Abstract
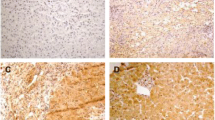
While the elimination of hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a common phenomenon at the end of the acute phase of disease, the persistence of HBV is characteristic for chronic hepatitis (CHB). Recent evidence indicates that the elimination of HBV is achieved by FAS/FAS-L induced apoptosis of infected hepatocytes. The aim of this study was to test the hypothesis that HBV persistence in the hepatocytes of CHB patients is due to the delayed onset of apoptosis caused by altered FAS/FAS-L interactions between lymphocytes and hepatocytes. The expression of FAS, FAS-L, BAX, BCL-2, ICE and PCNA in the liver biopsies of 55 patients (14 HBsAg positive, 20 patients with alcoholic hepatopathy, 21 patients with other hepatopathies) was tested by immunohistochemistry. Apoptosis of hepatocytes was evaluated by morphological as well as by TUNEL method. The results were correlated with a grading/staging score and analysed statistically using a one way analysis of variance and the Duncan test. Significantly higher numbers of BAX positive hepatocytes were observed in HBsAg positive patients when compared to control groups. Similarly, both BAX and FAS positive lymphocytes were more frequent in HBsAg positive patients. FAS-L positive lymphocytes and hepatocytes were numerous in all patient groups. Increased numbers of BAX positive hepatocytes in CHB may reflect the increased readiness of these cells to undergo apoptosis. However, the increased numbers of both BAX and FAS positive lymphocytes in CHB suggest that these cells may be particularly sensitive to FAS-L mediated apoptosis potentially resulting in lowered viability of these lymphocytes. This may explain, at least in part, the defective removal of virus-infected cells in chronic hepatitis. However, we cannot rule out the possibility that survival of hepatocytes during CHB may be due to other mechanisms such as defects in apoptosis activation triggered by CD40, defects involving DNase and/or other caspases downstream in the apoptotic cascade within these cells, or to defects in CTL function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JM, Cory S: The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science 281:1322–26, 1998.
Afford SC, Randhawa S, Eliopoulos AG, et al: CD40 activation induces apoptosis in cultured human hepatocytes via induction of cell surface fas ligand expression and amplifies fas-mediated hepatocyte death during allograft rejection. J Exp Med 189:441–6, 1999.
Ando K, Guidotti LG, Wirth S, et al: Class I-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes are directly cytopathic for their target cells in vivo. J Immunol. 152:3245–3253, 1994.
Bellgrau D, Gold D, Selawry H, et al: A role for CD95 ligand in preventing graft rejection. Nature 377: 630–632, 1995
Berke G:The CTL’s kiss of death Cell 81:9–12, 1995.
Beutler B, van Huffel C: Unraveling function in the TNF ligand and receptor families. Science 264:667–668, 1994.
Dayan CM: FasL expression on epithelial cells: the BotazzoFeldmann hypothesis revisited. Immunology Today 18:203, 1997.
Dervan PA, Magee HM, Buckley C, et al: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen counts in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue correlate with Ki-67 in fresh tissue. Am J Clin Pathol 97 (Suppl. 1): S21-S28, 1992.
Ehrmann J jr, Jezdinská V, Ehrmann J, et al: Immunohistochemical study of the expression of BCL-2, PCNA and p53 proteins in the patients with hepatitis B. The pilot study. Acta Univ Palacki Olomuc, Fac Med 10:83–85, 1996.
Enari M, Hug H, Nagata S: Involvement of an ICE-like protease in FAS-mediated apoptosis. Nature 375:78–81, 1995.
Ferrari C, Penna A, Bertoletti A, et al: Hepatitis B virus-specific immune response: from antigen recognition to liver damage. Forum 6:203–216, 1996.
French LE, Tschopp J: Thyroiditis and hepatitis: FAS on the road to disease. Nature Medicine 3:387–388, 1997.
Galle PR, Hofmann WJ, Walczak H, et al: Involvement of the CD 95 (APO-1/Fas) receptor and ligand in liver damage. J Exp Med 182:1223–30, 1995.
Golstein P: Controlling cell death. Science 275:1081–1082, 1997.
Griffith TS, Brunner T, Fletcher SM, et al: Fas ligand-induced apoptosis as a mechamism of immune privilege. Science 270:1189–1192, 1995.
Guidotti LG, Borrow P, Hobbs MV, et at Viral cross talk: intracellular inactivation of the hepatitis B virus during an unrelated viral infection of the liver. Immunology 93:4589–4594, 1996.
Guidotti LG, Chisari FV: The transgenic mouse model of hepatitis B virus infection. Forum 6:189–200, 1996.
Guidotti LG, Ishikawa T, Hobbs MV, et al: Intracellular inactivation of the hepatitis B virus by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Immunity 4:25–26, 1996.
Guilhot S, Miller T, Cornman G, et al: Apoptosis induced by tumor necrosis factor in rat hepatocyte cell lines expressing hepatitis B virus. Am J Pathol 148:801–814, 1996.
Hahne M, Rimoldi D, Schröter M, et al: Melanoma cell expression of FAS (Apo-1/CD95) ligand: implications for tumor immune escape. Science 274:1363–1366, 1996.
