Summary
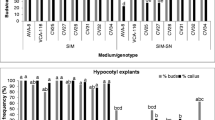
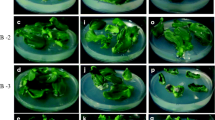
Chile pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) plants were regenerated from cotyledon explantsin vitro in four major stages: bud induction, bud enlargement, shoot elongation, and root development. Bud induction medium contained 0.5 mg/L (2.9μM) indole-3-acetic acid and 2 mg/L (8.9 μM) N6-benzyladenine. Bud enlargement occurred, and an occasional shoot appeared when medium with 2 mg/L (6μM) gibberellic acid, 2 mg/L (8.9 μM) N6-benzyladenine, and 5 mg/L (29.4 μM) silver nitrate was used. Most shoots elongated after placement on a third medium without plant growth regulators or on fresh plates of bud enlargement medium. Incubations were for 2, 2, and 4 weeks, respectively, at 28.5°C and continuous light. Treatment with silver nitrate was necessary for multiple shoot production and elongation to occur in the third culture stage and was most effective when present in the second-stage medium but not in the bud induction medium. Sixteen to 26% of the shoots rooted in medium with 1 mg/L (5.4 μM) 1-naphthaleneacetic acid after 1 month. Additional shoots transferred to a second rooting medium with 0.1 or 1.0 mg/L (0.54 or 5.4 μM) 1-naphthaleneacetic acid developed roots, increasing the overall rooting efficiency to 70–72%. Most rooted shoots grew well and produced viable seeds when grown in the greenhouse. Other cytokinins tested for plant regeneration were zeatin and thidiazuron. Zeatin induced few shoots and fewer well-developed plants. Thidiazuron induced multiple shoots 4 months after culture began, but many were small and did not elongate further. Phytagar tissue culture grade proved superior to other agars tested, increasing bud induction frequency from 0-33% to 80–93% and eliminating explant hyperhydricity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal, S.; Chandra, N.; Kothari, S. L. Plant regeneration in tissue cultures of pepper (Capsicum annuum L. cv.mathania). Plant Cell Tissue Organ. Cult. 16:47–55; 1989.
Arroyo, R.; Revilla, A. In vitro plant regeneration from cotyledon and hypocotyl segments in two bell pepper cultivars. Plant Cell Rep. 10:414–416; 1991.
Beyer, E. M. A potent inhibitor of ethylene action in plants. Plant Physiol. 58:268–271; 1976.
Chi, G. L.; Barfield, D. G. Sim, G. E., et al. Effect of AgNO3 and amino-ethoxyvinylglycine on in vitro shoot and root organogenesis from seedling explants of recalcitrantBrassica genotypes. Plant Cell Rep. 9:195–198; 1990.
Dunstan, D. I.; Short, K. C.. Improved growth of tissue cultures of the onion,Allium cepa. Physiol. Plant. 41:70–72; 1977.
Ebida, A. I. A.; Hu, C. Y. In vitro morphogenetic responses and plant regeneration from pepper (Capsicum annum L. cv. Early California Wonder) seedling explants. Plant Cell Rep. 13:107–110; 1993.
Fari, M.; Andrasfalvy, A. Regeneration and cloning of pepper (Capsicum sp.) in vitro: a review. Hort. Sci. (Hungary) 26:9–18; 1994.
Fari, M.; Czako, M. Relationship between position and morphogenetic response of pepper hypocotyl explants cultured in vitro. Scientia Hort. 15:207–213; 1981.
Gunay, A. L.; Rao, P. S. In vitro plant regeneration from hypocotyl and cotyledon explants of red pepper (Capsicum). Plant Sci. Lett., 11:365–372; 1978.
Harini, I.; Lakshmi Sita, G. Direct somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from immature embryos of chili (Capsicum annum L.). Plant Sci. 89:107–112; 1993.
Jacobs, J. L.; Stephens, C. T. Factors affecting the regeneration of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Abstr. no. 408, HortScience 25:120; 1990.
Lee, S. J.; Kim, B. D.; Paek, K. H.. In vitro plant regeneration andAgrobacterium-mediated transformation from cotyledon explants of hot pepper (Capsicum annum cv. Golden Tower). Korean J. Plant Tissue Cult. 20:289–294; 1993.
Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15:473–497; 1962.
Nitsch, J. P. Experimental androgenesis inNicotiana. Phytomorphology 19:389–404; 1969.
Phillips, G. C.; Collins, G. B.. In vitro tissue culture of selected legumes and plant regeneration from callus cultures of red clover. Crop Sci. 19:59–64; 1979.
Phillips, G. C.; Hubstenberger, J. F. Organogenesis in pepper tissue cultures. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 4:261–269; 1985.
Purnhauser, L.; Medgyesy, P.; Czako, M., et al. Stimulation of shoot regeneration inTriticum aestivum L. andNicotiana plumbaginifolia Viv. Tissue cultures using the ethylene inhibitor AgNO3. Plant Cell Rep. 6:1–4; 1987.
Szasz, A.; Nervo, G.; Fari, M. Screening for in vitro shoot-forming capacity of seedling explants in bell pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) genotypes and efficient plant regeneration using thidiazuron. Plant Cell Rep. 14:666–669; 1995.
Valera-Montero, L. L.; Ochoa-Alejo, N. A novel approach for chili pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) plant regeneration: shoot induction in rooted hypocotyls. Plant Sci. 84:215–219; 1992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hyde, C.L., Phillips, G.C. Silver nitrate promotes shoot development and plant regeneration of chile pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) via organogenesis. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Plant 32, 72–80 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02823134
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02823134