Abstract
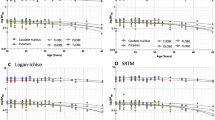
We have characterized and localized phorbol ester binding sites in human autopsied brains, using [3H]phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate ([3H]PDBu). When the tissue was homogenized in the absence of Ca2+ chelator (10 mM EGTA/2 mM EDTA), Scatchard analysis of the specific [3H]PDBu bindings to both particulate and soluble fractions yielded a single class of high-affinity binding site (K d = 7.1 and 7.4 nM:B max = 45.4 and 3.1 pmol/mg protein, respectively). The particulate fraction retained the majority of [3H]PDBu binding (98% of total binding activity), while the soluble fraction was almost devoid of binding activity (2%). In the presence of Ca2+ chelator, more of the activity was found in the soluble fraction (30%). The binding of [3H]PDBu was potently inhibited by active phorbol esters and related diterpenes withK i of nanomolar concentration but not by inactive ones. Diolein (OAG), a synthetic diacylglycerol, and polymixin B, an inhibitor of protein kinase C (PKC), inhibited the binding moderately (K i = 5.8 and 1.3 µM, respectively). H-7, an inhibitor of PKC and cyclic nucleotides-dependent kinase, did not compete with [3H]PDBu for the binding sites (K i > 100,000 nM). The regional distribution of specific [3H]PDBu binding in the human brain was rather uneven and resembled that of [3H]PDBu autoradiograms and PKC-like immunoreactivities in the rat brain. The binding capacities were generally in the order: rhinencephalon > basal ganglia > cerebral cortex > diencephalon > cerebellum > mesencephalon. Age-related loss of binding sites was observed in the prefrontal cortex of the subjects 33–81 years of age. In Parkinson’s disease, the phorbol ester binding showed a significant reduction in the substantia nigra, caudate putamen, and pallidum, whereas it was unchanged in the prefrontal cortex and caudate nucleus of schizophrenics, when compared with the relevant controls.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashendel, C.L., Staller, J.M., Boutwell, R.K. (1983) Identification of a calcium- and phospholipid-dependent phorbol ester binding activity in the soluble fraction of mouse tissues. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 111:340–345
Baraban, J.M., Snyder, S.H., Alger, B.E. (1985) Protein kinase C regulates ionic conductance in hippocampal pyramidal neurons: Electrophysiological effects of phorbol esters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82:2538–2542
Blumberg, P.M. (1980) In vitro studies on the mode of action of the phorbol esters, potent tumor promoters: part 1. C.R.C. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 8:153–234
Bruns, R.F., Lawson-Wendling, K., Pugsley, T.A. (1983) A rapid filtration assay for soluble receptors using polyethyleneimine-treated filters. Anal. Biochem. 132:74–81
Castagna, M., Takai, Y., Kaibuchi, K., Sano, K., Kikkawa, U., Nishizuka, Y. (1982) Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor promoting phorbol esters. J. Biol. Chem. 257:7847–7851
Coussens, L., Parker, P.J., Rhee, L., Yang-Feng, T.L., Chen, E., Waterfield, M.D., Francke, U., Ullrich, A. (1986) Multiple, distinct forms of bovine and human protein kinase C suggest diversity in cellular signaling pathways. Science 233:859–866
Delclos, K.B., Nagle, D.S., Blumberg, P.M. (1980) Specific binding of phorbol ester tumor promoters to mouse skin. Cell 19:1025–1032
Diamond, L., O’Brien, T.G., Baird, W.M. (1980) Tumor promoters and the mechanism of tumor promotion. Adv. Cancer Res. 32:1–74
Driedger, P.E., Blumberg, P.M. (1980) Specific binding of phorbol ester tumor promoters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 77:567–571
Dunn, J.A., Blumberg, P.M. (1983) Specific binding of [20-3H]12-deoxyphorbol 13-isobutyrate to phorbol ester receptor subclasses in mouse skin particulate preparations. Cancer Res. 43:4632–4637
Dunphy, W.G., Delclos, K.B., Blumberg, P.M. (1980) Characterization of specific binding of [3H]phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate and [3H]phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate to mouse brain. Cancer Res. 40:3635–3641
