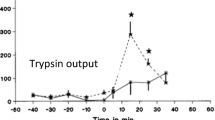
Abstract
Although earlier studies indicated that GLP-1 (7–36) amide was an intestinal peptide with a potent effect on glucose-dependent insulin secretion, later on it was found that several biological effects of this peptide occur in the brain, rather than in peripheral tissues. Thus, proglucagon is expressed in pancreas, intestine, and brain, but post translational processing of the precursor yields different products in these organs, glucagon-like peptide-1 (7–36) amide being one of the forms produced in the brain. Also, GLP-1 receptor cDNA from human and rat brains has been cloned and sequenced, and the deduced amino acid sequences are the same as those found in pancreatic islets. Through these receptors, GLP-1 (7–36) amide from gut or brain sources induces its effects on the release of neurotransmitters from selective brain nuclei, the inhibition of gastric secretion and motility, the regulation of food and drink intake, thermoregulation, and arterial blood pressure. Central administration (icv) of GLP-1 (7–36) amide produces a marked reduction in food and water intake, and the colocalization of the GLP-1 receptor, GLUT-2, and glucokinase mRNAs in hypothalamic neurons involved in glucose sensing suggests that these cells may be involved in the transduction of signals needed to produce a state of fullness. In addition, GLP-1 (7–36) amide inhibits gastric acid secretion and gastric emptying, but these effects are not found in vagotomized subjects, suggesting a centrally mediated effect. Similar results have been found with the action of this peptide on arterial blood pressure and heart rate in rats. Synthesis of GLP-1 (7–36) amide and its own receptors in the brain together with its abovementioned central physiological effects imply that this peptide may be considered a neuropeptide. Also, the presence of GLP-1 (7–36) amide in the synaptosome fraction and its calcium-dependent release by potassium stimulation, suggest that the peptide may act as a neurotransmitter although further electrophysiological and ultrastructural studies are needed to confirm this possibility.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez E., Roncero I., Chowen J. A., Thorens B., and Blázquez E. (1996) Expression of the glucagon-like receptor gene in rat brain.J. Neurochem. 66, 920–927.
Banting F. G. and Best C. H. (1922) The internal secretion of the pancreas.J. Lab. Clin. Med. 7, 251–266.
Barners S., Whistler H. L., Hughes J., Woodruff G. N., and Hunter J. C. (1991) Effect of cholecystokinin octapeptide on endogenous amino acid release from the rat ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus and striatum.J. Neurochem. 56, 1409–1416.
Barragán J. M., Rodriguez R., and Blázquez E. (1994) Changes in arterial blood pressure and heart rate induced by glucagon-like peptide-1-(7–36) amide in rats.Am. J. Physiol. 266, E459-E466.
Barragán J. M., Rodriguez R., Eng J., and Blázquez E. (1996) Interactions of exendin-(9–39) with the effects of glucagon-like peptide-1-(7–36) amide and of exendin-4 on arterial blood pressure and heart rate in rats.Regul. Pept. 67, 63–68.
Beak S. A., Small C. J., Ilovaiskaia I., Hurley J. C., Ghatei M. A., Bloom S. R., and Smith D. M. (1996) Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) releases thyrotropin (TSH): characterization of binding sites for GLP-1 on α-TSH cells.Endocrinology 137, 4130–4138.
Bell G. I., Santerre R. F., and Mullenbach G. T. (1983) Hamster preproglucagon contains the sequence of glucagon and two related peptides.Nature 302, 716–718.
Bullock B. P., Scottheller R., and Habener J. F. (1996) Tissue distribution of messenger ribonucleic acid encoding the rat glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor.Endocrinology 137, 2968–2978.
Calvo J. C., Yusta B., Mora F., and Blázquez E. (1995a) Structural characterization by affinity cross-linking of glucagon-like peptide-1 (7–36) amide receptor in rat brain.J. Neurochem. 64, 299–306.
Calvo J. C., Gisolfi C. V., Blázquez E., and Mora F. (1995b) Glucagon-like peptide-1 (7–36) amide induces the release of aspartic acid and glutamine by the ventromedial hypothalamus of the conscious rat.Brain Res. Bull. 38, 435–439.
