Abstract
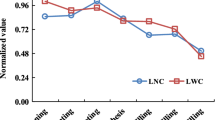
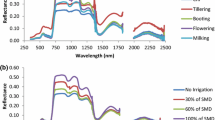
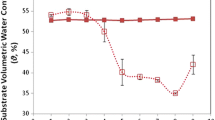
A total of 110 wheat leaf samples were collected in the field and their spectral reflectances were measured with a spectroradiometer in laboratory. After a spectral normalizing technique, the spectral absorption feature parameters such as the absorption depth and area, were extracted from each leaf spectrum. The relative water content (RWC) was measured for samples. The experimental results indicated that the spectral absorption depth and area of wheat leaves at 1 450 nm were correlated with their RWC. So we can diagnose wheat water status by using their spectral reflectances. Furthermore, we discuss the possibility of developing new instruments based on the analysis of the spectroradiometer data for non-destructive and instantaneous measurement of the wheat water status in the field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kramer, P. J., Water Relations of Plants, New York: Academic Press, New York Press, 1983.
Kriedemamn, P. E., Barrs, H. D., Photosynthetic adaptation to water stress and implication for drought resistance, Boulder, Colorado: Westbiew Press, 1983.
Tanner, C. B., Plant temperature, Agron, J., 1963, 50: 210.
Zhang, R., A new model for estimating water shortage based on the near-infrared radiation, Science in China, Ser. B, (in Chinese), 1987, 7: 776.
Idso, S. B., Jackson, R. D., Pinter, P. J. et al., Normalizing the stress-degree-day parameter for environmental variability, Agric Meteorol., 1981, 24: 45.
Curran, P. J., Remote sending of foliar chemistry, Remote Sens., 1989, 30: 271.
Penuelas, J., Filella, I., Biel, C. et al., The reflectance at the 950–970 nm region as an indicator of plant water status, International Journal of Remote Sensing, 1993, 14: 1887.
Raymond, F. K., Roger, N. C., Spectroscopic determination of leaf biochemistry using band-depth analysis of absorption features and stepwise multiple linear regression, Remote Sens., 1999, 67: 267.
Bo-Cai, G., Goetz, A. F. H., Extraction of dry leaf spectral features from reflectance spectra of green vegetation, Remote Sens., 1994, 47: 369.
Jackson, R. D., Spectral response of cotton to studdenly induced water stress, International Journal of Remote Sensing, 1985, 6: 177.
Michio, S., Tsugoshi, A., Seasonal visible, near-infrared and mid-infrared spectra of rice canopies in relation to LAI and above-ground dry phytomass, Remote Sens. Environ., 1989, 27: 119.
Clark, R. N., Roush, T. L., Reflectance Spectroscopy: Quantitative analysis techniques for remote sensing application, J. Geophys. Res., 1984, 89(B7): 6329.
Tian, Q., Tong, Q., Pu, R. et al., Spectroscopic determination of wheat water status using 1650–1850 nm spectral absorption features, International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, Q., Gong, P., Zhao, C. et al. A feasibility study on diagnosing wheat water status using spectral reflectance. Chin. Sci. Bull. 46, 666–669 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03182831
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03182831