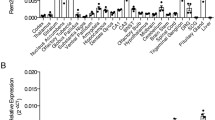
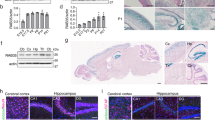
Abstract
Prenylated Rab acceptor family, member 2 (PRAF2) is a four transmembrane domain protein of 19 kDa that is highly expressed in particular areas of mammalian brains. PRAF2 is mostly found in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) of neurons where it plays the role of gatekeeper for the GB1 subunit of the GABAB receptor, preventing its progression in the biosynthetic pathway in the absence of hetero-dimerization with the GB2 subunit. However, PRAF2 can interact with several receptors and immunofluorescence studies indicate that PRAF2 distribution is larger than the ER, suggesting additional biological functions. Here, we conducted an immuno-cytochemical study of PRAF2 distribution in mouse central nervous system (CNS) at anatomical, cellular and ultra-structural levels. PRAF2 appears widely expressed in various regions of mature CNS, such as the olfactory bulbs, cerebral cortex, amygdala, hippocampus, ventral tegmental area and spinal cord. Consistent with its regulatory role of GABAB receptors, PRAF2 was particularly abundant in brain regions known to express GB1 subunits. However, other brain areas where GB1 is expressed, such as basal ganglia, thalamus and hypothalamus, contain little or no PRAF2. In these areas, GB1 subunits might reach the cell surface of neurons independently of GB2 to exert biological functions distinct from those of GABAB receptors, or be regulated by other gatekeepers. Electron microscopy studies confirmed the localization of PRAF2 in the ER, but identified previously unappreciated localizations, in mitochondria, primary cilia and sub-synaptic region. These data indicate additional modes of GABAB regulation in specific brain areas and new biological functions of PRAF2.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 10cb:
-
Tenth cerebellar lobule
- 10N:
-
Dorsal motor nucleus of vagus
- 12N:
-
Hypoglossal nucleus
- 7N:
-
Facial nucleus
- aca:
-
Anterior commissure anterior part
- AcbC:
-
Accumbens nucleus core
- AcbSh:
-
Accumbens nucleus shell
- aci:
-
Anterior commissure intrabulbar part
- AD:
-
Anterodorsal thalamic nucleus
- Amb:
-
Ambiguus nucleus
- AOV:
-
Anterior olfactory nucleus ventral part
- AP:
-
Area postrema
- BM:
-
Basomedial amygdaloid nucleus
- BST:
-
Bed nucleus of the stria terminalis
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- Cp:
-
Corpus callosum
- CPu:
-
Caudate putamen
- cu:
-
Cuneate fasciculus
- Cu:
-
Cuneate nucleus
- DAB:
-
Diaminobenzidine
- DC:
-
Dorsal cochlear nucleus
- Den:
-
Dorsal endopiriform nucleus
- DG:
-
Dentate gyrus
- DH:
-
Dorsal horn
- DR:
-
Dorsal raphe nucleus
- Ecu:
-
External cuneate nucleus
- EPL:
-
External plexiform layer
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- GABA:
-
Gamma-amino butyric acid
- GCL:
-
Granule cell layer
- Gi:
-
Gigantocellular reticular nucleus
- Gl:
-
Glomerular layer of the olfactory bulb
- GPCRs:
-
G protein coupled receptors
- Gr:
-
Gracile nucleus
- GR:
-
Granular cells layer
- H:
-
Hilus
- Io:
-
Inferior olive
- IOC:
-
Inferior olive subnucleus C
- IP:
-
Interpeduncular nucleus
- LGP:
-
Lateral globus pallidus
- LH:
-
Lateral hypothalamic area
- LHb:
-
Lateral habenular nucleus
- LM:
-
Lateral mammillary nucleus
- LRt:
-
Lateral reticular nucleus
- M2:
-
Secondary motor cortex
- MdV:
-
Medullary reticular nucleus ventral part
- Med:
-
Medial fastigial cerebellar nucleus
- MePD:
-
Medial amygdaloid nucleus posterodorsal part
- MG:
-
Medial geniculate nucleus
- MHb:
-
Medial habenular nucleus
- Mi:
-
Mitral cell layer of the olfactory bulb
- ML:
-
Molecular layer
- MM:
-
Medial mammillary nucleus
- MnR:
-
Median raphe nucleus
- MO:
-
Medial orbital cortex
- MVB:
-
Multivesicular bodies
- MVePC:
-
Medial vestibular nucleus parvicellular part
- Or:
-
Strata oriens
