Abstract
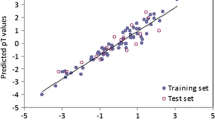
The kinetics of the reductive transformation rates of a set of 17 halogenated aliphatic hydrocarbons in anaerobic sediment-water mixtures are examined using different QSAR methods. Statistical experimental design in combination with multivariate chemical characterization of the compounds was used to select a representative training and validation set. The aim of the QSARs is to generate predictions for priority setting and risk assessment purposes, and to better understand the kinetics of the dehalogenation of aliphatic hydrocarbons. The first QSAR was constructed with multiple linear regression using readily available descriptors. Subsequently, a multivariate QSAR was constructed using the partial least squares (PLS) method with 36 (physico)-chemical descriptors. Finally, a transition state approach has been used in which quantum chemically calculated activation energies for the transition state of the most probable reaction mechanism are used to model the reaction rate constantsk. Because of the relatively small size of the training set (10 compounds) the linear regression QSAR using multiple descriptors does not show good predictive capabilities on the validation set. The PLS relationship and the transition state QSAR are both capable of generating predictions of rate constants within one order of magnitude. Moreover, the transition state QSAR closely follows, and thus corroborates the assumed reaction mechanism for reductive dehalogenation. Predictions for 23 non tested halogenated aliphatics are given and compared using both the PLS and the transition state model.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
W. Karcher;B.G. Hansen;C. van Leeuwen;P. Wagner;C. Auer: Predictions for existing chemicals — A multilateral QSAR project. SAR & QSAR Environ. Res.3 (1995) 217–221
J. Hermens;S. Balaz;J. Damborsky;W. Karcher;M. Müller;W. Peijnenburg;A. Sabljic;M. Sjöström: Assessment of QSARs for predicting fate and effects of chemicals in the environment: an international european project. SAR & QSAR Environ. Res.3 (1995) 223–236
J.M. Suflita;A. Horowitz;D.R. Shelton;J.M. Tiedje: Dehalogenation: a novel pathway for the anaerobic biodegradation of haloaromatic compounds. Science218 (1982) 1115–1117
J. Struijs;J.E. Rogers: Reductive dehalogenation of dichloroanilines by anaerobic microorganisms in fresh and dichlorophenol-acclimated pond sediment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.55 (1989) 2527–2531
W.J.G.M. Peijnenburg;M.J. ′t Hart;H.A. den Hollander;D. van de Meent;H.H. Verboom;N.L. Wolfe: Reductive transformations of halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons in anaerobic water-sediment systems: Kinetics, mechanisms and products. Environ. Toxicol. Chem.11 (1992) 286–300
J.E.M. Beurskens: Microbial transformation of chlorinated aromatics in sediments. PhD. Thesis Landbouwuniversiteit Wageningen, Wageningen, The Netherlands 1995
H.B. Krop;L.C.M. Commandeur;H.A.J. Govers: Prediction of redox potentials and isomer distribution yields for reductive dechlorination of chlorobenzenes. SAR & QSAR Environ. Res.2 (1994) 271 -287
E. Rorije;J.H. Langenberg;J. Richter;W.J.G.M. Peijnenburg: Modeling reductive dehalogenation with quantum chemically derived descriptors. SAR & QSAR Environ. Res.4 (1995) 237–252
R.P. Richards;J.W. Kramer;D.B. Baker;K.A. Krieger: Pesticides in rainwater in the Northern United States. Nature327 (1987) 129–131
K.H. Reinert;J.H. Rodgers: Fate and persistence of aquatic herbicides. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.98 (1987) 61
G.M. Klecka;S.J. Gonsior: Reductive dechlorination of chlorinated methanes and ethanes by reduced iron(II)porphyrins. Chemosphere13 (1984) 391–402
G.P. Curtis; M. Reinhard: Reductive dehalogenation of hexachloroethane, carbon tetrachloride, and bromoform by anthraquinone disulfonate and humic acid. Environ. Sci. Technol.28 (1994) 2393–2401
H.J.M. Verhaar;E. Rorije;H. Borkent;W. Seinen;J.L.M. Hermens. Modelling the nucleophilic reactivity of small organochlorine electrophiles. A mechanistically-based Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship. Environ. Toxicol. Chem.15 (1996) 1011–1018.