Campos R. V., Lee Y. C., and Drucker D. J. (1994) Divergent tissue-specific and developmental expression of receptors for glucagon and glucagon-like peptide-1 in the mouse.Endocrinology 134, 2156–2164.
Cechetto D. F. (1987) Central representation of visceral function.Fed. Proc. 46, 17–23.
Dillon J. S., Tanizawa Y., Wheeler M. B., Leng X. H., Ligon B. B., Rabin D. H., et al. (1993) Cloning and functional expression of the human glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor.Endocrinology 133, 1907–1910.
Drucker D. J. and Asa S. (1988) Glucagon gene expression in vertebrate brain.J. Biol. Chem. 263, 13,475–13,478.
Drucker D. J., Philippe J., Mojsov S., Chick W. L., and Habener J. F. (1987) Glucagon-like peptide I stimulates insulin gene expression and increases cyclic AMP levels in a rat islet cell line.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 3434–3438.
Drucker D. J., Ehrlich P., Asa S. L., and Brubaker P. (1996) Induction of intestinal proliferation by glucagon-like peptide-2.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 7911–7916.
Eng J., Kleiman W. A., Singh L., Singh G., and Raufman J. P. (1992) Isolation and characterization of exendin-4 and exendin-3 analogues from Heloderma suspectum venom. Further evidence for an exendin receptor on dispersed acini from guinea pig pancreas.J. Biol. Chem. 267, 7402–7405.
Fürnsinn C. and Ebner K. W. W. (1995) Failure of GLP-1 (7–36) amide to affect glycogenesis in rat skeletal muscle.Diabetologia 38, 864–867.
Ghiglione M., Blázquez E., Uttenthal L. O., de Diego J. G., Alvarez E., George S. K., et al. (1985) Glucagon-like peptide-1 does not have a role in hepatic carbohydrate metabolism.Diabetologia 28, 920–921.
Göke R. and Conlon J. M. (1988) Receptors for glucagon-like peptide-1 (7–36) amide on rat insulinoma-derived cells.J. Endocrinol. 116, 357–362.
Göke R., Fehmann H. C., Linn T., Schmidt H., Krause M., Eng J., et al., (1993) Exendin-4 is a high potency agonist and truncated exendin-9 (9–39) amide an antagonist at the glucagon-like peptide-1-(7–36) amide receptor of insulin-secreting β-cells.J. Biol. Chem. 268, 19,650–19,655.
Göke R., Larsen P. J., Mikkelsen J. C., and Sheikb S. P. (1995a) Distribution of GLP-1 binding sites in the rat brain: evidence that exendin-4 is a ligand of brain GLP-1 binding sites.Eur. J. Neurosc. 7, 2294–2300.
Göke R., Larsen P. J., Mikkelsen J. C., and Sheikh S. P. (1995b) Identification of specific binding sites for glucagon-like peptide-1 on the posterior lobe of the rat pituitary.Neuroendocrinology 62, 130–134.
Gutniak M., Orskov C., Holst J. J., Ahrén B., and Efendic S. (1992) Antidiabetogenic effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 (7–36) amide in normal subjects and patients with diabetes mellitus.N. Engl. J. Med. 326, 1316–1322.
Gutzwiller J. P., Göke B., Drewe J., Ketterer S., Handschin D., Hildebrand B., et al. (1997) Glucagon-like peptide-1 is a physiologic regulator of food intake in humans, inInvited Workshop: Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) 7th Annual Meeting of European Neuropeptide Club. May 21–24, 1997, Marburg, Germany.
Heinrich G., Gross P., and Habener J. F. (1984) Glucagon gene sequence: four of six exons encode separate functional domains of rat preproglucagon.J. Biol. Chem. 259, 14082–14087.
Herrmann C., Vöge A., and Göke B. (1993) Regulation of glucagon-like peptide (GLP-1) release from the isolated perfused rat ileum by nutrients, peptides and neuromediators.Digestion 54, 367.
Hertz L. and Schousboe A. (1986) Role of astrocytes in compartimentation of amino acids and energy metabolism, in:Biochemistry, Physiology and Pharmacology of Astrocytes (Fedoroff S. and Vernadakis A., eds), Academic, New York, p. 179.
