Abstract
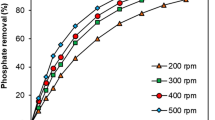
The removal of copper from aqueous solution by ion exchange resins, such as 1200H and IRN97H, is described. Effect of initial metal ion concentration, agitation time and pH on adsorption capacities of ion exchange resins was investigated in a batch mode. The adsorption process, which is pH dependent, shows maximum removal of copper in the pH range 2–7 for an initial copper concentration of 10 mg/L. The experimental data have been analyzed by using the Freundlich, Langmuir, Redlich-Peterson, Temkin and Dubinin-Radushkevich isotherm models. The batch sorption kinetics have been tested for a first-order, pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order kinetic reaction models. The rate constants of adsorption for all these kinetic models have been calculated. Results showed that the intraparticle diffusion and initial sorption into resins of Cu(II) in the ion exchange resins was the main rate limiting step. The uptake of copper by the ion exchange resins was reversible and thus has good potential for the removal/recovery of copper from aqueous solutions. We conclude that such ion exchange resins can be used for the efficient removal of copper from water and wastewater.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bae, E., Chah, S. and Yi, J., “Preparation and Characterization of Ceramic Hollow Microspheres for Heavy Metal Ion Removal in Wastewater,”J. Colloid Interf. Sci.,230, 367 (2000).
Camp, R. T., “Water and its Impurities,” 2nd Ed. Reinhold, New York (1964).
Chah, S., Kim, J. S. and Yi, J., “Separation of Zinc Ions from Aqueous Solutions using Modified Silica Impregnated with CYANEX 272,”Separ. Sci. Technol.,37, 701 (2002).
Dean, J.G., Borqui, F. L. and Labouette, K.H., “Removing Heavy Metals from Waste Water,”Environ. Sci. Tech.,6, 518 (1972).
Hosseini, M., Mertens, S. F. L., Ghorbani, M. and Arshadi, M. R., “Asymmetrical Schiff Bases as Inhibitors of Mild Steel Corrosion in Sulphuric Acid Media,”Mater. Chem. Phys.,78, 800 (2003).
Kang, T., Park, T., Park, J. C., Cho, Y. S. and Yi, J., “Preparation of Chemically Active Mesoporous Adsorbent for Pt(II) and Pd(II) Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,19, 685 (2002).
Kim, J. S., Chah, S. and Yi, J., “Preparation of Modified Silica for Heavy Metal Removal,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,17, 118 (2000).
Kim, S. J., Lim, K. H., Joo, K.H., Lee, M. J., Kil, S.G. and Cho, S.Y., “Removal of Heavy Metal Cyanide Complexes by Ion Exchange,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,19, 1078 (2002).
Kim, Y., Lee, B. and Yi, J., “Preparation of Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Containing Magnetite (MSM) for the Removal of Copper Ions in Aqueous Solutions and its Magnetic Separation,”Separ. Sci. Technol.,38, 2533 (2003).
Lee, B., Kim, Y., Lee, H. and Yi, J., “Synthesis of Functionalized Porous Silicas via Templating Method as Heavy Metal Ion Adsorbents: The Introduction of Surface Hydrophilicity onto the Surface of Adsorbents,”Micropor. Mesopor. Mat.,50, 77 (2001).
Namasivayam, C. and Kadirvelu, K., “Uptake of Mercury(II) from Wastewater by Activated Carbon from an Unwanted Agricultural Solid By-product,”Carbon,37, 79 (1999).
Namasivayam, C. and Ranganathan, K., “Removal of Cd(II) from Wastewater by Adsorption on Waste Fe(III)/Cr(III) Hydroxide,”Water Res.,29, 1737 (1995).
Quek, S.Y., Wase, D.A. J. and Forster, C. F., “The Use of Sago Waste for the Sorption of Lead and Copper,”Water SA,24, 251 (1998).
Redlich, O. and Peterson, D. L., “A Useful Adsorption Isotherm,”J. Phys. Chem.,63, 1024 (1959).
Rengaraj, S. and Moon, S.H., “Kinetics of Adsorption of Co(II) Removal from Water and Wastewater by Ion Exchange Resins,”Water Res.,36, 1783 (2002).
Rengaraj, S., Joo, C., Kim, Y. and Yi, J., “Kinetics of Removal of Chromium from Water and Electronic Process Wastewater by Ion Exchange Resins: 1200H, 1500H and IRN97H,”J. Hazard. Mater.,B102, 257 (2003).
Sun, Q. and Yang, L., “The Adsorption of Basic Dyes from Aqueous Solution on Modified Peat-resin Particle,”Water Res.,37, 1535 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper is dedicated to Professor Hyun-Ku Rhee on the occasion of his retirement from Seoul National University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rengaraj, S., Kim, Y., Joo, C.K. et al. Batch adsorptive removal of copper ions in aqueous solutions by ion exchange resins: 1200H and IRN97H. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 21, 187–194 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02705397
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02705397