Abstarct
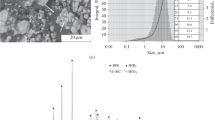
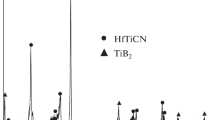
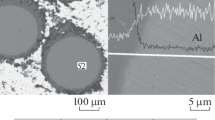
This study covers the elemental synthesis features of Hf–Ta–B–Ti–Si ceramic materials used to obtain promising high-temperature ceramics and analyze its structure and properties. The macrokinetics of self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS) are studied. Combustion temperature and velocity as a function of initial temperature are plotted. It is established that chemical interactions occurring in the liquid phase play a pivotal role in the combustion process. Structure and phase formation processes are studied using the stopped combustion front technique. The mechanism of phase formation in the combustion wave is determined. The primary crystals of hafnium, titanium, and tantalum diborides are precipitated from the super-saturated melt after the Si and Ti contact melting and B, Hf, and Ta dissolution in the melt through the reactive diffusion process. A two-phase structure consisting of complex solid solutions based on diboride and borosilicide is formed due to the similarity of the crystal lattices. Porous synthesis products of the specified composition are milled into powders with the required particle-size distribution for subsequent hot pressing (HP) or spark plasma sintering (SPS). It is found that specimens produced by HP, SPS, and SHS pressing feature a similar phase composition containing solid solutions based on diboride (Hf,Ti,Ta)B2 and borosilicide (Hf,Ti,Та)5Si3В. Specimens of ceramics produced using the above technologies for physical–mechanical testing are made. It is found that the hardness and elastic modulus of the (Hf,Ti,Ta)B2 solid solution are 2–3 times higher than that of (Hf,Ti,Ta)5Si3B borosilicide. Depending on the composition, the density of the ceramics varies from 8 to 6.5 g/cm3, which corresponds to a porosity of less than 5%. Temperature dependences of heat capacity and diffusivity are determined. The heat conductivity of ceramics produced by HP and SPS is 24.05 and 23.1 W/(m K), respectively.













Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Opeka, M.M., Talmy, I.G., and Zaykoski, J.A., Oxidation-based materials selection for 2000°C + hypersonic aerosurfaces: theoretical considerations and historical experience, J. Mater. Sci., 2004, vol. 39, pp. 5887–5904. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSC.0000041686.21788.77
Zhang, Z., Nan, C., Xu, J., Gao, Z., Li, M., and Wang, J., Oxidation behaviors of C–ZrB2–SiC composite at 2100°C in air and O2, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2014, vol. 30, no. 12, pp. 1223–1229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2014.04.013
Guo, S-Q., Densification of ZrB2-based composites and their mechanical and physical properties: a review, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2009, vol. 29, no. 6, pp. 995–1011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2008.11.008
Schlichting, K.W., Padture, N.P., and Klemens, P.G., Thermal conductivity of dense and porous yttria-stabilized zirconia, J. Mater. Sci., 2001, vol. 36, no. 12, pp. 3003–3010. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017970924312
Fahrenholtz, W.G., Hilmas, G.E., Talmy, I.G., and Zaykoski, J.A., Refractory diborides of zirconium and hafnium, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2007, vol. 90, no. 5, pp. 1347–1364. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2007.01583.x
Wuchina, E., Opila, E., Opeka, M., Fahrenholtz, W., and Talmy, I., UHTCs: Ultra-high temperature ceramic materials for extreme environment applications, Interface, 2007, vol. 16, no. 4, pp. 30–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-0857-4
Rodríguez-Sánchez, J., Sánchez-González, E., Guiberteau, F., and Ortiz, A.L., Contact-mechanical properties at intermediate temperatures of ZrB2 ultra-high-temperature ceramics pressureless sintered with Mo, Ta, or Zr disilicides, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2015, vol. 35, pp. 3179–3185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.04.023
Zhang, X., Hilmas, G.E., and Fahrenholtz, W.G., Synthesis, densification, and mechanical properties of TaB2, Mater. Lett., 2008, vol. 62, pp. 4251–4253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2008.06.052
Zhang, L., Pejaković, D.A., Marschall, J., and Gasch, M., Thermal and electrical transport properties of spark plasma-sintered HfB2 and ZrB2 ceramics, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2011, vol. 94, pp. 2562–2570. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2011.04411.x
Sciti, D., Balbo, A., and Bellosi, A., Oxidation behavior of a pressureless sintered HfB2-MoSi2 composite, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2009, vol. 29, pp. 1809–1815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2008.09.018
Justin, J.F. and Jankowiak, A., Ultra-high temperature ceramics: Densification, properties and thermal stability, Aerospace Lab, 2011, no. 3, pp. 1–11. https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01183657/.