Holst J. J., and Ørskov C. (1994) Glucagon and other proglucagon-derived peptides, inGut Peptides: Biochemistry and Physiology (Walsh J. H. and Dockray G. J., eds). Raven, New York, p. 305
Hoosein N. M. and Gurd R. S. (1984) Human glucagon-like peptides 1 and 2 activate rat brain adenylate cyclase.FEBS Lett. 178, 83–86.
Hupe-Sodmann K., McGregor G. P., Bridenbaug R., Göke R., Göke B., Thole H., et al. (1995) Characterisation of the processing by human neutral endopeptidase 24.11 of GLP-1 (7–36) amide and comparison of the substrate specificity of the enzyme for other glucagon-like peptides.Regul. Pept. 58, 149–156.
Jetton T. L., Liang Y., Petepher C. C., Zimmerman E. C., Cox F. G., Horvath K., et al. (1994) Analysis of upstream glucokinase promoter activity in transgenic mice and identification of glucokinase in rare neuroendocrine cells in the brain and gut.J. Biol. Chem. 269, 3641–3654.
Jin S. L. C., Han V. K. M., Simmons J. E., Towle A. C., Lander J. M., and Lund P. K. (1988) Distribution of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), glucagon and glicentin in the rat brain: an immunocytochemical study.J. Comp. Neurol. 271, 519–532.
Kanse S. M., Kreymann B., Ghatei M. A., and Bloom S. R. (1988) Identification and characterization of glucagon-like peptide-1 (7–36) amide binding sites in the rat brain and lung.FEBS Lett. 241, 209–212.
Kimball C. P. and Murlin J. R. (1923) Aqueous extracts of pancreas. III. Some precipitation reactions of insulin.J. Biol. Chem. 58, 337–346.
Kreymann B., Williams G., Ghatei M. A., and Bloom S. R. (1987) Glucagon-like peptide-1 (7–36): a physiological incretin in man.Lancet 2, 1300–1304.
Kreymann B., Ghatei M. A., Burnet P., Williams G., Kanse S., Diani A. R., et al. (1989) Characterization of glucagon-like peptide-1 (7–36) amide in the hypothalamus.Brain Res. 502, 325–331.
Lambert P. C., Wilding J. P. H., Ghatei M. A., and Bloom S. R. (1994) A role for GLP-1 (7–36) NH2 in the central control of feeding behavior.Digestion 54, 360–361.
Layer P., Franke A., Holst J. J., Grandt D., and Goebell H. (1996) Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) inhibits pancreatic enzyme secretion in humans. Gastroenterology,110, F1409.
Mojsov S., Heinrich G., Wilson I. B., Ravazzola M., Orci L., and Habener J. F. (1986) Preproglucagon gene expression in pancreas and intestine diversifies at the level of post-transcriptional processing.J. Biol. Chem. 261, 11880–11889.
Mojsov S., Weir G. C., and Habener J. F. (1987) Insulinotropin: glucagon-like peptide-1 (7–37) co-encoded in the glucagon gene is a potent stimulator of insulin release in the perfused rat pancreas.J. Clin. Invest. 79, 616–619.
Mora F., Expósito I., Sanz B., and Blázquez E. (1992) Selective release of glutamine and glutamic acid produced by perfusion of GLP-1 (7–36) amide in the basal ganglia of the conscious rat.Brain Res. Bull. 29, 359–361.
Murphy S. and Pearce B. (1987) Functional receptors for neurotransmitters on astroglial cells.Neuroscience 22, 381–394.
Navarro M., Rodriguez de Fonseca F., Zueco J. A., Gómez R., and Blázquez E. (1994) Changes in food intake induced by GLP-1 (7–36) amide in the rat Abstract in15th International Diabetes Federation Congress, Kobe, Japan.
Navarro M., Rodriguez de Fonseca F., Alvarez E., Chowen J. A., Zueco J. A., Gómez R., et al. (1996) Colocalization of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptors, glucose transporter GLUT-2, and glucokinase mRNAs in rat hypothalamic cells: Evidence for a role of GLP-1 receptor agonists as an inhibitory signal for food and water intake.J. Neurochem. 67, 1982–1991.
