Abstract
Background
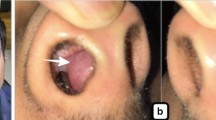
Amyloidosis refers to a group of depositional diseases that are classified into two main types: systemic and localized. Large nodules of localized cutaneous amyloidosis of the nasal ala and surrounding skin are rare and the treatment is often unsatisfactory.
Objective
We report a case of rapidly enlarging, localized, nodular cutaneous amyloidosis of the nose and the surrounding skin with a brief review of the current literature regarding treatment of this rare disease.
Conclusion
Nodular amyloidosis can be treated successfully with cold steel excision in combination with carbon dioxide laser. Close followup of these patients is warranted, as nodular amyloidosis may be the precursor to systemic amyloidosis.
Sommaire
Antécédents
L’amyloïdose se rapporte à un groupe de maladies caractérisées par le dépôt de substance amyloïde et classées en deux grands types, généralisé et localisé. L’amyloïdose cutanée localisée sous forme de gros nodules siégeant sur les ailes du nez et dans les tissus cutanés avoisinants est une affection rare dont le traitement donne souvent des résultats peu satisfaisants.
Objectif
Rapporter un cas d’amyloïdose cutanée localisée sous forme de nodules à évolution rapide au niveau du nez et des tissus cutanés avoisinants en donnant un bref aperçu de la documentation actuelle sur le traitement de cette rare maladie.
Conclusion
L’amyloïdose nodulaire peut être traitée avec succès par exérèse à l’acier à froid combinée à un traitement au laser à gaz carbonique. Comme l’amyloïdose nodulaire peut être un signe avant-coureur d’amyloïdose généralisée, les patients qui en sont atteints doivent faire l’objet d’un suivi étroit.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breathnach DM. Amyloid and amyloidosis. J Am Acad Dermatol 1988; 18:1–16.
Shirahama T, Cohen AS. High resolution electron microscopic analysis of the amyloid fibril. J Cell Biol 1967; 33:679–708.
Hashimoto K., H. Kobayashi Histiogenesis of amyloid in the skin. Am J Dermatopathol 1980; 2:165–171.
Eanes ED, Glenner GG. X-ray diffraction studies on amyloid filaments. J Histochem Cytochem 1968; 16:673–677.
Nothcutt A, Vanover ML. Nodular cutaneous amyloidosis involving the vulva. Arch Dermatol 1985; 121:518–521.
Brownstein MH, Helwig EB. Secondary systemic amyloidosis: analysis of underlying disorders. South Med J 1971; 64:491–496.
Kitajima Y, Seno J, Aoki S, et al. Nodular primary cutaneous amyloidosis: isolation and characterization of amyloid fibrils. Arch Dermatol 1986; 122:1425–1430.
Brownstein M, Helwig E. The cutaneous amyloidosis. Arch Dermatol 1970; 102:8–9.
Touart D, Sau P. Cutaneous deposition disease. Part I. J Am Acad Dermatol 1998; 39:149–171.
Trau H, Shpiro D, Schewach-Millet M, et al. Nodular cutaneous amyloidosis. Am J Dermatopathol 1991; 13:414–417.
Husby G, Sletten K, Blumernkrantz N, et al. Characterization of an amyloid fibril protein from localized amyloidosis of the skin as lambda immunoglobulin light chains of variable subgroup I (A lamda I). Clin Exp Immunol 1981; 45:90–96.
Sletten K, Westermark P, Pitkanen P, et al. Amino acid sequences in amyloid proteins in kappa III immunoglobulin light-chain origin. Scand J Immunol 1983; 18:557–560.
Hagari Y, Mihara M, Konohana I, et al. Nodular localized cutaneous amyloidosis: further demonstration of monoclonality of infiltrating plasma cells in four additional Japanese patient. Br J Dermatol 1998; 138:652–654.
Ratz JL, Bailin PL. Cutaneous amyloidosis: A case report of the tumefactive variant and review of the spectrum of clinical presentations. J Am Acad Dermatol 1981; 4:21–26.
Lien M, Railan D, Nelson B. The efficacy of dermabrasion in the treatment of nodular amyloidosis. J Am Acad Dermatol 1997; 36:315–316.
Vesty JP, Tidman MF, McClaren KM. Primary nodular cutaneous amyloidosis⤜ong term follow-up and treatment. Clin Exp Dermatol 1994; 19:159–162.
Hamzavi I, Lui H. Excess tissue friability during CO2 laser vaporization of nodular amyloidosis. Dermatol Surg 1999; 25:726–728.
Alster TS, Manaloto RM. Nodular amyloidosis treatment with a pulse dye laser. Dermatol Surg 1999; 25:133–135.
Sullivan T, Lloyd K, Boyd A. Colchicine in dermatology. J Am Acad Dermatol 1998; 39:993–999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kakani, R.S., Goldstein, A.E., Meisher, I. et al. Nodular amyloidosis: Case report and literature review. J Cutan Med Surg 5, 101–104 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02737862
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02737862