L. Eriksson;J. Jonsson;S. Hellberg,;F. Lindgren;B. Skager-BERG;M. Sjöström;S. Wold;R. Berglind: A strategy for ranking environmentally occurring chemicals. Part III: Multivariate Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships for halogenated aliphatics. Environ. Toxicol. Chem.9 (1990) 1339–1351
G.E.P. Box;W.G. Hunter;J.S. Hunter: Statistics for Experimenters, Wiley, New York 1978
L. Eriksson;J. Jonsson;S. Hellberg;F. Lindgren;M. Sjöström;S. Wold;B.E. Sandström; I. Svensson: A strategy for ranking environmentally occurring chemicals. Part V: The development of two genotoxicity QSARs for halogenated aliphatics. Environ. Toxicol. Chem.10 (1991) 585–569
W.J.G.M. Peijnenburg; L. Eriksson; A. de Groot; M. Sjöström; H. Verboom: The kinetics of reductive dehalogenation of a set of halogenated aliphatic hydrocarbons in anaerobic sediment slurries. submitted (1996)
R.S. Wade;C.E. Castro: Oxidation of iron(II)porphyrins by alkyl halides. J. Am. Chem. Soc.95 (1973) 226
T.M. Vogel;C.S. Criddle;P.L. McCarty: Transformations of halogenated aliphatic compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol.21 (1987) 722
L.P. Wackett;M.S.P. Logan;F.A. Blocki;C. Bao-li: A mechanistic perspective on bacterial metabolism of chlorinated methanes. Biodegradation3 (1992) 19–36
C.J. Gantzer;L.P. Wackett: Reductive dechlorination catalyzed by bacterial transition-metal coenzymes. Environ. Sci. Technol.25 (1991) 715–722
U.E. Krone;R.K. Thauer;H.P.C. Hogenkamp: Reductive dehalogenation of chlorinated C1-hydrocarbons mediated by corrinoids. Biochemistry28 (1989) 4908–4914
D. Leo;D. Weininger: MedChem Software manual. Daylight Chemical Information Systems Inc. USA 1989
C. Hansch;A.J. Leo: Substituent constants for correlation analysis in chemistry and biology. John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY, USA 1979
L. Eriksson: A strategy for ranking environmentally occurring chemicals. PhD. Thesis University of Umeå, Umeå, Sweden 1991
L. Eriksson;H. Verboom;W.J.G.M. Peijnenburg: Multivariate QSAR modelling of the rate of reductive dehalogenation of haloalkanes. Journal of Chemometrics10 (1996) 483–492
S. Wold. In:H.v.d. Waterbeemd (ed.) Chemometric methods in molecular design-methods and principles in medicinal chemistry, VCH, Weinheim (1995)
A. Höskuldsson: Journal of Chemometrics9 (1995) 91
SIMCA-S 6.0, Umetri AB, P.O.Box 7960, 90719 Umeå, Sweden (1995)
M.J. Frisch; G.W. Trucks; M. Head-Gordon; P.M.W. Gill; M.W. Wong; J.B. Foresman; B.G. Johnson; H.B. Schlegel; M.A. Robb; E.S. Replogle; R. Gomperts; J.L. Andres; K. Raghavachari; J.S. Binkley; C. Gonzalez; R.L. Martin; D.J. Fox; D.J. Defrees; J. Baker; J.J.P. Stewart; and J.A. Pople: Gaussian 92, Revision E.1. Gaussian Inc., Pittsburgh USA 1992
J.B. Foresman; Æ. Frisch: Exploring Chemistry with Electronic Structure Methods, Gaussian, Inc., Pittsburgh USA 1993
W.J.G.M. Peijnenburg, H. den Hollander, D. van de Meent, H. Verboom, N.L. Wolfe: De ontwikkeling van een struktuur-aktiviteits relatie voor de reductie van gehalogeneerde koolwaterstoffen in anaerobe water-sediment Systemen. RIVM-report nr. 718817001, Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 1988
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rorije, E., Eriksson, L., Verboom, H. et al. Predicting reductive transformation rates of halogenated aliphatic compounds using different QSAR approaches. Environ. Sci. & Pollut. Res. 4, 47–54 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02986265
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02986265
Keywords
- Reductive dehalogenation
- haiogenated aliphatics, in sediment-water mixtures
- halogenated aliphatics, reductive dehalogenation, in sediment-water mixtures
- QSARs
- multivariate statistics
- partial least squares, PLS
- statistical design
- transition state theory, molecular orbital calculations
- activation energy
- molecular orbital calculations
- transition state theory, reaction kinetics