Abstract
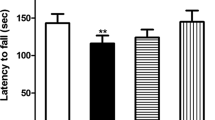
Mercury pollution and acute neurotoxicity of mercury is well known. The recent reports suggest the adverse effect of low dose mercury, though the available literature is still silent on its mechanism. This study was therefore undertaken to probe the effect of low dose methyl mercury induced heavy metal toxicity on free radical stress and its impact on behaviour of male albino rats. Male albino rats were exposed to 1 mg/kg body wt of methylmercury chloride for seven days, on day 8 they were tested for motor and memory functions. They were sacrificed later for biochemical estimations for rate of lipid peroxidation, nucleic acids, proteins in cerebrum, cerebellum and brain stem. There was an increase in the rate of lipid peroxidation showing methyl mercury induced free radical stress. The motor and memory functions demonstrated a clear decline, besides there was a lowering in the levels of nucleic acids and proteins as compared to controls. The results are important in view of recent reports that methyl mercury induced free radical stress results in early ageing and may serve as an initiating factor more specifically for neurodegenerative disorders like Alzeihemer's disease and dementias. The current findings support the notion that incorporating dietary antioxidants like curcumin, ascorbic acid and α-tocopherol in routine diet from early age may help combat the risk of developing such disorders in ensuing years.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marsh, D.O. and Turner, M.D. (1995) Foetal methylmercury studying Peruvian fish eating population. Neurotoxicol. 16 (4), 717–26.
Grandjean, P. and Weihe, P. (1998) Cognitive performance of children prenatally exposed to safe levels of methyl mercury. Environ. Res. 77, 165–72.
Yokoo, E.M., Valente, J.G., Grattan, L., Schmidt, S.L., Platt, I. and Silbergeld, E.K. (2003) Low level methyl mercury exposure effects neuropsychological function in adults. Environ. Health 2 (1), 8.
Murray, M. and Holmes, S.A. (2004) Assessment of mercury emissions inventories for the Great Lakes states. Environ. Res. 95 (3), 282–97.
Domagalski, J.L., Alpers, C.N., Slotton, D.G., Suchanek, T.H. and Ayers, S.M. (2004) Mercury and methylmercury concentrations and loads in the Cache Creek watershed, California. Sci. Total Environ. 327 (1–3), 215–37.
Hansen, J.C. and Dasher, G. (1997) Organic mercury: an environmental threat to the health of dietary exposed societies? Rev. Environ. Health 12(2), 107–16.
Soo, Y.O., Chow, K.W., Lam, C.W., Lai, F.M., Szeto, C.C., Chan, M.H. and Li, P.K. (2003) A whitened face woman with nephrotic syndrome. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 41(1), 250–3.
Westphal, G. and Hallier, E. (2003) Mercury in infants given vaccines containing thiomersal. Lancet 361 (9358), 699.
Lanka, M., Panda, K.K. and Panda, B.B. (1992) Monitoring and assessment of Mercury pollution in the vicinity of chloralkali plant. Bioconcentration of mercury in situ aquatic and terrestrial plants at Ganjam, India. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 22, 195–202.
Gothberg, A., Greger, M., Holm, K. and Bengtsson, B.E. (2004) Influence of nutrient levels on uptake and effects of mercury, cadmium, and lead in water spinach. Environ. Qual. 33(4), 1247–55.
Alonso, J., Salgado, M.J., Garcia, M.A. and Melgar, M.J. (2000) Accumulation of mercury in edible macrofungi: influence of some factors. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 38(2), 158–62.
Rowland, AS. and Baird, D.O. (1994) The effect of occupational exposure to mercury vapour on the fertility of female dental assistants. Occup. Environ. Med 51 (1), 28–34.
Barregard, L. and Lindstedt, G. (1994) Endocrine function in mercury exposed chloralalkali workers. Occup. Environ. Med. 51 (8), 536–40.
Grandjean, P., White, R.F., Nielson, A., Cleary, D., de Oliveira and Santos, E.C. (1999) Methylmercury neurotoxicity in Amazonian children downstream from goldmining Environ: Health Perspect 107 (7), 587–592.
Zahir, F., Rizvi, S. J., Khan, R. H. and Haq, S. K. (2005) Low dose mercury toxicity and human health. Environmental toxicology and Pharmacology 20, 351–360.
Utley, G.H., Bernheim, F., Hochstein, P. (1967) Effect of sulphydryl reagents on peroxidation in microsomes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 118, 29–32.
Searcy, D.G. and MacInnis, A.J. (1970) Hybridization and renaturation of the nonrepetitive DNA of higher organisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 209(2), 574–7.
Burton, K. (1956) A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamien reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem. J. 62(2), 315–23.
Dische, Z. (1955) Colour reaction of nucleic acid components. In: The nucleic acids (Chargaff E and Davidson JN editor. Academic Press, New York 1, 285–305
Lowry, O.H., Rosenbrough, N.J., Farr, A.L. and Randall, R.J. (1951) Protein measurement with Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275.
King, L.D. and Arendash, G.W. (2002) Behavioural characterization of the Tg2576 transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease through 19 months. Physiology and Behaviour 75, 627–642.
Ali, S.F., LeBel, C.P. and Bondy, S.C. (1992) Reactive oxygen species formation as a biomarker of methyl mercury and trimethyltin neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 13, 637–648.
Chao, E.S., Gierthy, J.F. and Frenkel, G.D. (1984) A comparative study of the effects of mercury compounds on cell viability and nucleic acid synthesis in HeLa cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 33(12), 1941–5.
Sarafian, T.A., Cheung, M.K. and Verity, M.A. (1984) In vitro methyl mercury inhibition of protein synthesis in neonatal cerebellar perikarya. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 10 (2), 85–100.
Verschaeve, L., Kirsch-Volders, M. and Hens, L.S. (1985) Comparative in vitro cytogenetic studies in mercury-exposed human lymphocytes. Mutat. Res. 157(2–3), 221–6.
Miura, K. (1989) Imura N-Mechanism of cytotoxicity of methyl mercury with special reference to microtubule disruption. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 21, 313–316.
Leong, C.C., Syed, N.I. and Lorscheider, F.L. (2001) Retrograde degeneration of neurite membrane structural integrity of nerve growth cones following in vitro exposure to mercury. Neuroreport. 12(4), 733–7.
Powell, T.J. (2000) Chronic neurobehavioural effects of mercury poisoning on a group of Zulu chemical workers. Brain Inj. 14(9), 797–814.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zahir, F., Rizvi, S.J., Haq, S.K. et al. Effect of methyl mercury induced free radical stress on nucleic acids and protein: Implications on cognitive and motor functions. Indian J Clin Biochem 21, 149–152 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02912931
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02912931