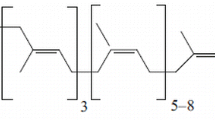
Abstract
Effects of squalene on humoral immune system in mice were investigated. Squalene exhibited significant incereases in the circulating leukocyte counts and relative spleen and thymus weights of the mice. However, the relative liver weight was slightly decreased. Hemagglutination titers (HA) were signficantly enhanced by squalene while Arthus reaction was not affected. Splenic plaque forming cells (PFC) were also greatly increased by squalene, especially at doses of 50 and 100 mg/kg of it.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Woodward, R. B. and Bloch, K.: The cyclization of squalene in cholesterol synthesis.J. Am. Chem. Soc. 75, 2023 (1953).
Eschenmoser, A., Ruzicka, L., Jeger, O. and Arigoni, D.: Zur kennthnis der triterpene, 190 mitteilung. Eine sterochemische interpretation der biogenetuschen Isoprenregel bei den triterpenen.Helv. Chim. Acta 38, 1890 (1955).
Grunwald, C.: Plant sterols.Ann. Rev. Plant. Physiol. 26, 209 (1975).
Miettinen, T. A.: Cholesterol and squalene in human adipose tissue.Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 6, 317 (1976).
Montagna, W. and Parakkal, P. F.: “The structure and function of skin”. Academic Press, New York, NY p. 305, 1974.
Strauss, J. S. and Pochi, P. E.: The quantitative gravimetric estimation of sebum production.J. Invest. Dermatol. 36, 293 (1961).
Masiak, S. and Lefevre, P. G.: Effects of membrane ateroid modification of human erythrocyte glucose transport.Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 162, 442 (1974).
Drowing, D. T., Stewart, M. E. and Strauss, J. S.: Estimation of sebrum production rates in man by measurement of squalene content of skin biopsies.J. Invest. Dermatol. 77, 4 (1981).
Peyronel, D., Artaud, J., Iatrides, M. C., Rancurel, P. and Chevalier, J. L.: Fatty acid and squalene compositions of mediterranean centrophorus SSP egg and liver oil in relation to age.Lipids 19, 9 (1984).
Lemperle, G.: Immunization against sarcoma 180 potentiated by RES stimulation.J. Reticuloendothel. Soc. 3, 385 (1966).
Ribi, E., McLaughlin, C. A., Cantrell, J. L., Brehmer, W., Azuma, I., Yamamura, Y., Stain, S. M., Hwang, K. M. and Toubiana, R.: Immunotherapy for tumors with microbial constituents or their synthetic analogues-review. In: The University of Texas System Cancer Center, M. D. Anderson Hospital and Tumor Institute (ed)., ⪙Immunotherapy of Human Cancer”, Raven Press, New York, NY p 131, 1978.
Masuda, A., Akiyama, S., Kuwano, M. and Ikekawa, N.: Potentiation of antifugal effect of amphotericin B by squalene, an intermediate for sterol biosynthesis.J. Antibiotics 35, 230 (1982).
Heller, J. H., Pasternak, V. Z., Ranson, J. P. and Heller, M. S.: A new reticuloendothelial system stimulation agent (Restim) from shark livers.Nature (London) 199, 904 (1963).
Liu, G. C. K., Arhens, E. H. J. and Schreibman, P. H.: Measurement of squalene in human tissue and plasma: Validation and application.J. Lipid Res. 17, 38 (1976).
Lewis, R. W.: The squalene content of plant tissue.Phytochemistry 11, 417 (1972).
Cohen, L. H., Griffioen, A. M., Wanders, R. J. A., Van Roermund, C. W. T., Huymans, C. M. G. and Princen, H. M. G.: Regulation of squalene synthetase activity in rat liver: Elavation by cholestyramine, but no diurnal variation.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 138, 169 (1986).
Tilvis, R. S. and Miettinen, T. A.: Dietary squalene increases tissue sterols and fecal bile acids in the rat.Lipids 18, 32 (1983).
Ichikawa, T., Tsuji, K., Hagiwara, K., Tsuda, A. and Yamanaka, Y.: Effects of oral administration of squalene on growth and lipids levels in serum and liver of rats. National Institute of Nutrition: 1-23-1,Toyama, Shinujuku, Tokyo, Japan, Sikiei Sshi 27, 44 (1986).
Reed, N. D., Crowle, P. K. and Ha, T.: Use of mast cell deficient mice to study host parasite relationships in immuno-deficient animals.B. Ssordeted. Karger Baselip 184 (1984).
Lake, J. P. and Reed, N. D.: Characterization of antigen specific immunogic paralysis induce by a single low dose of polyvinylpyrrolidone.J. Reticuloendothel. Soc. 20, 307 (1976).
Mishell, B. B., Shiigi, S. M., Henry, C., Chan, E. L., North, J., Gallily, R., Slomich, M., Miller, K., Marbrook, J., Parks, D. and Good, A. H.: Preparation of mouse cell suspensions. In: Mishell, B. B. and Shiigi, S. M. (Eds.) “Selected Methods in Cellular Immunology”. Freeman. San Francisco, CA3, p. 27 1980.
Sever, J. L.: Application of microtenchnique to virual serological investigations.J. Immunol. 88, 320 (1962).
Coombs, R. R. A. and Fiset, M. L.: Detection of complete antiboties to egg albumin by means of a sheep red cell egg albumin antigen unit.Brit. J. Exp. Path. 35, 472 (1954).
Stavistsky, A. B.: Micromethods for the study of proteins and antibiotics.J. Immunol. 72, 360 (1954).
Cunningham, A. J. and Szenberg, A.: Further improvements in the plaque technique for detecting single antibody forming cells.Immunol. 14, 599 (1968).
Titus, R. G. and Chiller, J. M.: A simple and effective methods to assess murine delayed type hypersensitivity to proteins.J. Immunol. Methods 45, 65 (1981).
Henningsen, G. M., Koller, L. D., Exon, J. H., Talcott, P. A. and Osborne, C. A.: A sensitive delayed type hypersensitivity model in the rats for assessingin vivo cell mediated immunity.J. Immunol. Methods 70, 153 (1984).
Brij, M. M.: “Clinical Biochemical and Hematological Reference Values”. Massion, NY p 31, 1981.
Snedecorm, G. W. and Cochrane, W. G.: “Statistical methods”, 6th ed. Iowa State University Press, Iowa, p. 1, 1967.
Diem, B. J. and Lentner, C.: “Documenta Geigy Scientific Tables”, Geigy, New York, NY p. 158, 1975.
Wachsmuth, E. D.: In “Advances in Pharmacology and Therapeutics II”. Pergamon Press. Oxford and New York5, p. 7 1982.
Ohkuma, T., Otagiri, K., Tanaka, S. and Ikekawa, J.: Intensification of host’s immunity by squalene in sarcoma 180 bearing ICR mice.J. Pharm. Dyn. 6, 148 (1983).
Ahn, Y. K., Kim, J. H., Lee, S. K. and Kim, H. S.: The effect of eicosapentaenoic acid on the immune response in mice (I).Yakhak Hoeji 33, 20 (1989).
Oh, Y. J.:Effect of evening primrose oil (EPO)on the immune response in mice. Thesis Collection, Graduate School of Won kwang Univeristy (1988).
Lagrange, P. H., Mackaness, G. B. and Miller, T. E.: Potentiation of T cell mediated immunity by selective suppression of antibody formation with cyclophosphamide.J. Exp. Med. 139, 1529 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahn, Y.K., Kim, J.H. Effects of squalene on the immune responses in mice(I): Humoral immune responses of squalene. Arch. Pharm. Res. 14, 370–378 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02876887
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02876887