Abstract
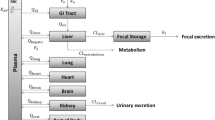
Concern about the carcinogenic potential of styrene (ST) is due to its reactive metabolite, styrene-7,8-oxide (SO). To estimate the body burden of SO resulting from various scenarios, a physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model for ST and its metabolite SO was developed. This PBPK model describes the distribution and metabolism of ST and SO in the rat, mouse and man following inhalation, intravenous (i.v.), oral (p.o.) and intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration of ST or i.v., p.o. and i.p. administration of SO. Its structure includes the oxidation of ST to SO, the intracellular first-pass hydrolysis of SO catalyzed by epoxide hydrolase and the conjugation of SO with glutathione. This conjugation is described by an ordered sequential ping-pong mechanism between glutathione, SO and glutathioneS-transferase. The model was based on a PBPK model constructed previously to describe the pharmacokinetics of butadiene with its metabolite butadiene monoxide. The equations of the original model were revised to refer to the actual tissue concentration of chemicals instead of their air equivalents used originally. Blood: air and tissue: blood partition coefficients for ST and SO were determined experimentally and have been published previously. Metabolic parameters were taken from in vitro or in vivo measurements. The model was validated using various data sets of different laboratories describing pharmacokinetics of ST and SO in rodents and man. In addition, the influences of the biochemical parameters, alveolar ventilation and blood: air partition coefficient for ST on the pharmacokinetics of ST and SO were investigated by sensitivity analysis. The PBPK model presented can be used to predict concentration-time curves of ST or SO in blood and different tissues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen ME, Gargas ML, Ramsey JC (1984) Inhalation pharmacokinetics: Evaluating systemic extraction, total in vivo metabolism, and the time course of enzyme induction for inhaled styrene in rats based on arterial blood: inhaled air concentration ratios. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 73: 176–187.
Armes AD, Travis CC (1988) Reference physiological parameters in pharmacokinetic modeling. US Environmental Protection Agency. EPA/600/6-88/004
Åstrand I, Kilbom A, Övrum P, Wahlberg I, Vesterberg O (1974) Exposure to styrene. I. Concentration in the alveolar air and blood at rest and during exercise and metabolism. Work Environ Health 11: 69–85
Beiswanger CM, Mandella RD, Graessle TR, Reuhl KR, Lowndes HE (1993): Synergistic neurotoxic effects of styrene oxide and acrylamide: glutathione-independent necrosis of cerebellar granule cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 118: 233–244
Bidoli F, Airoldi L, Pantarotto C (1980) Quantitative determination of styrene-7,8-oxide in blood by combined gas chromatography-multiple ion detection mass fragmentography. J Chromatogr 196: 314–318
Bogan R, Csanády GyA, Filser JG (1993) Michaelis-Menten parameters of styrene metabolism in hepatocytes of rat and mouse. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Toxicol Suppl 347: R6
Bois FY, Zeise L, Tozer TN (1990) Precision and sensitivity of pharmacokinetic models for cancer risk assessment: tetrachloroethylene in mice, rats and humans. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 102: 300–315
Bond JA (1989) Review of the toxicology of styrene. CRC Crit Rev Toxicol 19: 227–249
Conti B, Maltoni C, Perino G, Ciliberti A (1988) Long-term carcinogenicity bioassays on styrene administered by inhalation, ingestion and injection and styrene oxide administered by ingestion in Sprague-Dawley rats, and para-methylstyrene administered by ingestion in Sprague-Dawley rats and mice. Ann NY Acad Sci 534: 203–234
Corley RA, Mendrala AL, Smith FA, Staats DA, Gargas ML, Conolly RB, Andersen ME, Reitz RH (1990) Development of a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model for chloroform. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 103: 512–517
Davis NR, Mapleson WW (1981) Structure and quantification of a physiological model of the distribution of injected agents and inhaled anaesthetics. Br J Anaesth 53: 399–495
Dedrick RL, Forrester DD, Cannon JN, El Dareer SM, Mellett LB (1973) Pharmacokinetics of 1-ß-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine (ARA-C) deamination in several species. Biochem Pharmacol 22: 2405–2417.