Zimmermann, J.W., Hilmas, G.E., Fahrenholtz, W.G., Dinwiddie, R.B., Porter, W.D., and Wang, H., Thermophysical properties of ZrB2 and ZrB2-SiC ceramics, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2008, vol. 91, pp. 1405–1411. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2008.02268.x
Opila, E. and Levine, S., Oxidation of ZrB2- and HfB2-based ultra-high temperature ceramics: Effect of Ta additions, J. Mater. Sci., 2004, vol. 39, pp. 5969–5977. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSC.0000041693.32531.d1
Sayir, A., Carbon fiber reinforced hafnium carbide composite, J. Mater. Sci., 2004, vol. 39, pp. 5995–6003. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSC.0000041696.64055.8c
Levashov, E.A., Mukasyan, A.S., Rogachev, A.S., and Shtansky, D.V., Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis of advanced materials and coatings, Int. Mater. Rev., 2017, vol. 62, pp. 203–239. https://doi.org/10.1080/09506608.2016.1243291
Kurbatkina, V.V., Patsera, E.I., Levashov, E.A., and Timofeev, A.N., Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis of refractory boride ceramics (Zr,Ta)B2 with superior properties, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2018, vol. 38, pp. 1118–1127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.12.031
Licheri, R., Orrù, R., Musa, C., Locci, A.M., and Cao, G., Spark plasma sintering of ZrB2- and HfB2-based ultra-high temperature ceramics prepared by SHS, Int. J. Self-Propag. High-Temp. Synth., 2009, vol. 18, pp. 15–24. https://doi.org/10.3103/S106138620901004X
Licheri, R., Orrù, R., Musa, C., and Cao, G., Processing and characterization of Zr-, Hf- and Ta-based ultra-high temperature ceramics, Adv. Sci. Technol., 2010, vol. 65, pp. 118–123. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AST.65118
Orrù, R. and Cao, G., Comparison of reactive and non-reactive spark plasma sintering routes for the fabrication of monolithic and composite UHTC materials, Materials, 2013, vol. 6, no. 5, pp. 1566–1583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6051566
Musa, C., Licheri, R., Orrù, R., and Cao, G., Synthesis, sintering and oxidative behavior of HfB2–HfSi2 ceramics, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2014, vol. 53, pp. 9101–9108. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie4032692
Licheri, R., Musa, C., Orrù, R., and Cao, G., Influence of the heating rate on the in-situ synthesis and consolidation of ZrB2 by reactive spark plasma sintering, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2015, vol. 35, pp. 1129–1137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2014.10.039
Licheri, R., Musa, C., Orrù, R., Cao, G., Sciti, D., and Silvestroni, L., Bulk monolithic zirconium and tantalum diborides by reactive and non-reactive spark plasma sintering, J. Alloys Compd., 2016, vol. 663, pp. 351–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.12.096
Kurbatkina, V.V., Patsera, E.I., and Levashov, E.A., Combustion synthesis of ultra-high-temperature materials based on (Hf,Ta)B2. Part 1: The mechanisms of combustion and structure formation, Ceram. Int., 2019, vol. 45, no. 3, pp. 4067–4075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.10.113
Potanin, A.Yu., Pogozhev, Yu.S., Levashov, E.A., Novikov, A.V., Shvindina, N.V., and Sviridova, T.A., Kinetics and oxidation mechanism of MoSi2-MoB ceramics in the 600–1200°C temperature range, Ceram. Int., 2017, vol. 43, pp. 10478–10486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.05.093
Vorotilo, S., Potanin, A.Y., Iatsyuk, I.V., and Levashov, E.A., SHS of silicon-based ceramics for the high-temperature applications, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2018, vol. 20, article no. 1800200. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201800200
Vorotilo, S., Potanin, A.Yu., Pogozhev, Yu.S., Levashov, E.A., Kochetov, N.A., and Kovalev, D.Yu., Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis of advanced ceramics MoSi2–HfB2–MoB, Ceram. Int., 2019, vol. 45, no. 1, pp. 96–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.09.138
Samsonov, G.V. and Vinitskii, I.M., Tugoplavkie soedineniya (Refractory Compounds. Handbook), Moscow: Metallurgiya, 1976. http://libarch.nmu.org.ua/handle/GenofondUA/78485.