- PAG:
-
Periaqueductal gray
- Par:
-
Parietal cortex
- PFl:
-
Paraflocculus
- Pir:
-
Piriform cortex
- PMCo:
-
Posteromedial cortical amygdaloid nucleus
- Pn:
-
Pontine nuclei
- PRAF2:
-
Prenylated Rab acceptor family, member 2
- Prl:
-
Prelimbic cortex
- Pur:
-
Purkinje cells layer
- PVA:
-
Paraventricular thalamic nucleus
- Pyr:
-
Pyramidal cells
- Rad:
-
Stratum radiatum
- RER:
-
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
- Rt:
-
Reticular thalamic nucleus
- sm:
-
Stria medullaris thalamus
- SNC:
-
Substancia nigra compacta
- SNR:
-
Substantia nigra pars reticulate
- Sol:
-
Nucleus of the solitary tract
- Sp5:
-
Spinal trigeminal nucleus
- VCP:
-
Ventral cochlear nucleus posterior part
- VH:
-
Ventral horn
- VL:
-
Ventrolateral nucleus
- VMH:
-
Ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus
- VPM:
-
Ventral posteromedial thalamic nucleus
- VTA:
-
Ventral tegmental area
- Zo:
-
Zonal layer of superior colliculus
References
Achour L, Labbe-Juillie C, Scott MGH, Marullo S (2008) An escort for G protein coupled receptors to find their path: implication for regulation of receptor density at the cell surface. Trends Pharmacol Sci 29:528–535
Akiduki S, Ikemoto MJ (2008) Modulation of the neural glutamate transporter EAAC1 by the addicsin-interacting protein ARL6IP1. J Biol Chem 283:31323–31332. doi:10.1074/jbc.M801570200
Akiduki S, Ochiishi T, Ikemoto MJ (2007) Neural localization of addicsin in mouse brain. Neurosci Lett 426:149–154. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2007.08.056
Anderton RS et al (2012) Co-regulation of survival of motor neuron and Bcl-xL expression: implications for neuroprotection in spinal muscular atrophy. Neuroscience 220:228–236. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.06.042
Baloucoune GA et al (2012) GABAB receptor subunit GB1 at the cell surface independently activates ERK1/2 through IGF-1R transactivation. PLoS One 7:e39698. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0039698
Benke D (2010) Mechanisms of GABAB receptor exocytosis, endocytosis, and degradation. Adv Pharmacol 58:93–111. doi:10.1016/S1054-3589(10)58004-9
Berbari NF, Johnson AD, Lewis JS, Askwith CC, Mykytyn K (2008a) Identification of ciliary localization sequences within the third intracellular loop of G protein-coupled receptors. Mol Biol Cell 19:1540–1547. doi:10.1091/mbc.E07-09-0942
Berbari NF, Lewis JS, Bishop GA, Askwith CC, Mykytyn K (2008b) Bardet-Biedl syndrome proteins are required for the localization of G protein-coupled receptors to primary cilia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:4242–4246. doi:10.1073/pnas.0711027105
Berman SB et al (2009) Bcl-x L increases mitochondrial fission, fusion, and biomass in neurons. J Cell Biol 184:707–719. doi:10.1083/jcb.200809060
Bjork S, Hurt CM, Ho VK, Angelotti T (2013) REEPs are membrane shaping adapter proteins that modulate specific g protein-coupled receptor trafficking by affecting ER cargo capacity. PLoS One 8:e76366. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0076366
Borsics T, Lundberg E, Geerts D, Koomoa DL, Koster J, Wester K, Bachmann AS (2010) Subcellular distribution and expression of prenylated Rab acceptor 1 domain family, member 2 (PRAF2) in malignant glioma: influence on cell survival and migration. Cancer Sci 101:1624–1631. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01570.x
Bowery NG, Hudson AL, Price GW (1987) GABAA and GABAB receptor site distribution in the rat central nervous system Neuroscience 20:365–383
Brailov I, Bancila M, Brisorgueil MJ, Miquel MC, Hamon M, Verge D (2000) Localization of 5-HT(6) receptors at the plasma membrane of neuronal cilia in the rat brain. Brain Res 872:271–275
Burman KJ et al (2003) GABAB receptor subunits, R1 and R2, in brainstem catecholamine and serotonin neurons. Brain Res 970:35–46