Droz PO, Guillemin MP (1983) Human styrene exposure. V. Development of a model for biological monitoring. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 53: 19–36
D’Souza RW, Francis WR, Andersen ME (1988) Physiological model for tissue glutathione depletion and increased resynthesis after ethylene dichloride exposure. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 245: 563–568
Ehrenberg L, Hiesche K, Osterman-Golkar S, Wennberg I (1974) Evaluation of genetic risk of alkylating agents: tissue doses in the mouse from air contaminated with ethylene oxide. Mutat Res 24: 83–103
Fernández JG, Caperos JR (1977) Exposition au Styrène. I. Etude expérimentale de l’absorption et de l’excrétion pulmonaires sur des sujets humans. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 40: 1–12
Filser JG (1992) The closed chamber technique — uptake, endogenous production, excretion, steady-state kinetics and rates of metabolism of gases and vapours. Arch Toxicol 66: 1–10
Filser JG, Bolt HM (1984) Inhalation pharmacokinetics based on gas uptake studies. VI. Comparative evaluation of ethylene oxide and butadiene monoxide as exhaled reactive metabolites of ethylene and 1,3-butadiene in rats. Arch Toxicol 55: 219–223
Filser JG, Denk B, Törnqvist M, Kessler W, Ehrenberg L (1992) Pharmacokinetics of ethylene in man; body burden with ethylene oxide and hydroxyethylation of hemoglobin due to endogenous and environmental ethylene. Arch Toxicol 66: 157–163
Filser JG, Johanson G, Kessler W, Kreuzer P, Stei P, Baur C, Csanády GyA (1993a) A pharmacokinetic model to describe toxicokinetic interactions between 1,3-butadiene and styrene in rats: predictions for human exposure. IARC Scientific Publications No. 127, IARC, 65–78
Filser JG, Schwegler U, Csanády GyA, Greim H, Kreuzer PE, Kessler W (1993b) Species-Specific pharmacokinetics of styrene in rat and mouse. Arch Toxicol 67: 517–530
Fiserova-Bergerova V (1983) Physiological models for pulmonary administration and elimination of inert vapours and gases. In: Fiserova-bergerova V (ed.) Modeling of inhalation exposure to vapours: uptake, distribution and elimination Vol I. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 73–101
Frederick CB, Potter DW, Chang-Mateu MI, Andersen ME (1992) A physiologically based pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic model to describe the oral dosing of rats with ethyl acrylate and its implications for risk assessment. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 114: 246–260
Gargas ML (1991) Chemical-specific constants for physiologicallybased pharmacokinetic models. CIIT Activities 11: 1–9
Gross EA, Morgan KT (1991) Architecture of nasal passages and larynx. In: Parent RA (eds) Treatise on pulmonary toxicology. I. Comparative biology of the normal lung, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Ann Arbor, London, Tokyo, pp 7–25
Haber F (1924) Zur Geschichte des Gaskrieges, Fünf Vorträge aus den Jahren 1920–1923. Julius Springer.
Jeffery EH, Haschek WM (1988) Protection by dimethylsulfoxide against acetaminophen-induced hepatic, but not respiratory toxicity in the mouse. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 93: 452–461
Johanson G, Filser JG (1992) Experimental data from closed chamber gas uptake studies in rodents suggest lower uptake rate of chemical than calculated from literature values on alveolar ventilation. Arch Toxicol 66: 291–295
Johanson G, Filser JG (1993) A physiologically based pharmacokinetic model for butadiene and its metabolite butadiene monoxide in rat and mouse and its significance for risk extrapolation. Arch Toxicol 67: 151–163
Johanson G, Näslund PH (1988) Spreadsheet programming — a new approach in physiologically based modeling of solvent toxicokinetics. Toxicol Lett 41: 115–127
Korn M, Gfrörer W, Filser JG, Kessler W (1994) Styrene-7,8-oxide in blood of workers exposed to styrene. Arch Toxicol (in press)
Krishnan K, Gargas ML, Fennell TR, Andersen ME (1992) A physiologically based description of ethylene oxide dosimetry in the rat. Toxicol Ind Health 8: 121–140
Kuwahira I, Gonzalez N, Heisler N, Piiper J (1993) Regional blood flow in conscious resting rats determined by microsphere distribution. J Appl Physiol 74: 203–210
Laib RJ, Filser JG, Kreiling R, Vangala RR, Bolt HM (1990) Inhalation pharmacokinetic of 1,3-butadiene and 1,2-epoxybutene-3 in rats and mice. Environ Health Perspect 86: 57–63
Langvardt PW, Nolan RJ (1991) Determination of styrene-7,8-oxide in whole rat blood by gas chromatography — mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr 567: 93–103
Lijinski W (1986) Rat and mouse fore stomach tumors induced by chronic oral administration of styrene oxide. J Natl Cancer Inst 77: 471–476
Löf A, Johanson G (1993) Dose-dependent kinetics of inhaled styrene in man. IARC Sciencetific Publications No. 127, IARC, 89–99
Löf A, Gullstrand E, Nordqvist BM (1983) Tissue distribution of styrene, styrene glycol and more polar styrene metabolites in the mouse. Scand J Work Environ Health 9: 419–430
Löf A, Gullstrand E, Lundgren A, Nordqvist MB (1984) Occurrence of styrene-7,8-oxide and styrene glycol in mouse after administration of styrene. Scand J Work Environ Health 10: 179–187
Löf A, Lundgren E, Nordqvist BM (1986) Kinetics of styrene in workers from plastics industry after controlled exposure: a comparison with subjects not previously exposed. Br J Ind Med 43: 537–543
MAK (ed) (1987) Styrol. Toxikologisch-arbeitsmedizinische Begründung von MAK-Werten (Maximale Arbeitsplatz-Konzentration). VCH, Weinheim, 13. Ed.
