Summary
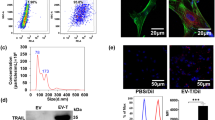
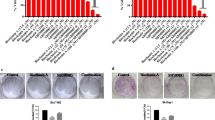
The therapeutic potential of soluble TRAIL (sTRAIL) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) was studied. The expression of TRAIL receptors was detected in 60 HCC tissues, 20 normal liver samples and 2 HCC cell lines (HepG2 and SMMC-7721) byin situ hybridization. Before and after HepG2 and SMMC-7721 were treated with sTRAIL protein with various concentrations, the apoptosis rate was observed by using flow cytometry andin situ terminal deoxynucleotidyl tranferase (TdT) labeling. The results showed death receptor 4 (DR4) and DR5 were expressed in 60 HCC tissues and 20 normal liver samples, while the expression intensity of DR in HCC tissues was stronger than in normal liver samples. DcR1 and DcR2 were not detectable in 54 (90%) and 25 (41.7%) HCC tissues, while in 20 normal liver samples. The expression of DR5, DR4 and DcR2 in both HCC cell lines was detectable, but the expression of DcR1 was not detectable. The expression of DR in HCC tissues was related to the differentiation and grades of HCC. In the poor differentiated HCC, the expression of DR was decreased (P<0.01). The expression of DR in III/IV grades was significantly lower than that in I/II grades (P<0.05). The expression of DR was not related to gender, age, HBsAg, AFP, tumor size and metastasis. The expression of DR in the HCC drugresistant lines was decreased. After treatment with TRAIL (100 ng/ml) for 24 h, the apoptosis rate of HCC cells, Jurkat cells and human cholangiocarcinoma cell line QBC939 was 10%, 70%, 50% respectively. It was suggested that the TRAILR expression is prevalent in HCC with different expression patterns of different receptor types. HCC is resistant to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. The treatment of TRAIL alone has a limited effect on inducing apoptosis of HepG2 and SMMC-7721.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wiley S R, Schooley K, Smolack P Jet al. Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity, 1995, 3:673
Pitti R M, Marsters S A, Ruppest Set al. Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2 ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family. J Biol Chem, 1996, 271:12 687
Sheridan J P, Marsters S A, Pitti R Met al. Control of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by a family of signaling and decoy receptors. Science, 1997, 277:818
Ashkenazi A, Dixit V M. Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science, 1998, 281:1305
Pan G, Rourke K O, Chinnaiyan A Met al. The receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL. Science, 1997, 276:111
Walczak H, Degli-Esposti M A, Johnson R Set al. TRAIL-R2: a novel apoposis-mediating receptor for TRAIL. EMBO J, 1997, 16:5386
Pan G, Wei Y F, Yu Get al. An antagonist decoy receptor and a death domain-containing receptor for TRAIL. Science, 1997, 277:815
Degli-Esposti M A, Dougall W C, Smolak P Jet al. The novel receptor TRAIL-R4 induces NF-kB and protects against TRAIL-mediated apoptosis, yet retains an incomplete death domain. Immunity, 1997, 7:813
Emery J G, McDonnell P, Burke M Bet al. Ostroprotegerin is a receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL. J Biol Chem, 1998, 273, 14 363
Keane M M, Ettenberg S A, Nau M Met al. Chemotherapy augments TRAIL-induced apoptosis in breast cell lines. Cancer Res, 1999, 59:734
Gliniak B, Le T. Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand's antitumor activity in vivo is enhanced by the chemotherapeutic agent CPT-11. Cancer Res, 1999, 59:6153
Gong B, Almasan A. Apo2 ligand/TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and death receptor 5 mediate the apoptotic signaling induced by ionizing radiation in leukemic cells. Cancer Res, 2000, 60:5754
Yamanaka T, Shiraki K, Sugimoto Ket al. Chemotherapeutic agents augment TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Hepatology, 2000, 32:482
Tanaka S, Sugimachi K, Shirabe Ket al. Expression and antitumor effects of TRAIL in human cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology, 2000, 32(3):523
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
He Songqing, male, born in 1970, M. D., Ph.D.
This project was supported by the major Foundation of Ministry of Health of China (No. 2001-2003).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Songqing, H., Yan, C., Xiaoping, C. et al. Antitumor effects of soluble TRAIL in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Current Medical Science 25, 51–54 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02831386
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02831386