Abstract
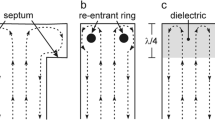
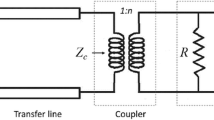
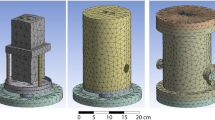
We present a convenient method for characterizing and optimizing the performance of quasioptical electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) sample cavities. The formalism is based on the transfer matrix method used in transmission line analysis. Transfer matrix representations are defined for each of the essential components of an open resonator, and the method is demonstrated by application to selected practical examples. Emphasis is given to optimization of quasioptical EPR for aqueous biological samples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes J.P., Freed J.H.: Rev. Sci. Instrum.68, 2838–2846 (1997)
Cardin J.T., Kolaczkowski S.V., Anderson J.R., Budil D.E.: Appl. Magn. Reson.16, 273–292 (1999)
Earle K.A., Freed J.H.: Appl. Magn. Reson.16, 247–272 (1999)
Collin R.E.: Foundations for Microwave Engineering, 2nd edn. New York: McGraw-Hill 1992.
Budil D.E., Ding Z., Smith G.R., Earle K.A.: J. Magn. Reson.144, 20–34 (2000)
Born M., Wolf E.: Optics, 6th edn. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1980.
Lesurf J.C.G.: Millimetre-Wave Optics, Devices, and Systems. Bristol: Adam Hilger 1990.
Ulrich R.: Infrared Phys.7, 37–55 (1967)
Goldsmith P.F. in: Infrared and Millimeter Waves (Button K., ed.), vol. 6, pp. 277–344. New York: Academic Press 1982.
Montgomery C.G., Dicke R.H., Purcell E.M.: Principles of Microwave Circuits. New York: McGraw-Hill 1948.
Harvey A.F.: Microwave Engineering. New York: Academic Press 1963.
Goldsmith P.F.: Quasioptical Systems. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press/Chapman and Hall 1998.
Barthel J., Bachhuber K., Buchner R., Hetzenauer H.: Chem. Phys. Lett.165, 369 (1990)
Hasted J.B., Husain S.K., Frescura F.A.M., Birch J.R.: Chem. Phys. Lett.118, 622–625 (1985)
Hasted J.B., Husain S.K., Frescura F.A.M., Birch J.R.: Infrared Phys.27, 11–15 (1987)
Afsar M.N., Hasted J.B.: J. Opt. Soc. Am.67, 902–904 (1977)
Hasted J.B.: Aqueous Dielectrics. London: Chapman and Hall 1973.
Wei Y.Z., Sridhar S.J.: Chem. Phys.92, 923–928 (1990)
Wei Y.Z., Sage J.T., Tian W.D., Kumbharkhane A.C., Sadeghi M., Champion P.M., Sridhar S., McDonald M.J.: J. Phys. Chem.98, 6644–6651 (1994)
Buckley F., Maryott A.A.: Tables of Dielectric Dispersion Data for Pure Liquids and Dilute Solutions. Washington, D.C.: National Bureau of Standards 1958.
Press W.H., Teukolsky S.A., Vetterling W.T., Flannery B.P.: Numerical Recipes in C: The Art of Scientific Computing, 2nd edn. New York: Cambridge University Press 1992.
The Math Works, I. MATLAB, 5.3.1 edn. Natick, MA: The Math Works, Inc. 1998.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Earle, K.A., Zeng, R. & Budil, D.E. Transfer matrix method for optimizing quasioptical EPR cavities. Appl. Magn. Reson. 21, 275–286 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03162407
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03162407