Mannervik B, Danielson UH (1988) Glutathione transferases — structure and catalytic activity. CRC Crit Rev Biochem 23: 283–337
Mendrala AL, Langvardt PW, Nitschke KD, Quast JF, Nolan RJ (1993) In vitro kinetics of styrene and styrene-7,8-oxide metabolism in rat, mouse and human. Arch Toxicol 67: 18–27
Menzel DB (1987) Physiological pharmacokinetic modeling. Environ Sci Technol 21: 944–950
Palin KJ, Whalley DR, Wilson CG, Davis SS, Philips AJ (1982) Determination of gastric-emptying profiles in the rat: Influence of oil structure and volume. Int J Pharm 12: 315–322
Pantarotto C, Fanelli R, Belletti I, Bidoli F (1980) Determination of styrene in biological specimens by gas chromatography — selected ion monitoring: distribution in mice. Anal Biochem 105: 340–347
Paterson S, Mackay D (1986) A pharmacokinetic model of styrene inhalation with the fugacity approach. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 82: 444–453
Perbellini L, Mozzo P, Turri PV, Zedde A, Brugnone F (1988) Biological exposure index of styrene suggested by a physiologico-mathematical model Int Arch Occup Environ Health 60: 187–193
Rabitz H (1981) Chemical sensitivity analysis theory with applications to molecular dynamics and kinetics. Comp Chem 5: 167–180
Ramsey JC, Andersen ME (1984) A physiologically based description of the inhalation pharmacokinetics of styrene in rats and humans. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 73: 159–175
Ramsey JC, Young JD (1978) Pharmacokinetics of inhaled styrene in rats and humans. Scand J Work Environ Health 4 [Suppl 2]: 84–91
Reits RH, McCroskey PS, Park CN, Andersen ME, Gargas ML (1990) Development of a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model for risk assessment with 1,4-dioxane. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 105: 37–54
Ross AM, Pohl TM, Piazza K, Thomas M, Fox B, Whalen DL (1982) Vinyl epoxide hydrolysis reactions. J Am Chem Soc 104: 1658–1665
Schmidt RF, Thews G (1977) Physiologie des Menschen. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York
Schwegler U (1991) Pharmacokinetik von Styrol bei Ratte und Maus. Institut für Toxikologie, GSF. GSF-Bericht 15/91
Schwegler U, Filser JG (1989) Inhalation kinetics of styrene in rat and mouse. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Toxicol Suppl 30: R14
Sies H, Ketterer B (1988) Glutathione conjugation, Mechanism and biological significance. Academic Press, London, San Diego
Stewart RD, Dodd HC, Baretta ED, Schaffer AW (1968) Human exposure to styrene vapor. Arch Environ Health 16: 656–662
Vujtovic-Ockenga N, Baur C, Kessler W, Filser JG (1993) Direct determination of partition coefficients tissue/blood of non-volatile substances — example: styrene-7,8-oxide. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Toxicol Suppl 347: R6
Wigaeus E, Löf A, Nordqvist BM (1984) Uptake, distribution, metabolism and elimination of styrene in man. A comparison between single exposure and co-exposure with acetone. Br J Ind Med 41: 539–546
Withey JR (1978) The toxicology of styrene monomer and its pharmacokinetics and distribution in the rat. Scand J Work Environ Health 4 [Suppl 2]: 31–40
Withey JR, Collins PG (1977) Pharmacokinetics and distribution of styrene monomer in rats after intravenous administration. J Toxicol Environ Health 3: 1011–1020
Withey JR, Collins PG (1979) The distribution and pharmacokinetics of styrene monomer in rats by the pulmonary route. J Environ Path Toxicol 2: 1329–1342
Young JD, Ramsey J, Blau GE, Karbowski RJ, Nitschke KD, Slauter RW, Braun WH (1979) Pharmacokinetics of inhaled and intraperitonially administered styrene in rats Proceedings of the Tenth Interamerican Conference on Toxicology and Occupational Medicine. Elsevier, North Holland, New York, pp 297–310
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Csanády, G.A., Mendrala, A.L., Nolan, R.J. et al. A physiologic pharmacokinetic model for styrene and styrene-7,8-oxide in mouse, rat and man. Arch Toxicol 68, 143–157 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03035414
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03035414