Abstract
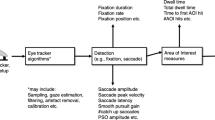
This study evaluated the effectiveness of three kinds of display methods for magnetic resonance (MR) image interpretation using an eye-tracking device. Seven radiologists interpreted head MR studies by using a single monitor (17-inch, 1,024×1,280 bit) in the 4 images/screen display format. Three paging modes were compared: (A) rapid paging only, (B) multiple image series display at the same slice position with consecutive rapid paging, and (C) simultaneous display of multiple series with each image series being browsed independently. Using an eye-mark camera, the radiologist's point of fixation and the duration of fixation were recorded during actual image interpretation. In mode A, the duration of fixation was short, and the points of fixation were distributed randomly over the visual field. In mode B, the points of fixation were clustered chiefly on a specific image series. In mode C, the points of fixation were not clustered on a specified series, but the duration of viewing the T2 series was relatively long. The total tracing area in mode B and C was smaller than that in mode A. Multiple series display, in which selected key series of slices could be viewed effectively, was found to be suitable for MR image interpretation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ishigaki T, Ikeda M, Shimamoto K, et al: Digital radiology and PACS. Nagoya J Med Sci 56:53–67, 1993
Hirota H, Shimamoto K, Yamakawa K, et al: Clinical evaluation of newly developed CRT viewing station: CT reading and observer's performance. Comput Med Imaging Graph 19:281–285, 1995
Shimamoto K, Yamakawa K, Ishigaki T, et al: Clinical evaluation of newly developed PACS at Nagoya University Hospital (abstract). Radiology 193(P):175, 1994
Shimamoto K: Recent advances and clinical evaluation of PACS at Nagoya University Hospital. Medical Imaging Technology 13:809–815, 1995
Beard DV, Johnston RE, Toki O, et al: A study of radiologists viewing multiple computed tomography examinations using an eyetracking device. J Digit Imaging 3:230–237, 1990
Saito T, Aoki S, Matsuno A, et al: Quantitative analysis of eye movement during VDT work. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi 96:1047–1054, 1992
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japanese Ministry of Education
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niimi, R., Shimamoto, K., Sawaki, A. et al. Eye-tracking device comparisons of three methods of magnetic resonance image series displays. J Digit Imaging 10, 147–151 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03168836
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03168836