Hammond, C., Paupardin-Tritsch, D., Nairn, A.C., Greengard, P., Gershenfeld, H.M. (1987) Cholecystokinin induces a decrease in Ca2+ current in snail neurons that appears to be mediated by protein kinase C. Nature 325:809–811
Hecker, E. (1978) Structure-activity relationships in diterpene esters irritant and cocarcinogenic to mouse skin. In Carcinogenesis, Vol. 2. T.J. Slaga, A. Sivak, R.K. Boutwell (eds). Raven Press, New York, pp. 11–48
Hidaka, H., Inagaki, M., Kawamoto, S., Sasaki, Y. (1984) Isoquinoline-sulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry 23:5036–5041
Huang, K-P., Huang, F.L. (1986) Immunochemical characterization of rat brain protein kinase C. J. Biol. Chem. 261:14781–14787
Huang, K.-P., Nakabayashi, H., Huang, F.L. (1986) Isozymic forms of rat brain Ca2+-activated and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83:8535–8539
Jaken, S., Kiley, S. (1987) Purification and characterization of three types of protein kinase C from rabbit brain cytosol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84:4418–4422
Kikkawa, U., Takai, Y., Minakuchi, R., Inohara, S., Nishizuka, Y. (1982) Calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase from rat brain: Subcellular distribution, purification, and properties. J. Biol. Chem. 257:13341–13348
Kikkawa, U., Takai, Y., Tanaka, Y., Miyake, R., Nishizuka, Y. (1983) Protein kinase C as a possible receptor protein of tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J. Biol. Chem. 258:11442–11445
Kikkawa, U., Ono, Y., Ogita, K., Fujii, T., Asaoka, Y., Sekiguchi, K., Kosaka, Y., Igarashi, K., Nishizuka, Y. (1987) Identification of the structures of multiple subspecies of protein kinase C expressed in rat brain. FEBS Lett. 217:227–231
Kishimoto, A., Kajikawa, N., Shiota, M., Nishizuka, Y. (1983) Proteolytic activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by calcium-dependent neutral protease. J. Biol. Chem. 258:1156–1164
Knopf, J.L., Lee, M.-H., Sultzman, L.A., Kritz, R.W., Loomis, C.R., Hewick, R.M., Bell, R.M. (1986) Cloning and expression of multiple protein kinase C cDNAs. Cell 46:491–502
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., Randall, R.J. (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. chem. 193:265–275
Makowske, M., Birnbaum, M.J., Ballester, R., Rosen, O.M. (1986) A cDNA encoding protein kinase C identifies two species of mRNA in brain and GH3 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 261:13389–13392
Malenka, R.C., Madison, D.V., Nicoll, R.A. (1986) Potentiation of synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. Nature 321:175–177
Mazzei, G.J., Katoh, N. Kuo, J.F. (1982) Polymixin B is a more selective inhibitor for phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase than for calmodulinsensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 109:1129–1133
McGeer, P.L., McGeer, E.G., Suzuki, J., Colman, C.E., Nagai, T. (1984) Aging, Alzheimer’s disease and the cholinergic system of the basal forebrain. Neurology 34:741–745
Michell, R.H. (1983) Polyphosphoinositide breakdown as the initiating reaction in receptor-stimulated inositol phospholipid metabolism. Life Sci. 32:2083–2085
Murphy, K.M.M., Gould, R.J., Oster-Granite, M.L., Gearhart, J.D., Snyder, S.H. (1983) Phorbol ester receptors: Autoradiographic identification in the developing rat. Science 222:1036–1038
Nagle, D.S., Jaken, S., Castagna, M., Blumberg, P.M. (1981) Variation with embryonic development and regional localization of specific [3H]phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate binding to brain. Cancer Res. 41:89–93
Nichols, R.A., Haycock, J.W., Wang, J.K.T., Greengard, P. (1987) Phorbol ester enhancement of neurotransmitter release from rat brain synaptosomes. J. Neurochem. 48:615–621
Niedel, J.E., Kuhn, L.J., Vanderbark, G.R. (1983) Phorbol diester receptor copurifies with protein kinase C. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80:36–40
