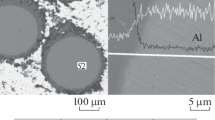
Abstract
The mechanism of phase changes in the Ti-B-Fe system in a combustion wave for a mixture of Ti, B, and Fe powders and a ferroboron alloy-titanium mixture with the same proportion of elements is studied. It is found that the mechanism of structure formation depends significantly on the type of contact between the initial components. An x-ray phase and x-ray spectrum and structural microanalyses of the quenched layers of specimens show that the first contact melts occurring in the combustion wave are ferroboron (the first type of mixture) or ferrotitanium (the second type) melts. In the first case, the calculated high-melting compound TiB2 forms as a result of the interaction between the two melts; in the second case, it forms as a result of the interaction of the melt with solid ferroboron, which, in turn, determines the different type of microstructure of the final combustion products. The highly disperse and more homogeneous structure of the products forms after combustion of the second-type mixture. A method of producing the Ti-B-Fe pore-free composite produced during the self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS-composite) by combining the combustion with rolling of the synthesis products is considered. In properties, theresulting material is similar to tungsten-carbide materials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. I. Serebryakova, V. A. Neronov, and P. D. Peshev,High-Temperature Borides [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1991).
Yu. M. Maksimov, A. T. Pak, A. G. Merzhanov, et al., “High-temperature synthesis of the Ti-B-Fe system,”Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser. Metals, No. 2, 219–223 (1985).
Yu. M. Maksimov, A. T. Pak, L. G. Raskolenko, and A. A. Zenin. “Specific features and the mechanism of combustion of the Ti-B-Fe system,”Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva,20, No. 2, 74–79 (1984).
Yu. M. Maksimov, A. G. Merzhanov, A. T. Pak, et al., “The mechanism of forming the product structure in self-propagating high-temperature synthesis,”Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR,276, No. 4, 881–894 (1984).
Yu. M. Maksimov, A. G. Merzhanov, L. G. Raskolenko, et al., “The role of contact melting in gas-free combustion,”Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR,286, No. 4, 911–914 (1986).
L. G. Raskolenko, Yu. M. Maksimov, and O. K. Lepakova, “Construction of a hypothetical Ti-B diagram by analysis of the combustion products of three-component systems,”J. Mater. Syn. Proc.,3, No. 3, 153–163 (1995).
Yu. M. Maksimov, O. K. Lepakova, and L. G. Raskolenko. “The mechanism of combustion of the titanium-boron system by quenching of the combustion front,”Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva,24, No. 1, 48–53 (1988).
V. M. Zalkin,Nature of Eutectic Melts and the Effect of Contact Melting [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated fromFizika Goreniya i Vzryva, Vol. 36, No. 5, pp. 27–34, September–October, 2000.
This work was supported by the Federal Program “Integration.”
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lepakova, O.K., Raskolenko, L.G. & Maksimov, Y.M. The mechanism of phase and structure formation of the Ti-B-Fe system in a combustion wave. Combust Explos Shock Waves 36, 575–581 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02699520
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02699520