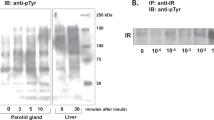
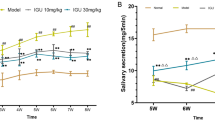
Summary
The present study examines the shortterm (i.e. 10 min after injection) influence of isoproterenol on cellular autophagy in the rat submandibular gland. The volume fraction of autophagic vacuoles was significantly reduced, suggesting that an anticatabolic reaction, namely inhibition of cellular autophagy, is an early and significant event in the growth of the submandibular gland which is known to occur with long-term isoproterenol treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe K, Dawes C (1980) The secretion of protein and of some electrolytes in response to α- and β-adrenergic agonists by rat parotid and submandibular salivary glands enlarged by chronic treatment with isoproterenol. J Dent Res 59:1081–1089
Barka T (1965) Stimulation of DNA synthesis by isoproterenol in the salivary gland. Exp Cell Res 39:355–364
Barka T (1968) Stimulation of protein and ribonucleic acid synthesis in rat submaxillary gland by isoproterenol. Lab Invest 18:38–41
Barka T, van der Noen H (1976) Stimulated growth of subman- dibular gland. Lab Invest 35:507–514
Barka T, Yagil C, van der Noen H, Naito Y (1986) Induction of the synthesis of a specific protein in rat submandibular gland by isoproterenol. Lab Invest 54:165–171
Baum BJ, Kuyatt BL, Takuma T (1984) Adrenergic regulation of protein synthesis in rat submandibular salivary gland cells. Archs Oral Biol 29:499–502
Bogart BI (1975) Secretory dynamics of the rat submandibular gland. An ultrastructural and cytochemical study of the isoproterenol-induced secretory cycle. J Ultrastr Res 52:139–155
Brenner GM, Wulf RG (1981) Adrenergic beta receptors me- diating submandibular salivary gland hypertrophy in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 218:608–612
Brown-Grant K (1961) Enlargement of salivary gland in mice treated with isopropylnoradrenaline. Nature (Lond) 191:1076–1078
Cutler LS, Boccuzzi J, Yaeger L, Bottaro B, Christian CP, Martinez JR (1981) Effects of reserpine treatment on β- adrenergic/adenylate cyclase modulated secretion and resyn- thesis by the rat submandibular gland. Virchows Arch [Pa- thol Anat] 392:185–198
Dämmrich J, Pfeifer U (1981) Acute effects of isoproterenol on cellular autophagy. Virchows Arch [Cell Pathol] 38:209–218
de Duve C, Wattiaux R (1966) Functions of lysosomes. Ann Rev Physiol 28:435–492
Deshaies Y, Willemot J, Leblanc J (1981) Protein synthesis, aminoacid uptake, and pools during isoproterenol-induced hypertrophy of the heart and tibialis muscle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 59:113–121
Durham JP (1980) Effect of ethanol upon isoproterenol stimu- lation of growth and secretion in the mouse parotid gland. Life Sci 26:1423–1430
Forssmann WG, Siegrist G, Orci L, Girardier L, Pictet R, Roul- lier C (1967) Fixation par perfusion pour la microscopie électronique essai de généralisation. J Microsc 6:297–304
Henell F, Glaumann H (1984) Effect of leupeptin on the au- tophagic vacuolar system of rat hepatocytes. Lab Invest 51:46–56
Mandel ID, Zengo A, Katz R, Wotman S (1975) Effect of adrenergic agents on salivary composition. J Dent Res 54:B27-B33
Menaker L, Sheetz J, Cobb CM, Navia JM (1974) Gel electro- phoresis of whole saliva and associated histologic changes in submandibular glands of isoproterenol-treated rats. Lab Invest 30:341–349
Muenzer J, Bildstein C, Gleason M, Carlson DM (1979) Purifi- cation of proline-rich proteins from parotid glands of isoproterenol-treated rats. J Biol Chem 254:5623–5628
Muenzer J, Bildstein C, Gleason M, Carlson DM (1979) Pro- perties of proline-rich proteins from parotid glands of isoproterenol-treated rats. J Biol Chem 254:5629–5634
Novi AM, Baserga R (1971) Association of hypertrophy and DNA synthesis in mouse salivary glands after chronic administration of isoproterenol. Am J Pathol 62:295–308
Papadopoulos T, Pfeifer U (1986) Regression of rat liver au- tophagic vacuoles by locally applied cycloheximide. Lab In- vest 54:100–107
Pfeifer U (1976) Lysosomen und Autophagie. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol 60:28–64
Pfeifer U (1978) Inhibition by insulin of the formation of au- tophagic vacuoles in rat liver. J Cell Biol 78:152–167
Pfeifer U (1980) The evaluation of large test fields for morpho- metric studies in electron microscopy. Pathol Res Pract 166:188–202
Pfeifer U (1987) Functional morphology of the lysosomal appa- ratus. In: Glaumann H, Ballard FJ (eds) Lysosomes: Their role in protein degradation. Academic Press, London, pp 1–59 (in press)
Pfeifer U, Guder WG (1975) Stimulation of cellular autophagy by parathyroid hormone and cyclic adenosine 3′, 5′: mono- phosphate in isolated tubular fragments from the rat’s kid- ney cortex. Virchows Arch [Cell Pathol] 19:51–67
Pfeifer U, Strauss P (1981) Autophagic vacuoles in heart muscle an liver. A comparative morphometric study including cir- cadian variations in meal-fed rats. J Mol Cell Cardiol 13:37–49
Quissell DO, Barzen KA, Lafferty JL (1981) Role of calcium and cAMP in the regulation of rat submandibular mucin secretion. Am J Physiol 241:C76-C85
Sasaki T, Litwack G, Baserga R (1969) Protein synthesis in the early prereplicative phase of isoproterenol-stimulated synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem 244:4831–4837
Schneyer CA (1962) Salivary gland changes after isoproterenol- induced enlargement. Am J Physiol 203:232–236
Selye H, Veilleux R, Cantin M (1961) Excessive stimulation of salivary gland growth by isoproterenol. Science 133:44–45
Shelburne JD, Arstila AU, Trump BF (1973) Studies on cellular autophagocytosis: cyclic AMP- and dibutyryl cyclic AMP- stimulated autophagy in rat liver. Am J Pathol 72:521–534
Stanton HC, Brenner G, Mayfield ED (1969) Studies on isopro- terenol-induced cardiomegaly in rats. Am Heart J 77:72–80
Tsang BK, Rixon RH, Whitfield JF (1980) A possible role for cyclic AMP in the initiation of DNA synthesis by isopro- terenol-activated parotid gland cells. J Cell Physiol 102:19–26
Weibel ER (1969) Stereological principles for morphometry in electron microscopic cytology. Int Rev Cytol 26:235–302
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bahro, M., Dämmrich, J. & Pfeifer, U. Short-term inhibition of cellular autophagy by isoproterenol in the submandibular gland. Virchows Archiv B Cell Pathol 53, 32–36 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02890221
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02890221