Abstract
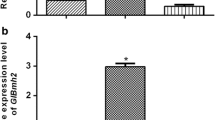
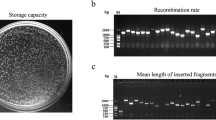
The 14-3-3 is a highly conserved, ubiquitous expressed protein in eukaryotes and very important in the regulation of such crucial cellular processes as metabolism, signal transduction, cell-cycle control, apoptosis, protein trafficking, transcription, stress responses, and malignant transformation. In this study, the full-length cDNA of 14-3-3 was cloned first time from a white-rot fungusPhanerochaete chrysosporium. Yeast two hybrid has been performed to fish out the proteins that can bind with 14-3-3 inP. chrysosporium. The results showed that 14-3-3 could form homodimers inP. chrysosporium. Two novel proteins containing predicted WD domain could interact with 14-3-3, too. In addition, the transcription of 14-3-3 gene under low-nitrogen medium was constitutional by RT-PCR analysis. These results indicate that 14-3-3 protein inP. chrysosporium may be involved in multiple cellular processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitken A., Howell S., Jones D., Madrazo J., Patel Y. (1995). 14-3-3 alpha and delta are the phosphorylated forms of raf-activating 14-3-3 beta and zeta.In vivo stoichiometric phosphorylation in brain at a Ser-Pro-Glu-Lys MOTIF. J. Biol. Chem., 270: 5706–5709.
Belinky P.A., Flikshtein N., Lechenko S., Gepstein S., Dosoretz C.G. (2003). Reactive oxygen species and induction of lignin peroxidase inPhanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 69 (11): 6500–6506.
Daugherty C.J., Rooney M.F., Miller P.W., Ferl R.J. (1996). Molecular organization and tissue-specific expression of anArabidopsis 14-3-3 gene. Plant Cell, 8 (8):1239–1248.
Gold M.H., Alic M. (1993). Molecular biology of the lignin-degrading basidiomycetePhanerochaete chrysosporium. Microbiol. Rev., 57: 605–622.
Horie M., Suzuki M., Takahashi E., Tanigami A. (1999). Cloning, expression, and chromosomal mapping of the human 14-3-3 gamma gene (YWHAG) to 7q11.23. Genomics, 60: 241–243.
Jones D.H., Ley S., Aitken A. (1995). Isoforms of 14-3-3 protein can form homo- and hetero-dimersin vivo andin vitro: implications for function as adapter proteins. FEBS Lett., 368: 55–58.
Kirk T.K., Farrell R.L. (1987). Enzymatic “combustion”: the microbial degradation of lignin. Annu Rev Microbiol., 41:465–505.
Liljas A. (1991). Comparative biochemistry and biophysics of ribosomal proteins. Int. Rev. Cytol. 124: 103–136.
Luk S.C., Ngai S.M., Tsui S.K., Chan K.K., Fung K.P., Lee C.Y., Waye M.M. (1998). Developmental regulation of 14-3-3 epsilon isoform in rat heart. J. Cell Biochem., 68: 195–199.
Martin H., Martin V., Tamara K., Mika S., Sarigalkin F.W. (1999). Production of manganese peroxides and organic acids and mineralization of14C-labelled lignin (14C-DHP) during solid state fermentation of wheat straw with the white-rot fungusNematolama frowardii. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 65: 1864–1870.
Martinez D., Larrondo L.F., Putnam N., Gelpke M.D., Huang K., Chapman J., Helfenbein K.G., Ramaiya P., Detter J.C., Larimer F., Coutinho P.M., Henrissat B., Berka R., Cullen D., Rokhsar D. (2004). Genome sequence of the lignocellulose degrading fungusPhanerochaete chrysosporium strain RP78. Nat. Biotechnol., 22: 695–700.
McConnell J.E., Armstrong J.F., Hodges P.E., Bard J.B. (1995). The mouse 14-3-3 epsilon isoform, a kinase regulator whose expression pattern is modulated in mesenchyme and neuronal differentiation. Dev. Biol., 169: 218–228.
Möller W., Maassen J.A. (1986). On the structure, function, and dynamics of L7/L12 fromEscherichia coli ribosomes. In: Hardesty B., Kramer G., Eds, Structure, Function and Genetics of Ribosomes, Springer-Verlag, New York, pp. 309–325.