Hiramatsu N, Hayashi A, Katayama K, et al: Immunohistochemical detection of Fas antigen in liver tissue of patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 19:1354–1359, 1994.
Chisari F: Hepatitis B virus transgenic mice: insights into the virus and disease. Hepatology 22:1316–1325, 1995.
Ishak K, Baptista A, Blanchi L, et al: Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. J Hepatol 22:696–699, 1995.
Kondo T, Suda T, Fukuyama H, et al: Essential roles of the FAS ligand in the development of hepatitis. Nature Medicine 3:409–413, 1997.
Koziel MJ: Immunology of viral hepatitis. Am J Med 100:98–109, 1996.
Kroemer G: The proto-oncogene Bcl-2 and its role in regulating apoptosis. Nature Medicine 3:614–620, 1997.
Lacronique V, Mignon A, Fabre A, et al: Bcl-2 protects from lethal hepatic apoptosis induced by an anti-Fas antibody in mice. Nature Medicine 2:80–86, 1996.
Liu CC, Walsh CM, Young JDE: Perforin: structure and function. Immunol Today 16:194–201, 1995.
Luo KX, Zhu YF, Zhang LX, et al: In situ investigation of Fas/FasL expression in chronic hepatitis B infection and related liver diseases. J Viral Hepat 4:303–7, 1997.
Los M, Van de Craen M, Penning LC, et al: Requirement of an ICE/CED-3 protease for FAS/APO-1-mediated apoptosis. Nature 375:81–83, 1995.
Marinos G, Torre F, Chokshi S, et al: Induction of T-helper cell response to hepatitis B core antigen in chronic hepatitis B: a major factor in activation of the host immune response to the hepatitis B virus. Hepatology 22:1040–1049, 1995.
Mochizuki K, Hayashi N, Hiramatsu N, et al: Fas antigen expression in liver tissues of patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatology 24:1–7, 1996.
Muschen M, Warskulat U, Douillard P, et al: Regulation of CD95 (APO-1/Fas) receptor and ligand expression by lipopolysaccharide and dexamethasone in parenchymal and nonparenchymal rat liver cells. Hepatology 27:200–208, 1998.
Nagata S, Golstein P: The FAS death factor. Science 267:1449–1456, 1995.
Nakamoto Y, Guidotti LG, Pasquetto V, et al: Differential target cell sensitivity to CTL-activated death pathways in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. J Immunol 158:5692–7, 1997.
Paroli M, Nisini R, Accapezzato D, et al: Viral escape from the immune systems control. Forum 6:122–127, 1996.
Patel T, Gores GJ, Kaufmann SH: The role of proteases during apoptosis. FASEB J 10:587–597, 1996.
Peters M: Actions of cytokines on the immune response and viral interactions: an overview. Hepatology 23:909–916, 1996.
Reed JC: Double identity for proteins of the Bcl-2 family. Nature 387:773–776, 1997.
Rehermann B, Lau D, Hoofnagle JH, et al: Cytotoxic T lymphocyte responsiveness after resolution of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Clin Invest 7:1655–1665, 1996.
Romero R, Lavine JE: Cytokine inhibition of the hepatitis B virus core promoter. Hepatology 23:17–23, 1996.
Ryo K, Kamogawa Y, Ikeda I, et al: FAS and FAS ligand strongly expressed in liver of fulminant hepatitis patients. Hepatology 22: AASLD Abstracts: 230 A, 1995.
Shibata S, Kyuwa S, Lee S, Toyota Y, et al: Apoptosis induced in mouse hepatitis virus infected cells by a virus specific CD8+ cytotoxic lymphocyte clone. J Virol 68:7540–7545, 1994.
Schaff Z, Lotz G, Schulte-Herman R: Pathomorphological characteristic and pathogenesis of viral hepatitis. Pathology Oncology Research 2:132–143, 1996.
Smyth MJ, Trapani JA: Granzymes: exogenous proteinases that induce target cell apoptosis. Immunology Today 16:202–206, 1995.
Strand S, Hofmann WJ, Hug H, et al: Lymphocyte apoptosis induced by CD95 (Apo-1/Fas) ligand-expressing tumor cells a mechanism of immune evasion? Nature Medicine 2:1361–1366, 1996.
Streilein JW. Unraveling immune privilege. Science 270:1158–1159, 1995.
Tang DG, Porter AT: Apoptosis: a current molecular analysis. Pathology Oncology Research 2:117–131, 1996.
Vaux DL: Ways around rejection. Nature 377:576–577, 1995.
Williams N: Tumor cells fight back to beat immune system. Science 274:1362–1363, 1996.
Yoffe B, Noonan CA: Hepatitis B virus new and evolving issues. Dig Dis Sciences 37:1–9, 1992.
Yoong KF, Afford SC, Randhawa S, et al: DH: Fas/Fas ligand interaction in human colorectal hepatic metastases: A mechanism of hepatocyte destruction to facilitate local tumor invasion. Am J Pathol 154:693–703, 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ehrmann, J., Galuszková, D., Ehrmann, J. et al. Apoptosis-related proteins, BCL-2, BAX, FAS, FAS-L and PCNA in liver biopsies of patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 6, 130–135 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03032363
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03032363