Norenberg M. C. and Martínez-Hernández A. (1979) Fine structural localization of glutamine-synthethase in astrocytes of rat brain.Brain Res. 161, 303–310.
Oomura Y., Sasaki K., Suzuki K., Muto T., Li A. J., Ogita Z., et al. (1992) A new brain glucosensor and its physiological significance.Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 55, 2785–2825.
Ørskov C., Rabenhoj L., Kofod H., Wettergren A., and Holst J. J. (1994) Production and secretion of amidated and glycine-extended glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) in man.Diabetes 43, 535–539.
Ørskov C., Wettergren A., Poulsen S. C. S., and Holst J. J. (1995) Is the effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 on gastric emptying centrally mediated.Diabetologia 38 (Suppl. 1), A39 (Abstract).
Ørskov C., Poulsen S. S., Moller M., and Holst J. J. (1996) Glucagon-like peptide I receptors in the subfornical organ and the area postrema are accesible to circulating glucagon-like peptide I.Diabetes 45, 832–835.
O’Shea D., Gunn I., Chen X., Bloom S., and Herbert J. (1996) A role for central glucagon-like peptide-1 in temperature regulation.Neuroreport 7, 830–832.
Panksepp J., Bekkedal M. Y. U., and Walter M. (1996) Potent suppresive effects of the putative agent GLP-1 on social-emotional behaviors.Soc. Neurosci. Abstrat.22, p 16.
Parmley W. W., Glick G., and Sonnenblick P. (1968) Cardiovascular effects of glucagon in man.N. Engl. J. Med. 279, 12–17.
Raufman J. P., Singh L., and Eng J. (1992) Truncated glucagon like peptide-1 interacts with exendin receptors on dispersed acini from guinea pig pancreas. Identification of a mammalian analogue of the reptilian peptide exendin-4.J. Biol. Chem. 267, 21,432–21,437.
Richter G., Göke R., Göke B., and Arnold R. (1990) Dexamethasone pretreatment of rat insulinoma cells decreases binding of glucagon-like peptide-1 (7–36) amide.J. Endocrinol. 126, 445–450.
Richter G., Göke G., Göke B., Schmidt H., and Arnold R. (1991) Characterization of glucagon-like peptide-1 (7–36) amide receptors of rat lung membranes by covalent cross-linking.FEBS Lett. 280, 247–250.
Richter G., Feddersen O., Wagner U., Barth P., Göke R., and Göke B. (1993) GLP-1 stimulates secretion of macromolecules from airways and relaxes pulmonary artery.Am. J. Physiol. 265, L374-L381.
Ruiz-Grande, C., Pintado J., Alarcón C., Castilla C., and Valverde I. (1990) Renal catabolism of human glucagon-like peptides 1 and 2.Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 68, 1568–1573.
Schjoldager B. T. G., Mortensen P. E., Christiansen J., Ørskov C., and Holst J. J. (1989) GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) and truncated GLP-1, fragments of human proglucagon, inhibit gastric acid secretion in man.Dig. Dis. Sci. 35, 703–708.
Shick R. R., Worm Walde T., Zimmerman J. P., Schusdziarra V., and Classen M. (1994) Glucagon-like peptide 1: a novel brain peptide involved in feeding regulation in:Obesity in Europe (Ditschuneit H., Gries F. A., Hanner H., Schusdziarra V., and Wechsler J. G., eds.), Libbey, London, 363–367.
Shima K., Suda T., Nishimoto K., and Yoshimoto S. (1990) Relationship between molecular structures of sugars and their ability to stimulate the release of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) from canine ileal loops.Acta Endocrinol. 123, 464–470.
Shimizu I., Hirota M., Obhoshi C., and Shima K. (1987) Identification and localization of glucagon-like peptide-1 and its receptor in rat brain.Endocrinology 121, 1076–1082.
Suda K., Takahashi H., Fukase N., Manaka H., Tomija M., and Sasaki H. (1989) Distribution of molecular forms of glucagon-like peptides in the dog.Life Sci. 45, 1793–1798.
Sugiyama K., Manaka H., Kato T., Yamatani K., Tominaga M., and Sasaki H. (1994) Stimulation of truncated glucagon-like peptide-1 release from isolated perfused canine ileum by glucose absorption.Digestion 55, 24–28.