Calver AR et al (2000) The expression of GABA(B1) and GABA(B2) receptor subunits in the cNS differs from that in peripheral tissues. Neuroscience 100:155–170
Charles KJ, Evans ML, Robbins MJ, Calver AR, Leslie RA, Pangalos MN (2001) Comparative immunohistochemical localisation of GABA(B1a), GABA(B1b) and GABA(B2) subunits in rat brain, spinal cord and dorsal root ganglion. Neuroscience 106:447–467
Charles KJ, Calver AR, Jourdain S, Pangalos MN (2003) Distribution of a GABAB-like receptor protein in the rat central nervous system. Brain Res 989:135–146
Chen L, Yung WH (2004) GABAergic neurotransmission in globus pallidus and its involvement in neurologic disorders. Sheng Li Xue Bao 56:427–435
Chiurchiu V, Maccarrone M, Orlacchio A (2014) The role of reticulons in neurodegenerative diseases. Neuromol Med 16:3–15. doi:10.1007/s12017-013-8271-9
Clark JA, Mezey E, Lam AS, Bonner TI (2000) Distribution of the GABA(B) receptor subunit gb2 in rat CNS. Brain Res 860:41–52
Colombo G et al (2004) Role of GABA(B) receptor in alcohol dependence: reducing effect of baclofen on alcohol intake and alcohol motivational properties in rats and amelioration of alcohol withdrawal syndrome and alcohol craving in human alcoholics. Neurotox Res 6:403–414
Davenport JR et al (2007) Disruption of intraflagellar transport in adult mice leads to obesity and slow-onset cystic kidney disease. Curr Biol 17:1586–1594. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2007.08.034
Doly S, Marullo S (2015) Gatekeepers controlling GPCR export and function. Trends Pharmacol Sci. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2015.06.007
Doly S et al (2015) GABA receptor cell-surface export is controlled by an endoplasmic reticulum gatekeeper. Mol Psychiatry. doi:10.1038/mp.2015.72
Domire JS, Green JA, Lee KG, Johnson AD, Askwith CC, Mykytyn K (2011) Dopamine receptor 1 localizes to neuronal cilia in a dynamic process that requires the Bardet–Biedl syndrome proteins. Cell Mol Life Sci 68:2951–2960. doi:10.1007/s00018-010-0603-4
Durkin MM, Gunwaldsen CA, Borowsky B, Jones KA, Branchek TA (1999) An in situ hybridization study of the distribution of the GABA(B2) protein mRNA in the rat CNS. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 71:185–200
Einstein EB et al (2010) Somatostatin signaling in neuronal cilia is critical for object recognition memory. J Neurosci 30:4306–4314. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5295-09.2010
Enoch MA, Baghal B, Yuan Q, Goldman D (2013) A factor analysis of global GABAergic gene expression in human brain identifies specificity in response to chronic alcohol and cocaine exposure. PLoS One 8:e64014. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0064014
Fan Y et al (2004) Mutations in a member of the Ras superfamily of small GTP-binding proteins causes Bardet–Biedl syndrome. Nat Genet 36:989–993. doi:10.1038/ng1414
Fenster SD et al (2000) Piccolo, a presynaptic zinc finger protein structurally related to bassoon. Neuron 25:203–214
Fo CS, Coleman CS, Wallick CJ, Vine AL, Bachmann AS (2006) Genomic organization, expression profile, and characterization of the new protein PRA1 domain family, member 2 (PRAF2). Gene 371:154–165. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2005.12.009
Fritschy JM, Sidler C, Parpan F, Gassmann M, Kaupmann K, Bettler B, Benke D (2004) Independent maturation of the GABA(B) receptor subunits GABA(B1) and GABA(B2) during postnatal development in rodent brain. J Comp Neurol 477:235–252. doi:10.1002/cne.20188
Gassmann M et al (2004) Redistribution of GABAB(1) protein and atypical GABAB responses in GABAB(2)-deficient mice. J Neurosci 24:6086–6097. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5635-03.2004
