Summary
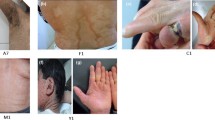
To investigate the gene mutation in a pedigree with X-linked ichthyosis (XLI) and to explore the relationship between the mutation and its clinical manifestations, genomic DNA of affected members, the normal member of the pedigree and 50 unrelated normal members was extracted with a whole blood genomic DNA extraction kit and the DNA was used as a template for the polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-mediated amplification of exon 1 and exon 10 of the STS gene. hHb6 (human hair basic keratin) gene was used as the internal control. Our results showed that the STS gene was deleted in affected members in the pedigree with X-linked ichthyosis. The normal member of the pedigree and 50 unrelated normal members had no such deletion. The proband and his mother had products in the internal control after PCR amplification. The blank control had no product. It is concluded that deletion of the STS gene existed in this pedigree with X-linked ichthyosis, and it is responsible for the unique skin lesions of X-linked ichthyosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ingordo V, DAndria G, Gentile Cet al. Frequency of X-linked ichthyosis in coastal southern Italy: a study on a representative sample of a young male population. Dermatology, 2003,207(2):148
Gonzalez-Huerta L M, Riviera-Vega M R, Kofman-Alfeuro S Het al. Novel missense mutation (Arg432Cys) in a patient with steroid sulphatase-deficiency. Clin Endocrinol (Oxford), 2003,59(2):263
Zhao B. Clinical Dermatology, 3rd ed. Jiangsu: Publication of Science & Technology, 2002, 1062
Valdes-Flores M, Kofman-Alfaro S H, Vaca A Let al. Deletion of exons 1–5 of the STS gene causing X-linked ichthyosis. J Invest Dermatol, 2001,116(3):456
Hernandez-Martin A, Gonzalez-Sarmiento R, De Unamuno P. X-linked ichthyosis: an update. Brit J Demerol, 1999,141(4):617
Lyon M F. Gene action in the X-chromosome of the mouse (Mus musculus L). Nature, 1961,190:372
Shapiro L J, Yen P, Pomerantz Det al. Molecular studies of deletion at the human steroid sulfatase locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1989,86:8477
Ballabio A, Ranier J E, Chamberlain J Set al. Screening for steroid sulfatase (STS) gene deletions by multiplex DNA amplification. Hum Genet, 1990,84:571
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Liu An, female, born in 1975, M. D., Ph. D.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, L., Shengxiang, X., Shengshun, T. et al. STS gene in a pedigree with X-linked ichthyosis. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 25, 468–469 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02828226
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02828226