Moore B.W., Perez V.J.(1967). Specific acidic proteins of the nervous system. In: Carlson F.D., Ed., Physiological and Biochemical Aspects of Nervous Integration, Englewood Ciffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, pp. 343–359.
Neer E.J., Schmidt C.J., Nambudripad R., Smith T. F. (1994). The ancient regulatory-protein family of WD-repeat proteins. Nature, 371: 297–300.
Roseboom P.H., Weller J.L., Babila T., Aitken A., Sellers L.A., Moiett J.R., Namboodiri M.A., Klein D.C. (1994). Cloning and characterization of the epsilon and zeta isoforms of the 14-3-3 proteins. DNA Cell Biol., 13: 629–640.
Rosenquist M., Alsterfjord M., Larsson C., Sommarin M. (2001). Data mining theArabidopsis genome reveals fifteen 14-3-3 genes. Expression is demonstrated for two out of five novel genes. Plant Physiol., 127: 142–149.
Smith T.F., Gaitatzesm C., Saxena K., Neer E.J. (1999). The WD repeat: a common architecture for diverse functions. Trends Biochem. Sci., 24: 181–185.
Stewart P., Cullen D. (1999). Organization and differential regulation of a cluster of lignin peroxidase genes ofPhanerochaete chrysosporium. J. Bacteriol., 181 (11): 3427–3432.
ter Haar E., Harrison S.C., Kirchhausen T. (2000). Peptide-ingroove interactions link target proteins to the β-propeller of clathrin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 97: 1096–1100.
Testerink C., van der Meulen R.M., Oppedijk B.J., de Boer A.H., Heimovaara-Dijkstra S., Kijne J.W., Wang M. (1999). Cell biology and signal transduction: differences in spatial expression between 14-3-3 isoforms in germinating barley embryos. Plant Physiol., 121: 81–88.
Tien M., Kirk T.K. (1988). Lignin peroxidase ofPhanerochaete Chrysosporium. In: Wood W.A., Kellogg S.T., Eds, Method in Enzymology, Academic Press, San Diego, 161B: pp. 238–249.
Vasara T., Keranen S., Penttila M., Saloheimo M. (2002). Characterization of two 14-3-3 genes fromTrichoderma reesei: interactions with yeast secretory pathway components. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1590: 27–40.
Wang W., Shakes D.C. (1996). Molecular evolution of the 14-3-3 protein family. J. Mol. Evol., 43: 384–398.
Watanabe M., Isobe T., Ichimura T., Kuwano R., Takahashi Y., Kondo H. (1993a). Molecular cloning of rat cDNAs for beta and gamma subtypes of 14-3-3 protein and developmental changes in expression of their mRNAs in the nervous system. Mol. Brain Res., 17: 135–146.
Watanabe M., Isobe T., Ichimura T., Kuwano R., Takahashi Y., Kondo H. (1993b). Developmental regulation of neuronal expression for the eta subtype of the 14-3-3 protein, a putative regulatory protein for protein kinase C. Dev. Brain Res., 73: 225–235.
Watanabe M., Isobe T., Ichimura T., Kuwano R., Takahashi Y., Kondo H., Inoue Y. (1994). Molecular cloning of rat cDNAs for the zeta and theta subtypes of 14-3-3 protein and differential distributions of their mRNAs in the brain. Mol. Brain Res., 25: 113–121.
Yaffe M.B., Rittinger K., Volinia S., Caron P.R., Aitken A., Leffers H., Gamblin S.J., Smerdon S.J., Cantley L.C. (1997). The structural basis for 14-3-3:phosphopeptide binding specificity. Cell 91, 961–971.
Zhou G.L., Yamamoto T., Ozoe F., Yano D., Tanaka K., Matsuda H., Kawamukai M. (2000). Identification of a 14-3-3 protein from Lentinus edodes that interacts with cap (adenylyl cyclaseassociated protein), and conservation of this interaction in fission yeast. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem., 64: 149–159.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, G., Feng, H., Zhang, T. et al. Molecular cloning of cDNAs for 14-3-3 and its protein interactions in a white-rot fungusPhanerochaete chrysosporium . Ann. Microbiol. 56, 191–196 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03175004
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03175004