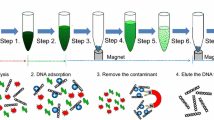
In this report, a universal protocol for extracting genomic DNA from whole blood, saliva, and bacterial culture by using magnetic nanobeads as solid-phase absorbents was presented. The enrichment of target cells and adsorption of DNA have been functionally integrated onto the surfaces of the carboxyl-modified magnetic nano-beads, and the DNA segments bound on the surface of the beads can be directly used as PCR templates to amplify a target gene. The PCR products were applied to an oligonucleotide array to perform gene typing. The protocol proves to be simple, rapid, biologically and chemically nonhazardous, and promising for the microfabrication of DNA preparation chip.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kutter, J. P., Current developments in electrophoretic and chromatographic separation methods on microfabricated devices, Trends Anal. Chem., 2000, 19: 352–363.
Hawkins, T. L., McKernan, K. J., Jacotot, L. B. et al., A magnetic attraction to high-throughput genomics, Science, 1997, 276: 1887–1889.
Hawkins, T. L., O’Connor-Morin, T., Tog, A. et al., DNA purifica-tion and isolation using a solid-phase, Nucleic Acids Res., 1994, 22: 4543–4544.
Taylor, J. I., Hurst, C. D., Davis, M. J. et al., Application of mag-netite and silica-magnetite composites isolation of genomic DNA, J. Chromatogr. A, 2000, 890: 159–166.
Yoza, B., Arakaki, A., Matsunaga, T., DNA extraction using bacte-rial magnetic particles modified with hyperbranched polyami-doamine dendrite, J. Biotechnol., 2003, 101: 219–228.
Hickman, P. J., Leigh, J. E., Mera, R. M. et al., Oropharyngeal can-didiasis in HIV+ patients may influence the selection of HIV-1 protease variants, Virus Res., 2002, 87: 97–106.
Street, S., Donoghue, H. D., Neild, G. H., Tropheryma whippelii DNA in saliva of healthy people, The Lancet, 1999, 354: 1178–1179.
Xie, X., Zhang, X., Chen, D. et al., Magnetism based nucleic acid amplification, PCT patent, PCT/CN02/00940, 2002-12-31.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F., Maniatis, T., Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1989.
Jacobsen, C. S., Microscale detection of specific bacterial DNA in soil with a magnetic capture-hybridization and PCR amplification assay, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1995, 61: 3347–3352.
Tsai, Y. L., Le J. Y., Olson, B. H., Magnetic bead hybridization to detect enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains associated with cat-tle in environmental water sources, Can. J. Microbiol., 2003, 49: 391–398.
Ghassemifar, M. R., Eckert, J. J., Houghton, F. D. et al., Gene expression regulating epithelial intercellular junction biogenesis during human blastocyst developmentin vitro, Mol. Hum. Reprod., 2003: 245–252.
Schie, R. C., Wilson, M. E., Saliva: a convenient source of DNA for analysis of bi-allelic polymorphisms of Fc γ receptor IIA(CD32) and Fc γreceptor IIIB (CD16), J. Immunol. Methods, 1997, 208: 91–101.
Takahama, U., Oniki, T., Hirota, S., Oxidation of ouercetin by sali-vary components quercetin-dependent reduction of salivary nitrite under acidic conditions producing nitric oxide, J. Agric. Food Chem., 2002, 50: 4317–4322.
Terasaki, P., Chia, D., Sugich, L., Saliva as DNA source for HLA typing, Hum. Immunol., 1998, 59: 597–598.
Ahrendt, S. A., Halachmi, S., Chow, J. T. et al., Rapid p53 sequence analysis in primary lung cancer using an oligonucleotide probe array, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1999, 96: 7382–7387.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, X., Zhang, X., Gao, H. et al. DNA purification and gene typing: Based on multifunctional nanobeads. Chin. Sci. Bull. 49, 886–889 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03184004
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03184004