Tang-Christensen M., Larsen P. J., Göke R., Fink-Jensen A., Jessop D. S., Moller M., et al. (1996) Central administration of GLP-1 (7–36) amide inhibits food and water intake in rats.Am. J. Physiol. 271, R848–856.
Thiele T. E., Van Dijk G., Campfield A., Smith F. J., Burn P., Woods S. C., et al. (1997) Central infusion of GLP-1, but not leptin, produces conditioned taste aversion in rats.Am. J. Physiol. 272, R726-R730.
Thorens B. (1992) Expression cloning of the pancreatic β cell receptor for the gluco-incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 8641–8645.
Thorens B., Ponet A., Bühler L., Deng S. P., Morel P., and Widmann C. (1993) Cloning and functional expression of the human islet GLP-1 receptor.Diabetes 42, 1678–1682.
Treherme J. M. and Ashford M. L. J. (1992) Extracellular cations modulate the ATP sensitivity of ATP-K+ channels in rat ventromedial hypothalamic neurons.Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Biol. Sci. 247, 121–124.
Turton M. D., O’Shea D., Gunn I., Beale S. A., Eduards C. M. B., Meeran K., Choi S. J., Taylor G. M., Heath M. M., Lambert P. D., Wilding J. P. H., Smith D. M., Elatei M. A., Herbert J., and Bloom S. R. (1996) A role for glucagon-like peptide-1 in the central regulation of feeding.Nature 379, 69–72.
Uttenthal O. and Blázquez E. (1990) Characterization of high-affinity receptors for truncated glucagon-like peptide-1 in rat gastric glands.FEBS Lett. 262, 139–141.
Uttenthal O., Toledano A., and Blázquez E. (1992) Autoradiographic localization of receptors from glucagon-like peptide-1 (7–36) amide in rat brain.Neuropeptides 21, 143–146.
Valverde I., Morales M., Clemente F., Lopez-Delgado M., Delgado E., Perea A., and Villanueva-Peñacarrillo M. (1994) Glucagon-like peptide 1: a potent glycogenic hormone.FEBS Lett. 283, 7–10.
Valverde I., Mérida E., Delgado E., Trapote M. A., and Villanueva-Peñacarrillo M. L. (1993) Presence and characterization of glucagon-like peptide-1 (7–36) amide receptors in solubilized membranes of rat adipose tissue.Endocrinology 132, 75–79.
Van Dijk G., Thiele T. E., Seeley R. J., Woods S. C., and Bernstein J. L. (1997) Glucagon-like peptide-1 and satiety.Nature 385, 214.
Villanueva-Peñacarrillo M. L., Alcántara A. I., Trapote M. A., Clemente F., Delgado E., and Valverde I. (1994) Potent glycogenic effect of GLP-1 (7–36) amide in rat skeletal muscle.Diabetologia 37, 1163–1166.
Wang T., Edwards G. L., and Baile C. A. (1996) Glucagon-like peptide-1 (7–36) amide (GLP-1) activates the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis of rats.Soc. Neurosci. Abstracts 22, 456.
Wei Y., and Mojsov S. (1995) Tissue-specific expression of the human receptor for glucagon-like peptide-1: brain, heart and pancreatic forma have the same deduced amino acid sequences.FEBS Lett. 358, 219–224.
Wettergren A., Schjoldager B., Mortensen P. E., Myhre J., Christiansen J. and Holst J. J. (1993) Truncated GLP-1 (proglucagon 72–107 amide) inhibits gastric and pancreatic functions in man.Dig. Dis. Sci. 38, 665–673.
Zullo J. A., Esquifino A. J., Chowder J. A., Alvarez E., Castrillion P. O., and Blázquez E. (1999) Coexpression of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor, vasopressin, and oxytocin mRNAs in neurons of the rat hypothalamic supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei: effect of GLP-1 (7–36) amide on vasopressin and oxytocin release.J. Neurochem., in press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blázquez, E., Alvarez, E., Navarro, M. et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (7–36) amide as a novel neuropeptide. Mol Neurobiol 18, 157–173 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02914270
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02914270