Abstract
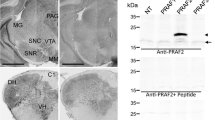
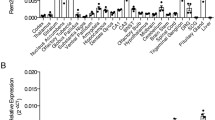
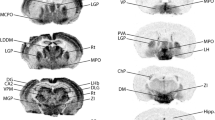
GTPase-activating protein is known to regulate the conversion between ras-GTP and ras-GDP. We studied the basal expression of GTPase-activating protein-like immunoreactivity in mouse cerebral regions using a polyclonal anti-GTPase-activating protein antibody. Cells with GTPase-activating protein-like immunoreactivity were distributed in frontal cortical layers IV and V, and in the parietal cortex, piriform cortex, amygdaloid area, septum, lateral thalamus, and hypothalamus. The GTPase-activating protein-like immunoreactivity was also observed in fiber-like structures in the caudate putamen, stria terminalis, internal capsule, and medial forebrain bundle, and around CA2 pyramidal cells in Ammon’s horn. These results imply that GTPase-activating protein is constitutively expressed in mouse brain regions and may have physiological functions in specific neuronal pathways in the brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballester R., Marchuk D., Boguski M., Saulino A., Letcher R., Wigler M., et al. (1990) The NF 1 locus encodes a protein functionally related to mammalian GAP and yeast IRA protein.Cell 63, 851–859.
Barbacid M. (1987) ras genes, inAnnual Reviews, vol. 56 (Richardson C. C., Boyer P. D., Diwid I. B., and Meister A., eds.), pp 779–827, Annual Reviews, Palo Alto, USA.
Bollag G., and McCormick F. (1991) Differential regulation of ras GAP and neurofibromatosis gene product activities.Nature 351, 576–579.
Diekmann D., Brill S., Garrett M. D., Totty N., Hsuan J., Monfries C., et al. (1991) Bcr encodes a GTPase-activating protein for p21ras.Nature 351, 400–402.
Ellis C., Moran M., McCormick F., and Pawson T. (1990) Phosphorylation of GAP and GAP-associated proteins by transforming and mitogenic tyrosine kinases.Nature 343, 377–381.
Gibbs J. B., Schaber M. D., Allard W. J., Sigal I. S., and Scolnick E. M. (1988) Purification of ras GTPase activating protein from bovine brain.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 5026–5030.
Gulbins E., Coggeshall K. M., Baier G., Katzav S., Burn P., and Altman A. (1993) Tyrosine-kinase-stimulated guanine nucleotide exchange activity of Vav in T cell activation.Science 260, 822–825.
Hsieh C. L., Vogel U. S., Dixon R. A., and Francke U. (1989) Chromosome localization and cDNA sequence of murine and human genes for ras p21 GTPase activating protein (GAP).Somat. Cell Mol. Genet. 15, 579–590.
Martin G. A., Viskochil D., Bollag G., McCabe P. C., Crosier W. J., Haubruck H., et al. (1990) The GAP-related domain of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene product interacts with ras p21.Cell 63, 843–849.
Molloy C. J., Bottaro D. P., Fleming, T. P., Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., and Aaronson S. A. (1989) PDGF induction of tyrosine phosphorylation of GTPase-activating protein.Nature 342, 711–714.
Molloy C. J., Fleming T. P., Bottaro D. P., Cuadrado A., and Aaronson S. A. (1992) Plateletderived growth factor stimulation of GTPase-activating protein tyrosine phosphorylation in control and c-H-ras expressing NIH 3T3 cells correlates with p21 ras activation.Mol. Cell Biol. 12, 3903–3909.
Reedijk M., Liu X. Q., and Pawson T. (1990) Interactions of phosphatidylinositol kinase, GTPase-activating protein (GAP), and GAP-associated proteins with the colonystimulating factor 1 receptor.Mol. Cell Biol. 10, 5601–5608.
Satoh T., Endo M., Nakafuku M., Akiyama T., Yamamoto T., and Kaziro Y. (1990) Accumulation of p21ras GTP in response to stimulation with epidermal growth factor and oncogene products with tyrosine kinase activityProc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 7926–7929.
Settleman J., Narasimhan V., Foster L. C., and Weinberg R. A. (1992) Molecular cloning of cDNAs encoding the GAP-associated protein p 190 implications for a signaling pathway from ras to the nucleus.Cell 69, 539–549.
Shiosaka S. and Tohyama M. (1986) Immunohistochemical techniques, inPeptides and Neurological Disease. Prog Brain Res., vol. 66 (Emson P. C., Rossor M., and Tohyama M., eds.), pp. 3–32, Elsevier, Amsterdam, Netherlands.
Shou C., Farnsworth C. L., Neel B. G., and Feig L. A. (1992) Molecular cloning of cDNAs encoding a guanine-nucleotide releasing factor for ras p21.Nature 358, 351–354.
Trahey M. and McCormick F. (1987) A cytoplasmic protein stimulates normal N-ras p21 GTPase, but does not affect oncogenic mutants.Science 238, 542–545.
Trahey M., Wong, G., Halenbeck R., Rubinfeld B., Martin G. A., Ladner M., et al. (1988) Molecular cloning of two types of GAP complementary DNA from human placenta.Science 242, 1697–1700.
Vogel U. S., Dixon R. A., Schaber M. D., Diehl R. E., Marshall M. S., Scolnick E. M., et al. (1988) Cloning of bovine GAP and its interaction with oncogenic ras p21.Nature 335, 90–93.
Wong G., Muller O., Clark R., Conroy L., Moran M. F., Polakis P., et al. (1992) Molecular cloning and nucleic acid binding properties of the GAP-associated tyrosine phosphoprotein p62Cell 69, 551–558.
Xu G. F., Lin B., Tanaka K., Dunn D., Wood D., Gesteland R., et al. (1990) The catalytic domain of the neurofibromatosis type I gene product stimulates ras GTPase and complements ira mutants ofS. cerevisiae.Cell 63, 835–841.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Namima, M., Takeuchi, K., Watanabe, Y. et al. Localization of GTPase-activating protein-(GAP) like immunoreactivity in mouse cerebral regions. Molecular and Chemical Neuropathology 35, 157–172 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02815122
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02815122