Abstract
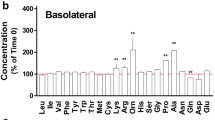
The uptake and transport kinetics of manganese (Mn) were investigated in the human intestinal Caco-2 cell line both from the absorption side (apical to basolateral) and from the exsorption side (basolateral to apical). With regard to the former, transport versus time revealed (as uptake) a biphasic pattern with an initial transient phase followed by steady-state conditions. Uptake versus Mn concentrations showed saturation-type kinetics with a 100% increase of Mn binding capacity when measurements were made from 0.5 to 2 h of incubation. The transport characteristics in steady-state conditions exhibited two components, saturable (Vmax = 3.70 ± 0.07 nmol/cm2/h, Km = 32.2 ± 3.4 μM) and nonsaturable (slope = [1.4 ± 0.2] x 10-6 cm-2/h) usually presumed to reflect transcellular (carrier mediated) and paracellular (diffusional) pathways, respectively. Mn fluxes were decreased by calcium and calcium antagonists, almost 100% inhibited at 4°C, and affected by quinacrine and ouabain. The inhibition of ATP synthesis was apparently ineffective. From the exsorption side, the Mn fluxes, without a transient period, had an approx 20-fold smaller rate than in the absorptive direction and showed mainly a nonsaturable route (slope = [0.6 ± 0.1] x 10-6 cm-2/h). The mechanisms participating in the Mn movements through the monolayer are discussed and proposed to be in common, at least partly, with other divalent cations such as calcium, zinc, or iron.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. S. Hurley and C. L. Keen, Manganese, inTrace Elements in Human and Animal Nutrition, W. Mertz, ed., Academic, New York, Vol. 1, pp. 185–192 (1987).
R. G. Banta and W. R. Markesbery, Elevated manganese levels associated with dementia and extrapyramidal signs,Neurology 213, 27–32 (1977).
X. G. Kondakis, N. Makris, M. Leotsinidis, M. Prinou, and T. Papapetropoulos, Possible health effects of high manganese concentration in drinking water,Arch. Environ. Health 44, 175–178 (1989).
J. A. Garcia-Aranda, R. A. Wapnir, and F. Lifshtiz, In vivo intestinal absorption of manganese in the rat,J. Nutr. 113, 2601–2607 (1983).
D. Y. Lee and P. E. Johnson, Factors affecting absorption and excretion of54Mn in rats,J. Nutr. 118, 1509–1516 (1988).
G. Testolin, S. Ciappellano, A. Alberio, F. Piccinini, L. Paracchini, and A. Jotti, Intestinal absorption of manganese: an in vitro study,Ann. Nutr. Metab. 37, 289–294 (1993).
M. Kato, Distribution and excretion of radiomanganese administered to the mouse,Quart, J. Exp. Physiol. 48, 355–369 (1963).
M. Cikrt, Enterohepatic circulation of64Cu,54Mn and203Hg in rats,Arch. Toxicol. 31, 51–59 (1973).
R. M. Leach and M. S. Liburn, Manganese metabolism and its function,World Rev. Nutr. Diet 32, 123–134 (1978).
B. Lönnerdal, C. L. Keen, J. G. Bell, and B. Sandström, Manganese uptake and retention, inNutritional Bioavailability of Manganese, C. Kies, ed., American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp. 9–20 (1987).
A. B. R. Thomson, D. Olatunbosun, and L. S. Valberg, Interrelation of intestinal transport system for manganese and iron,J. Lab. Clin. Med. 78, 642–655 (1971).
A. B. R. Thomson, and L. S. Valberg, Kinetics of intestinal iron absorption in the rat: effect of cobalt,Am. J. Physiol. 220, 1080–1085 (1971).
T. A. Lutz, A. Schroff, and E. Scharrer, Effect of calcium and sugars on intestinal manganese absorption,Biol. Trace Element Res. 39, 221–227 (1993).
I. J. Hidalgo, T. J. Raub, and R. T. Borchardt, Characterization of the human colon carcinoma cell line (Caco-2) as a model system for intestinal epithelial permeability,Gastroenterology 96, 736–749 (1989).
P. Artursson, Epithelial transport of drugs in cell culture, a model for studying the passive diffusion of drugs over intestinal absorptive (Caco-2) cells,J. Pharm. Sci. 79, 476–782 (1990).
A. R. Hilgers, R. A. Conradi, and P. S. Burton, Caco-2 cell monolayers as a model for drug transport for study transport across the intestinal mucosa,Pharm. Res. 7, 902–910 (1990).
