Summary
Histologic and ultrastructural lesions in thyroid follicular cells of Osborne-Mendel rats produced by feeding diets containing 5, 50, and 500 ppm polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) for 4 weeks were compared with alterations produced by low (Remington diet) and high (1%KI) iodide diets, chronic thyroxine administration, and a single injection of thyrotropin.
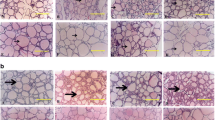
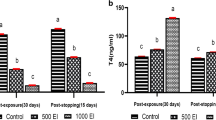
Exposure to PCB resulted in a dose-dependent hypertrophy and hyperplasia of follicular cells with an abnormal accumulation of large colloid droplets and irregular lysosomes. There was limited evidence of colloid droplet-lysosome interaction necessary for the secretion of thyroid hormones. Microvilli on luminal surfaces were decreased, abnormally shaped, and short. Serum thyroxine and triiodothyronine were decreased significantly after feeding PCB.
Follicular cells in rats fed the iodine-deficient diet underwent hypertrophy and hyperplasia with increased development of rough endoplasmic reticulum. They had increased numbers of round lysosomes and colloid droplets. There were numerous uniformly long microvilli and occasional pseudopodia were present engulfing colloid. Serum thyroxine was significantly decreased but triiodothyronine levels were increased. The iodide-excess diet resulted in hypertrophy and hyperplasia of follicular cells which contained numerous colloid droplets and abnormally shaped lysosomes with little evidence of fusion. Numerous long microvilli extended into the lumen. Many follicular cells contained unique intracytoplasmic microfollicles lined by uniform microvilli. Serum thyroxine was significantly reduced.
Follicular cells of rats chronically administered thyroxine underwent involution and had only a few short microvilli, scattered round lysosomes, and poorly developed organelles. Serum thyroxine and triiodothyronine were elevated significantly. Thyrotropin (TSH) produced hypertrophy of follicular cells by 30 min post-injection with increased large colloid droplets and small round lysosomes. Large pseudopod-like projections of follicular cells were involved in endocytosis of colloid. There was evidence of fusion of lysosomal membranes with colloid droplets. Circulating thyroid hormone levels were significantly elevated from 30 min to 8 h after administration of thyrotropin but normal by 24 h.
The ultrastructural alterations produced by PCB in the luminal plasma membrane and structure of microvilli were distinct from changes observed with acute stimulation by TSH, long-term stimulation by iodide excess or deficient diets, and chronic suppression by thyroxine. The changes in lysosomal structure and the accumulation of colloid droplets with little evidence of fusion in follicular cells of rats fed PCB closely resembled the findings in rats fed the iodide-excess diet. The principal effect of PCB on follicular cells appeared to be on limiting colloid droplet-lysosome interaction thereby inhibiting the proteolysis of thyroglobulin necessary for the release of thyroid hormones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anon (1972) Polychlorinated biphenyls Environmental impact. A review by the panel on hazardous trace substances. Environm Res 5:249–362
Ax RL, Hansen LG (1975) Effects of purified polychlorinated biphenyl analogs on chicken reproduction. Poult Sci54:895–900
Bastomsky CH (1974) Effects of a polychlorinated biphenyl mixture (Arochlor 1254) and DDT on biliary thyroxine excretion in rats. Endocrinology95:1150–1155
Bastomsky CH, Murphy PVN (1976) Enhanced in vitro hepatic glucuronidation of thyroxine in rats following cutaneous application or ingestion of polychlorinated biphenyls. Canad J Physiol Pharmacol54:23–25
Bastomsky CH, Wyse JM (1975) Enhanced thyroxine metabolism following cutaneous application of microscope immersion oil. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol10:725–733
Bastomsky, CH, Murphy PVN, Banovac K (1976) Alterations in thyroxine metabolism produced by cutaneous application of microscope immersion oil: Effects due to polychlorinated biphenyls. Endocrinology98:1309–1314
Bruckner JV, Khanna KL, Cornish HH (1973) Biological responses of the rat to polychlorinated biphenyls. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol24:434–448
Bruckner JV, Khanna KL, Cornish HH (1974) Polychlorinated biphenyl-induced alteration of biologic parameters in the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol28:189–199
Collins WT, Capen CC, Kasza L, Carter C., Dailey RE (1977) Effect of polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) on the thyroid gland: Ultrastructural and biochemical investigations. Am J Pathol89:119–136
Finklea J, Priester LE, Creason JP, Hauser T, Hinners T, Hammer DI (1972) Polychlorinated biphenyl residues in human plasma expose a major pollution problem. Am J Publ Hlth62:645–651
Grant DL, Moodie CA, Phillips WEJ (1974) Toxicodynamics of Aroclor 1254 in the male rat. Environm Physiol Biochem4:214–225
Gustafson CG (1970) PCB’s -Prevalent and persistent. Environm Sci Technol4:814–819
Hammond AL (1972) Chemical pollution: Polychlorinated biphenyls. Science175:155–156
Hansen LG, Wilson DW, Byerly CS (1976) Effects on growing swine and sheep of two polychlorinated biphenyls. Am J Vet Res37:1021–1024
Hansen LG, Byerly CS, Metcalf RL, Bevill RF (1975) Effect of a polychlorinated biphenyl mixture on swine reproduction and tissue residues. Amer J Vet Res3:23–26
Litterst CL, Farber TM, Baker AM, VanLoon EJ (1972) Effect of polychlorinated biphenyls on hepatic microsomal enzymes in the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol23:112–122
Kasza L, Weinberger MA, Carter C., Hinton DE, Trump BF, Brouwer EA (1976) Acute, subacute and residual effects of polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) in rats. II Pathology and electron microscopy of liver and serum enzyme study. J. Toxicol Environm Health1:689–703
Kimbrough RD (1974) The Toxicity of polychlorinated polycyclic compounds and related chemicals. CRC Crit Rev Toxicol2:445–498
Kimbrough RD, Kinder RE, Gaines TB (1972) Morphological changes in livers of rats fed polychlorinated biphenyls: Light microscopy and ultrastructure. Arch Environm Health25:354–364
Kolbye AC (1972) Food exposures to polychlorinated biphenyls. Environm Health Perspect1:85–88
Price NO, Young RW, Dickinson JK (1972) Pesticide residues and polychlorinated biphenyl levels in diets, urine and fecal matter of preadolescent girls. Proc Soc Exp Biol139:1280–1283
Takeuchi K, Suzuki H, Sawada M, Horiuchi Y (1970) Effect of excessive iodide administration on the proteolytic activity of the thyroid gland. Endocrinology86:1236–1244
Villeneuve DC, Grant DL, Phillips WEJ, Clark ML, Clegg DJ (1971) Effects of PCB administration on microsomal enzyme activity in pregnant rabbits. Bull Environm Contam Toxicol6:120–127
Vos JG, Beems RB (1971) Dermal toxicity studies of technical polychlorinated biphenyls and fractions thereof in rabbits. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol19:617–633
Vos JG, Koeman HH (1970) Comparative toxicologic study with polychlorinated biphenyls in chickens with special reference to porphyria, edema formation, liver necrosis and tissue residues. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol17:656–668
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by Research Fellowship 1-F32-ES05128, Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Institutes of Health; and NIH grant RR-05463
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Collins, W.T., Capen, C.C. Ultrastructural and functional alterations of the rat thyroid gland produced by polychlorinated biphenyls compared with iodide excess and deficiency, and thyrotropin and thyroxine administration. Virchows Archiv B Cell Pathol 33, 213–231 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02899183
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02899183