Shiryaev, A.A., Thermodynamic of SHS: Modern approach, Int. J. Self-Propag. High-Temp. Synth., 1995, vol. 4, pp. 351–362.
Bjrovinskaya, I.P., Gromov, A.A., Levashov, E.A., Maksimov, Yu.M., Mukasyan, A.S., and Rogachev, A.S., Concise Encyclopedia of Self-Propagated High-Temperature Synthesis, Elsevier, 2017.
Shelekhov, E.V. and Sviridova, T.A., Programs for X‑ray analysis of polycrystals, Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., 2000, no. 8, pp. 16–19.
Petrzhik, M.I. and Levashov, E.A., Modern methods for investigating functional surfaces of advanced materials by mechanical contact testing, Crystallogr. Rep., 2007, vol. 52, no. 6, pp. 966–974.
Lyakishev, N.P., Diagrammy sostoyaniya dvoinykh metallicheskikh system. Spravochnik (Dual Metal System Status Diagrams. Handbook), Moscow: Mashinostroyeniye, 1996. http://www.vixri.ru/?p=4635. Lyakishev, N.P., Diagrammy sostoyaniya dvoinykh metallicheskikh system. Spravochnik (State Diagrams of Binary Metal Systems. Handbook), Moscow: Mashinostroyeniye, 1996. http://www.vixri.ru/?p=4635.
Klopotov, A.A., Abzayev, Yu.A., Petrikova, E.A., Budovskikh, E.A., and Gromov, V.E., Electron-ion-plasma methods for nano-structuring surface layer of alloys based on titanium and aluminium, Materialy 10-oi Mezhdunarodnoi konferentsii “Vzaimodeystviye izluchenii s tverdym telom” (Minsk, Belarus’, 2013) (Proc. 10th Int. Conference “Interaction of Radiation with Solids”, Minsk, 2013), Minsk: Belarusian State Univ., 2013, pp. 254–259. http://elib.bsu.by/handle/123456789/48353.
Kurbatkina, V.V., Patsera, E.I., Smirnov, D.V., Levashov, E.A., Vorotilo, S., and Timofeev, A.N., Combustion synthesis of ultrahigh-temperature ceramics based on (Hf,Ta)B2. Part 2: Structure, mechanical and thermophysical properties of consolidated ceramics, Ceram. Int., 2019, vol. 45, pp. 4076–4083. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.10.165
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Cand. Tech. Sci. N.A. Kochetov for help in carrying out the study of combustion parameters, Dr. Tech. Sci. M.I. Petrzhik for assistance in measuring mechanical properties, and Senior Researcher S.I. Rupasov for help in carrying out experiments on HP and SPS.
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation as part of project no. 19-19-00117 “Conducting Fundamental Scientific Research and Exploratory Research by Individual Scientific Groups.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Translated by Sh. Galyaltdinov
About this article
Cite this article
Kurbatkina, V.V., Patsera, E.I., Smirnov, D.V. et al. Synthesis Features, Structure, and Properties of Promising High-Temperature Ceramics in the Hf–Ta–B–Ti–Si System. Russ. J. Non-ferrous Metals 61, 691–703 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1067821220060140
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1067821220060140