Geerts D, Wallick CJ, Koomoa DL, Koster J, Versteeg R, Go RC, Bachmann AS (2007) Expression of prenylated Rab acceptor 1 domain family, member 2 (PRAF2) in neuroblastoma: correlation with clinical features, cellular localization, and cerulenin-mediated apoptosis regulation. Clin Cancer Res 13:6312–6319. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0829
Geng J, Shin ME, Gilbert PM, Collins RN, Burd CG (2005) Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rab-GDI displacement factor ortholog Yip3p forms distinct complexes with the Ypt1 Rab GTPase and the reticulon Rtn1p. Eukaryot Cell 4:1166–1174. doi:10.1128/EC.4.7.1166-1174.2005
Handel M et al (1999) Selective targeting of somatostatin receptor 3 to neuronal cilia. Neuroscience 89:909–926
Horowitz JM, Pastor DM, Goyal A, Kar S, Ramdeen N, Hallas BH, Torres G (2003) BAX protein-immunoreactivity in midbrain neurons of Parkinson’s disease patients. Brain Res Bull 62:55–61
Hutt DM, Da-Silva LF, Chang LH, Prosser DC, Ngsee JK (2000) PRA1 inhibits the extraction of membrane-bound rab GTPase by GDI1. J Biol Chem 275:18511–18519. doi:10.1074/jbc.M909309199
Inoue K, Akiduki S, Ikemoto MJ (2005) Expression profile of addicsin/GTRAP3-18 mRNA in mouse brain. Neurosci Lett 386:184–188. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2005.06.013
Kaufmann T, Schlipf S, Sanz J, Neubert K, Stein R, Borner C (2003) Characterization of the signal that directs Bcl-x(L), but not Bcl-2, to the mitochondrial outer membrane. J Cell Biol 160:53–64. doi:10.1083/jcb.200210084
Kaupmann K et al (1997) Expression cloning of GABA(B) receptors uncovers similarity to metabotropic glutamate receptors. Nature 386:239–246. doi:10.1038/386239a0
Kaupmann K et al (1998) GABA(B)-receptor subtypes assemble into functional heteromeric complexes. Nature 396:683–687. doi:10.1038/25360
Kim J et al (2010) Functional genomic screen for modulators of ciliogenesis and cilium length. Nature 464:1048–1051. doi:10.1038/nature08895
Kiseleva E, Morozova KN, Voeltz GK, Allen TD, Goldberg MW (2007) Reticulon 4a/NogoA locates to regions of high membrane curvature and may have a role in nuclear envelope growth. J Struct Biol 160:224–235. doi:10.1016/j.jsb.2007.08.005
Koomoa DL, Go RC, Wester K, Bachmann AS (2008) Expression profile of PRAF2 in the human brain and enrichment in synaptic vesicles. Neurosci Lett 436:171–176. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2008.03.030
Krajewski S, Krajewska M, Shabaik A, Miyashita T, Wang HG, Reed JC (1994) Immunohistochemical determination of in vivo distribution of Bax, a dominant inhibitor of Bcl-2. Am J Pathol 145:1323–1336
Kulik A, Vida I, Lujan R, Haas CA, Lopez-Bendito G, Shigemoto R, Frotscher M (2003) Subcellular localization of metabotropic GABA(B) receptor subunits GABA(B1a/b) and GABA(B2) in the rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 23:11026–11035
Lee HJ, Kang SJ, Lee K, Im H (2011) Human alpha-synuclein modulates vesicle trafficking through its interaction with prenylated Rab acceptor protein 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 412:526–531. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.07.028
Li H et al (2008) Bcl-xL induces Drp1-dependent synapse formation in cultured hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:2169–2174. doi:10.1073/pnas.0711647105
Lin CI, Orlov I, Ruggiero AM, Dykes-Hoberg M, Lee A, Jackson M, Rothstein JD (2001) Modulation of the neuronal glutamate transporter EAAC1 by the interacting protein GTRAP3-18. Nature 410:84–88. doi:10.1038/35065084
Liu Q et al (2007) The proteome of the mouse photoreceptor sensory cilium complex. Mol Cell Proteomics 6:1299–1317. doi:10.1074/mcp.M700054-MCP200
Lux-Lantos VA, Bianchi MS, Catalano PN, Libertun C (2008) GABA(B) receptors in neuroendocrine regulation. Cell Mol Neurobiol 28:803–817. doi:10.1007/s10571-008-9263-4
Maccioni P, Colombo G (2009) Role of the GABA(B) receptor in alcohol-seeking and drinking behavior. Alcohol 43:555–558. doi:10.1016/j.alcohol.2009.09.030