Nishino, N., Noguchi-Kuno, S.A., Sugiyama, T., Tanaka, C. (1986) [3H]Nitrendipine binding sites are decreased in the substantia nigra and striatum of the brain from patients with Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res. 377:186–189
Nishizuka, Y. (1986) Studies and perspective of protein kinase C. Science 233:305–312
Ohno, S., Kawasaki, H., Imajoh, S., Suzuki, K., Inagaki, M., Yokokura, H., Sakoh, T., Hidaka, H. (1987) Tissue-specific expression of three distinct types of rabbit protein kinase C. Nature 325:161–166
Ono, Y., Kurokawa, T., Fujii, T., Kawahara, K., Igarashi, K., Kikkawa, U., Ogita, K., Nishizuka, Y. (1986) Two types of complementary DNAs of rat brain protein kinase C: Heterogeneity determined by alternative splicing. FEBS Lett. 206:347–352
Ono, Y., Kikkawa, U., Ogita, K., Kurokawa, T., Asaoka, Y., Sekiguchi, K., Ase, K., Igarashi, K. Nishizuka, Y. (1987) Expression and properties of two types of protein kinase C determined by alternative splicing from a single gene. Science 236:1116–1120
Parker, P.J., Coussens, L., Totty, N., Rhee, L., Young, S., Cheng, E., Stabel, S., Waterfield, M.D., Ullrich, A. (1986) The complete primary structure of protein kinase C: The major phorbol ester receptor. Science 233:853–859
Pozzan, T., Gatti, G., Dozio, N., Vicentini, L.M., Meldolesi, J. (1984) Ca2+-dependent and -independent release of neurotransmitters from PC12 cells: A role for protein kinase C activation? J. Cell Biol. 99:628–638
Saitoh, T., Dobkins, K.R. (1986) Protein kinase C in human brain and its inhibition by calmodulin. Brain Res. 379:196–199
Saitoh, N., Kikkawa, U., Nishizuka, Y., Tanaka, C. (1988) Distribution of protein kinase C-like immunoreactive neurons in rat brain. J. Neurosci. 8:369–382
Shapira, R., Silbergerg, S.D., Ginsberg, S., Rahamimoff, R. (1987) Activation of protein kinase C augments evoked transmitter release. Nature 325:58–60
Shearman, M.S., Naor, Z., Kikkawa, U., Nishizuka Y. (1987) Differential expression of multiple protein kinase C subspecies in rat central nervous tissue. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 147:911–919
Shoyab, M., Todaro, G.J., Tallman, J.F. (1982) Chlorpromazine and related antipsychotic tricyclic compounds competitively inhibit the interaction between tumor-promoting phorbol esters and their specific receptors. Cancer Lett. 16:171–177
Shuntoh, H., Tanaka, C. (1986) Activation of protein kinase C potentiates norepinephrine release from sinus node. Am J. Physiol. 251:C833-C840
Tanaka, C., Fujiwara, H., Fujii, Y. (1986) Acetylcholine release from guinea pig caudate slices evoked by phorbol ester and calcium. FEBS Lett. 195:129–134
Walaas, S.I., Nairn, A.C., Greengard, P. (1983) Regional distribution of calcium- and cyclic adenosine 3′:5′-monophosphate-regulated protein phosphorylation systems in mammalian brain: II Soluble systems. J. Neurosci. 3:302–311
Worley, P.F., Baraban, J.M., Snyder, S.H. (1986) Heterogeneous localization of protein kinase C in rat brain: Autoradiographic analysis of phorbol ester receptor binding. J. Neurosci. 6:199–207
Wrenn, R.W., Katoh, N., Schatzman, R.C., Kuo, J.F. (1981) Inhibition by phenothiazine antipsychotic drugs of calcium-dependent phosphorylation of cerebral cortex proteins regulated by phospholipid or calmodulin. Life Sci. 29:725–733
Zurgil, N., Zisapel, N. (1985) Phorbol ester and calcium act synergistically to enhance neurotransmitter release by brain neurons in culture. FEBS Lett. 185:257–261
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Special Project Research of Selected Intractable Neurological Disorders from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture, Japan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nishino, N., Kitamura, N., Nakai, T. et al. Phorbol ester binding sites in human brain: Characterization, regional distribution, age-correlation, and alterations in Parkinson’s disease. J Mol Neurosci 1, 19–26 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02896852
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02896852