Abstract
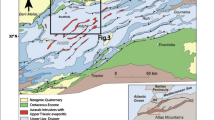
The Dhanbad district in Jharkhand faces acute water scarcity and is chronically drought-prone. The groundwater resources in the area have not been fully exploited. The present study was undertaken to evaluate the groundwater prospective zones. Landsat-5 Multi Spectral Scanner (MSS) data of band 2 and band 4 and false colour composite (FCC) of band 2, 3, 4 were interpreted visually to differentiate different hydromorphogeological units and to delineate the major trends of lineaments. The different geomorphic features identified are linear ridges, residual hills, and pediplain, buried pediment and dissected pediplain, besides lineaments. The study shows that the pediplain and buried pediments are promising zones for groundwater prospecting. The occurrence and movement of groundwater is restricted to the unconsolidated material, weathered and fractured rocks. For the selection of tube well sites, geoelectrical resistivity investigations have been carried out at the sites, which were found suitable based on hydrogeomorphological and hydrogeological studies. Twenty-six Vertical Electrical Soundings (VES) have been carried out by using Schlumberger electrode configuration, which have brought out 3 to 7 layered sub-surface layers. The resistivity of water-bearing weathered/fractured rocks varies from 120–150 ohm m. The integrated studies have revealed that the blue colour zones are most promising for groundwater exploration and dug wells may be dug up to depths of 30±5m.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhattacharya P K and Patra H P 1968 Direct current electrical sounding; (Elsevier, Amsterdam).
Fox C S 1930 The Jharia coalfield;Mem. GSI 56(1) 225.
Ghose R 1993 Remote sensing for analysis of groundwater availability in an area with long unplanned mining history;J. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing 21(3) 119–126.
Gupta A 1980 Correlation of Landsat and airborne magnetic anomaly data of a part of the Bihar mica belt;Proc. Symp. Remote Sensing in subsurface exploration, held on 25 Oct., Bangalore, India, pp. 23–30.
Knig L C 1950 The study of the worlds plain lands. A new approach in geomorphology;Q. Geol. Soc. London 106 101–103.
Keller G V and Frischnecht F C 1966 Electrical methods in Geophysical prospecting; (Pergamon, Oxford).
Kunetz G 1966 Principles of Direct current Resistivity prospecting; (Gebruder Borntraeger, Berlin).
Mehta DRS and Murthy BRL 1957 Revision of the geology of coal resources of the Jharia coalfield;Mem. GSI 84(2) 113.
Orellana E and Mooney H M 1966 Master tables and curves for vertical electrical sounding over layered structures, (Intercientia, Madrid).
Prakash S Ravi and Mishra D 1993 Identification of groundwater prospective zones by using Remote Sensing and geoelectrical methods in and around Saidnagar area. Dakor block, Jalaun district, U.P;J. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing 21(4) 217–227.
Sharma N L and Agrawal Y K 1950 A note on the rapakivi structure in the epidiorite and injection gneiss of Dhanbad area.Q.J.G. Min. Met. Soc. India 22 11–13.
Sparks B W 1960 Landform in arid and semi-arid climates; Geomorphology 2nd edn, (Longman Group Ltd.), pp. 335–341.
Tiwari O N 1993 Lineament identification for groundwater drilling in a hard rock terrain of Sirohi district, Western Rajasthan;J. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing 21(1) 13–19.
Tiwari A and Rai B 1996 Hydromorphological Mapping for groundwater prospecting using Landsat-MSS images — A case study of part of Dhanbad district, Bihar;J. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing 24(4) 281–285.
Verma R K, Rao M K and Rao C V 1980 Resistivity investigations for groundwater in metamorphic area near Dhanbad, India;Ground Water 18 46–55.
Zohdy A A R 1974b A computer program for the calculation of Schlumberger curves by convolution, U.S. Geological Survey report USGS-GD-74-010, U.S Department of Commerce, NT IS, (Springfield, VA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rai, B., Tiwari, A. & Dubey, V.S. Identification of groundwater prospective zones by using remote sensing and geoelectrical methods in Jharia and Raniganj coalfields, Dhanbad district, Jharkhand state. J Earth Syst Sci 114, 515–522 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02702027
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02702027