Abstract
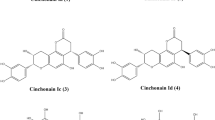
Nine known diarylheptanoids (1–9) isolated from the barks ofAlnus japonica were evaluated for their inhibitory activities on nitric oxide (NO) and prostagrandin E2 (COX-2) production in interferon-γ (INF-γ) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated RAW 264.7 cellsin vitro. The NO and COX-2 levels were moderately reduced by the addition of compounds (1–9). Among these compounds, compounds6 and8 inhibited NO production in a dose dependent manner with an IC50of 16.7 and 27.2 μg/mL, respectively (positive control, L-NMMA; 22.8 μg/mL), and compounds6,7,8, and9 reduced the COX-2 level in a dose dependent manner with an IC50 of 20.7, 25.7, 25.0, and 27.3 μg/mL, respectively (positive control, indomethacin; 26.2 μg/mL). An analysis of the structural activity relationship among these diarylheptanoids suggests that the presence of a keto-enol group in the heptane moiety or a caffeoyl group in the aromatic ring were important for the efficacy on the inhibitory activities of NO and COX-2 production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jang D. S., Muriel C., Alison D. P., Leonardus B. S. K., Kazuko K., Norman R. R., Harry H. S. F., John M. P., and A. Douglas K., Potential cancer chemopreventive constituents of the leaves ofMacaranga triloba.Phytochemistry, 65, 345–350 (2004)
Je K. H., Jan A. R., Lee H. T., Mar W. C., and Seo E. K., The inhibitory Principle of lipopolysaccharide-lnduced Nitric Oxide Production fromInula britannica var.chinensis.Arch. Pharm. Res., 27, 83–85 (2004).
Kim, H. J., Kim, K. H., Yeom, S. H., Kim, M. K., Shim, J. G., and Lee M. W., New Diarylheptanoid from the Barks ofAlnus japonica steudel.Chinese Chem. Lett., submitted (2004).
Lee, M. W., Kim N. Y., Park, M. S., Ahn, K. H., Toh, S. H., Hahn, D. R., Kim, Y. C, and Chung, J. T., Diarylheptanoids withIn vitro inducible nitric oxide synthesis inhibitory activity fromAlnus hirsuta. Planta Med., 66, 551–553 (2000).
Lee, M. W., Kim J. H., Jeong, D. W., Ahn, K. H., Toh, S. H., and Surh, Y. J., Inhibition of Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression by Diarylheptanoids from the Bark ofAlnus hirsuta var.sibirica.Biol. Pharm. Bull., 23, 517–518 (2000).
Moncada S., Palmer R. M., and Higgs E. A., Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology.Pharmacol. Rev., 43, 1091–1042 (1991).
Mosmann, T., Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxic assays.J.limmunol. Methods., 65, 55–63 (1983).
Rie I., Koichi S., Masakazu H., Takeshi S., Susumu K., and Fumio A., Inhibitory Effects of Hydrolyzable Tannins fromMelastoma dodecandrum Lour. On Nitric Oxide Production by a Murine Macrophage-Like cell Line, RAW 264.7, Activated with Lipopolysaccharide and Interferon-γ.Biol. Pharm. Bull., 22, 647–653 (1999)
Subbaramiah K., Telang N., Ramonetti J. T., Araki T., DeVito B., Weksler B. B., and Dannenberg A. J., Transcription of cyclooxygenase-2 is enhanced in transformed mammary epithelial cells.Cancer Res., 56, 4424–4429 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, HJ., Yeom, SH., Kim, MK. et al. Nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 synthesis inhibitory activities of diarylheptanoids from the barks ofAlnus japonica steudel. Arch Pharm Res 28, 177–179 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02977711
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02977711