E. Walter and T. Kissel, Heterogeneity in the human intestinal cell line Caco-2 leads to differences in transepithelial transport,J. Pharm. Sci. 3, 215–230 (1995).
D. Pansu, C. Bellaton, and F. Bronner, Effect of Ca intake on saturable and non saturable components of duodenal Ca transport,Am. J. Physiol. 240, G32-G37 (1981).
D. Triglia, S. S. Braa, C. Yonan, and G. K. Naughton, In vitro toxicity of various classes of test agents using the neutral red assay on a human three-dimensional physiologic skin model,In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 27A, 239–244 (1991).
B. Gumbiner, Structure, biochemistry and assembly of epithelial tight junctions,Am. J. Physiol. 253, C749-C758 (1987).
D. R. Pitelka, B. N. Taggart, and S. T. Hamamoto, Effect of extracellular calcium depletion on membrane topography and occluding junctions of mammary epithelial cell in culture,J. Cell Biol. 96, 613–624 (1983).
P. L. Nicklin, W. J. Irwin, I. F. Hassan, and M. Mackay, Development of a minimum calcium Caco-2 monolayer model: calcium and magnesium ions retard the transport of pamidronate,Int. J. Pharm. 123, 187–197 (1995).
M. W. Walling, Intestinal calcium and phosphate transport: differential responses to vitamin D3 metabolites,Am. J. Physiol. 233, 488–494 (1977).
I. Nemere, U. Leathers, and A. W. Norman, 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D2 mediated intestinal calcium transport,J. Biol. Chem. 261, 16106–16114 (1986).
J. C. Fleet, A. J. Turnbull, M. Bourcier, and R. J. Wood, Vitamin-D sensitive and quinacrine-sensitive zinc transport in human intestinal cell line Caco-2,Am. J. Physiol. 264, G1037-G1045 (1993).
X. A. Hernandez, G. M. Nichols, and J. Glass, Caco-2 cell line: a system for studying intestinal transport across epithelia cell monolayer,Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1070, 205–208 (1991).
T. Galeotti, G. Palombini, and D. V. van Rossum, Manganese content and high-affinity transport in liver and hepatoma,Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 322, 453–459 (1995).
M. Aschner and M. Gannon, Manganese (Mn) transport across the rat blood-brain barrier: saturable and transferrin-dependent transport mechanisms,Brain Res. Bull. 33, 345–349 (1994).
F. Bronner, D. Pansu, and W. D Stein, An analysis of intestinal calcium transport across the rat intestine,Am. J. Physiol. 250, G561-G569 (1986).
L. Davidsson, A. Cederblad, B. Lnnerdal, and B. Sandstrm, The effect of individual dietary components on manganese absorption in humans,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 54, 1065–1070 (1991).
A. Miller, S. T. Li, and F. Bronner, Characterization of calcium binding to brush-border membranes from rat duodenum,Biochem. J. 208, 773–781 (1982).
N. Surendran, L. D. Nguyen, A. R. Giuliano, and J. Blanchard, Mechanisms of acylcarnitine-mediated enhancement of calcium transport in the Caco-2 cell monolayer model,J. Pharm. Sci. 84, 269–274 (1995).
K. Thorstensen and I. Romslo, Uptake of iron from transferrin by isolated rat hepatocytes,J. Biol. Chem. 263, 8844–8850 (1988).
W. Breuer, S. Epsztejn, P. Millgram, and I. Z. Cabantchik, Transport of iron and other transient metals into cells as revealed by a fluorescent probe,Am. J. Physiol. 268, C1354-C1361 (1995).
R. D. Raffaniello, S. Y. Lee, S. Teichberg, and R. A. Wapnir, Distinct mechanisms of zinc uptake at the apical and basolateral membranes of Caco-2 cells,J. Cell Physiol. 152, 356–361 (1992).
W. E. J. M. Ghijjen, M. D. De Jong, and C. H. Van Os, Kinetic properties of Na+/Ca2+ exchange in basolateral plasma membranes of rat small intestine,Biochim. Biophys. Acta 730, 85–94 (1983).
A. L. Salzman, M. J. Menconi, N. Unno, R. M. Ezzell, D. M. Casey, P. K. Gonzalez, et al., Nitric oxide dilate tight junctions and deplete ATP in cultured Caco-2BBe intestinal epithelial monolayer,Am. J. Physiol. 268, G361-G373 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leblondel, G., Allain, P. Manganese transport by caco-2 cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 67, 13–28 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02784271
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02784271