Abstract
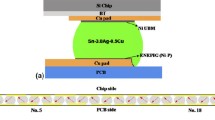
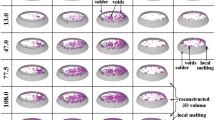
Eutectic PbSn flip chip solder joint was subjected to 5×103 A/cm2 current stressing at 150°C and 3.5 × 104 A/cm2 current stressing at 30°C. The under bump metallurgy (UBM) on the chip was sputtered Ni/Cu, and the substrate side was a thick Cu trace. It was shown through in-situ observation that the local temperature near the entrance of electrons from the Al interconnect to the solder became higher than the rest of the joint. The accelerated local Ni UBM consumption near the entrance was also observed. Once the Ni was consumed at a location, a porous structure formed, and the flow of the electrons was blocked there. It was found that the formation of the void and the formation of the porous structure were competing with each other. If the porous structure formed first, then the void would not be able to nucleate there. On the other hand, if the void could nucleate before the UBM above lost its conductivity, then the joint would fail by the void formation-and-propagation mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Brandenberg and S. Yeh,Proceedings of the 1998 Surface Mount International Conference and Exhibition (Edina, MN: SMTA, 1998), p. 337.
T.Y. Lee, K.N. Tu, and D.R. Frear,J. Appl. Phys. 90, 4502 (2001).
E.C.C. Yeh, W.J. Choi, K.N. Tu, P. Elenius, and H. Balkan,Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 580 (2002).
Y.C. Hu, Y.H. Lin, C.R. Kao, and K.N. Tu,J. Mater. Res. 18, 2544 (2003).
H. Ye, C. Basaran, and D. Hopkins,Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 1045 (2003).
H. Ye, C. Basaran, and D. Hopkins,Int. J. Solids Struct. 40, 4021 (2003).
W.J. Choi, E.C.C. Yeh, and K.N. Tu,J. Appl. Phys. 94, 5665 (2003).
J.W. Nah, K.W. Paik, J.O. Suh, and K.N. Tu,J. Appl. Phys. 94, 7560 (2003).
Y.C. Hsu, T.L. Shao, C.J. Yang, and C. Chen,J. Electron. Mater. 32, 1222 (2003).
T.L. Shao, K.C. Lin, and C. Chen,J. Electron. Mater. 32, 1278 (2003).
A.T. Wu, K.N. Tu, J.R. Lloyd, N. Tamura, B.C. Valek, and C.R. Kao,Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 2490 (2004).
K. Jung and H. Conrad,J. Mater. Sci. 39, 1803 (2004).
Y.H. Lin, C.M. Tsai, Y.C. Hu, Y.L. Lin, and C.R. Kao,J. Electron. Mater. 34, 27 (1985).
Y.H. Lin, C.M. Tsai, Y.C. Hu, Y.L. Lin, J.Y. Tsai, and C.R. Kao,Mater. Sci. Forum 475–479, 2655 (1985).
Y.H. Lin, Y.C. Hu, C.M. Tsai, C.R. Kao, and K.N. Tu,Acta Mater. 53, 2029 (1985).
D. Gupta, K. Vieregge, and W. Gust,Acta Mater. 47, 5 (1999).
K.N. Tu,J. Appl. Phys. 94, 5451 (2003).
W.C. Luo, C.E. Ho, J.Y. Tsai, Y.L. Lin, and C.R. Kao,Mater. Sci. Eng. A 396, 384 (1985).
C.M. Tsai, W.C. Luo, C.W. Chang, Y.C. Shieh, and C.R. Kao,J. Electron. Mater. 33, 1424 (2004).
Y.L. Lin, W.C. Luo, Y.H. Lin, C.E. Ho, and C.R. Kao,J. Electron. Mater. 33, 1092 (2004).
W.T. Chen, C.E. Ho, and C.R. Kao,J. Mater. Res. 17, 263 (2002).
C.E. Ho, L.C. Shiau, and C.R. Kao,J. Electron. Mater. 31, 1264 (2002).
C.E. Ho, Y.L. Lin, and C.R. Kao,Chem. Mater. 14, 949 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Y.L., Chang, C.W., Tsai, C.M. et al. Electromigration-induced UBM consumption and the resulting failure mechanisms in flip-chip solder joints. J. Electron. Mater. 35, 1010–1016 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02692561
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02692561