Abstract
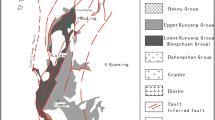
The peridotite xenoliths from Wangqing display a downward-concave PGE pattern with Pt at maximum due to Pt-Pd fractionation, which is different from the flat or negatively sloped patterns commonly observed for worldwide peridotite xenoliths and massifs. Taking into account the difference in partition coefficients of Pt and Pd between alloy and sulfide melt, it is suggested that some of the Wangqing peridotites must have been equilibrated with a melt in which alloy and sulfide coexisted. Segregation of Pt-rich alloy from Pd-sulfide melts due to density contrast and extraction of residual melts without sulfide saturation resulted in the fractionation of Pt from Pd.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mitchell, R. H., Keays, R. R., Abundance and distribution of gold, palladium and iridium in some spinel and garnet Iherwlites: implications for the nature and origin of precious metal-rich intergranular components in the upper mantle,Geochim. Cosmachim. Acta, 1981, 45: 2425.
Morgan, J. W. J., Wandless, G. A., Petrie, R. K. et al., Composition of the Earth’s upper mantle-I: siderophile trace elements in ultramafic nodules,Tectonophysics, 1981, 75: 47.
Wilson, M. R., Kyser, T. K., Gagan, R., Sulphur isotope systematic and platinum element behavior in REE-enriched metasomatic fluids: a study of mantle xenoliths from Dish Hill, California, USA,Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1993, 60: 1933.
Kimura, K., Lewis, R. S., Anders, E., Distribution of gold and rhenium between nickel-iron and silicate melts: implications for the abundance of siderophile elements on the Earth and Moon,Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1974, 38: 683.
Pattou, L., Lorand, J. P., Gros, M., Non-chondritic platinum-group element ratios in the Earth’s mantle,Nature, 1996, 379: 712.
Lorand, J. P., Keays, R. R., Bodinier, J. L., Capper and noble metal enrichments across the lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary of the mantle diapir: evidence from the Lanzo lherzolite massif,J. Petrol., 1993, 34: 1110.
Xu, Y. G., Menzies, M. A., Vrwn, P. et al., Texture-temperature-geochemistry relationship in the upper mantle as revealed from spinel peridotite xenoliths from Wangqing, NE China,J. Petrol., 1998, 39(3): 469.
Xu, Y. G., Lin, C. Y., Menzies, M. A. et al., Significance of mineral chemistry of the spinel peridotite xenolith from Wangqing, Jilin Province: thermal history and mantle metasomatism,Geochimica, 1996, 25: 481.
Barnes, S. J., Body, R., Korneliussen, A. et al., The use of mantle normalization and metal ratios in discriminating between the effects of partial melting, crystal fractionation and sulphide segregation on platinum-group elements, gold, nickel, copper: examples from Norway, inGeoplatinum 87 (eds. Prichard, H. M., Bowles, J. W., Potts, P. et al.), Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1988, 113–143.
Gueddari, K., Piboule, M., Amosee, J., Differentiation of platinum-group element (PGE) and of gold during partial melting of peridotites in the lherwlitic massifs of the BeticeRifean range (Ronda and Beni Bousera),Chem. Geol., 1996, 134: 181.
Peach, C. L., Mathez, E. A., Keays, R. R. et al., Experimentally determined sulfide melt-silicate melt partition coefficients for iridum and palladium,Chem. Geol., 1994, 117: 361.
Ionov, D. A., Hoefs, J., Wdepohl, K. H. et al., Content and isotopic composition of sulfur in ultramsfic xenoliths from central Asia,Earth Planet Sci. Lett., 1992, 111: 235.
Lorand, J. P., Pattou, L., Platinum-group element contents of mantle peridotite xenoliths from France,J. Conference Abstracts, Goldschmide Conference, March 31—April 4, 1996, l(1): 369.
Keays, R. R., The role of komatiitic and picritic magmatism and S-saturation in the formation of ore deposits,Lithos, 1995, 34: 1.
Fleet, M. E., Stone, W. E., Partitioning of platinum-group element in the Fe-Ni-S system and their fractionation in nature,Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1991, 55: 245.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Project supported by the Ministry of Human Affairs and a part of an international collaboration program between the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Centre National de Recherche Scientifique (CNRS, France), and Australian Institute of Nuclear Sciences and Engineering (AINSE) grant to SJR.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Orberger, B. & Reeves, S.J. Fractionation of platinum group elements in upper mantle: Evidence from peridotite xenoliths from Wangqing. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 41, 354–361 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02932685
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02932685