Margeta-Mitrovic M, Mitrovic I, Riley RC, Jan LY, Basbaum AI (1999) Immunohistochemical localization of GABA(B) receptors in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 405:299–321
Martincic I, Peralta ME, Ngsee JK (1997) Isolation and characterization of a dual prenylated Rab and VAMP2 receptor. J Biol Chem 272:26991–26998
Ng EL, Tang BL (2008) Rab GTPases and their roles in brain neurons and glia. Brain Res Rev 58:236–246. doi:10.1016/j.brainresrev.2008.04.006
Ng TK, Yung KK (2001) Differential expression of GABA(B)R1 and GABA(B)R2 receptor immunoreactivity in neurochemically identified neurons of the rat neostriatum. J Comp Neurol 433:458–470
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL, Korsmeyer SJ (1993) Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell 74:609–619
Pfeffer S, Aivazian D (2004) Targeting Rab GTPases to distinct membrane compartments. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:886–896. doi:10.1038/nrm1500
Richer M et al (2009) GABA-B(1) receptors are coupled to the ERK1/2 MAP kinase pathway in the absence of GABA-B(2) subunits. J Mol Neurosci 38:67–79. doi:10.1007/s12031-008-9163-6
Schweneker M, Bachmann AS, Moelling K (2005) JM4 is a four-transmembrane protein binding to the CCR5 receptor. FEBS Lett 579:1751–1758. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2005.02.037
Shim JW et al (2004) Enhanced in vitro midbrain dopamine neuron differentiation, dopaminergic function, neurite outgrowth, and 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridium resistance in mouse embryonic stem cells overexpressing Bcl-XL. J Neurosci 24:843–852. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3977-03.2004
Slot JW, Geuze HJ (2007) Cryosectioning and immunolabeling. Nat Protoc 2:2480–2491. doi:10.1038/nprot.2007.365
Ulrich D, Besseyrias V, Bettler B (2007) Functional mapping of GABA(B)-receptor subtypes in the thalamus. J Neurophysiol 98:3791–3795. doi:10.1152/jn.00756.2007
van der Heide LP, Smidt MP (2013) The BCL2 code to dopaminergic development and Parkinson’s disease. Trends Mol Med 19:211–216. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2013.02.003
Vander Heiden MG, Li XX, Gottleib E, Hill RB, Thompson CB, Colombini M (2001) Bcl-xL promotes the open configuration of the voltage-dependent anion channel and metabolite passage through the outer mitochondrial membrane. J Biol Chem 276:19414–19419. doi:10.1074/jbc.M101590200
Vento MT, Zazzu V, Loffreda A, Cross JR, Downward J, Stoppelli MP, Iaccarino I (2010) Praf2 is a novel Bcl-xL/Bcl-2 interacting protein with the ability to modulate survival of cancer cells. PLoS One 5:e15636. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0015636
Vila M, Przedborski S (2003) Targeting programmed cell death in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:365–375. doi:10.1038/nrn1100
Yang YS, Strittmatter SM (2007) The reticulons: a family of proteins with diverse functions. Genome Biol 8:234. doi:10.1186/gb-2007-8-12-234
Yco LP, Geerts D, Koster J, Bachmann AS (2013) PRAF2 stimulates cell proliferation and migration and predicts poor prognosis in neuroblastoma. Int J Oncol 42:1408–1416. doi:10.3892/ijo.2013.1836
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Ligue Contre le Cancer, comité de l’Oise to SD; from the PIC (projets inter-équipes) to SD; from the French Agency for AIDS Research (ANRS-09) and the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (Equipe FRM-2012) to SM; SM team is member of the ‘Who-am-I’ research consortium.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cifuentes-Diaz, C., Marullo, S. & Doly, S. Anatomical and ultrastructural study of PRAF2 expression in the mouse central nervous system. Brain Struct Funct 221, 4169–4185 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-015-1159-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-015-1159-8