Abstract
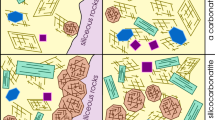
A primary carbonate phase with Ca/(Ca+Mg) in the range 0.85–0.95 has been identified in a metasomatized, depleted harzburgite nodule from Montana Clara Island, Canary Islands; textural relations show that this carbonate represents a quenched liquid. Although magnesian carbonate melts have been described from upper mantle peridotites, this is the first reported occurrence of a primary magma within peridotite nodules which has the composition of calciocarbonatite, by far the most common carbonatite type occurring in crustal complexes. The carbonate in the Montana Clara harzburgite host is restricted to wehrlitic alteration zones and is intimately associated with a second generation of minerals, mainly olivine, clinopyroxene and spinel, with glass of syenitic composition, and with Fe−Cu-rich sulphides. The metasomatic assemblage was formed by reaction of a sodiumbearing dolomitic melt, derived from a somewhat deeper level in the upper mantle, with the harzburgite mineral assemblage at a pressure of 15 kbars, or lower. As a result of the reaction the residual carbonatite melt became more enriched in calcium. The calciocarbonatite and sulphide phases almost invariably form globules in the silicate glass, indicating the existence of three immiscible liquids under upper mantle conditions. Several alkaline complexes contain carbonatites occurring with syenitic rock types and its seems feasible that the formation of such close associations might have been influenced by processes of liquid immiscibility which took place under upper mantle conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amundsen HEF (1987) Evidence for liquid immiscibility in the upper mantle. Nature 327:692–696.
Andrews E, Ebihara M (1982) Solar system abundances of elements. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 46:2363–2380.
Bailey DK (1993) Carbonate magmas. J Geol Soc London 150:637–651
Baker MB, Wyllie PJ (1990) Liquid immiscibility in a nephelinite-carbonate system at 25 kbar and implications for carbonatite origin. Nature 346:168–177
Barker DS, Nixon PH (1989) High-Ca, low-alkali carbonatite volcanism at Fort Portal, Uganda. Contrib Mineral Petrol 103:166–177
Bassard ET (1970) Crustal structure of western Canary island from seismic refraction and gravity data. J Geophys Res 75:4901–4918
Berg GW (1986) Evidence for carbonate in the mantle. Nature 324:50–51
Brenan JM, Watson EB (1991) Partitioning of trace elements between carbonate melt and clinopyroxene and olivine at mantleP-T conditions. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 55:2203–2214
Brey GP, Kohler T (1990) Geothermometry in four-phase Iherzolites. II. New thermobarometers and practical assessment of existing thermobarometers. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 31:1353–1378
Canil D (1990) Experimental study bearing on the absence of carbonate in mantle-derived xenoliths. Geology 18:1011–1013
Comin Chiaramonti P, Demarchi G, Girardi VAV, Princivalle F, Sinigoni S (1986) Evidence of mantle metasomatism and heterogeneity from peridotite inclusions of northeastern Brazil and Paraguay. Earth Planet Sci Lett 77:203–217
Dalton JA, Wood BJ (1993) The compositions of primary carbonate melts and their evolution through wallrock reactions in the mantle. Earth Planet Sci Lett 119:511–525
Dautria JM, Dupuy C, Takherist D, Dostal J (1992) Carbonate metasomatism in the lithospheric mantle: peridotitic xenoliths from a melilitic district of the Sahara basin. Contrib Mineral Petrol 111:31–52
Dawson JB (1962) Sodium carbonate lavas from Oldonyo Lengai, Tanganyika. Nature 195:1075–1076
Dernov-Pegarev VF, Malinin SD (1976) Calcite solubility in high temperature aqueous solutions of alkaline carbonatites and problems of carbonatite formation. Geochemie 5:643–657
Edgar AD, Lloyd FE, Forsyth DM, Barnett RL (1989) Origin of glass in upper mantle xenoliths from the Quaternary volcanics of Gees, West Eifel, Germany. Contrib Mineral Petrol 103:277–286
Eriksson SC (1989) Phalaborwa: a saga of magmatism, metasomatism, and miscibility. In: Bell K (ed) Carbonatites genesis and evolution. Unwin Hyman. London, pp 221–249
Freeston IC, Hamilton DL (1980) The role of liquid immiscibility in the genesis of carbonatites. Contrib Mineral Petrol 73:105–117
Green DH, Wallace ME (1988) Mantle metasomatism by ephemeral carbonatite melts. Nature 336:459–462
Hamilton DL, Kjarsgaard BA (1993) The immiscibility of silicate and carbonate liquids. S Afr J Geol 96:139–142
Hauri EN, Shimizu N, Dieu JJ, Hart SR (1993) Evidence for hotspot-related carbonatite metasomatism in the oceanic upper mantle. Nature 365:221–227
Ionov DA, Dupuy C, O'Reilly SY, Kopylova MG, Genshaft YS (1993) Carbonated peridotite xenoliths from Spitsbergen: implication for trace element signature of mantle carbonate metasomatism. Earth Planet Sci Lett 119:283–297
Ionov DA, Hofmann AW, Shimuzu NJ (1994) Metasomatism-induced melting in mantle xenoliths from Mongolia. J Petrol 35:753–785
Jones AP, Wyllie PJ (1986) Solubility of rare earth elements in carbonatite magmas, indicated by the liquidus surface in CaCo3−Ca(OH)2−La(OH)3 at 1 kbar pressure. Appl Geochem 1:95–102
Keller J (1989) Extrusive carbonatites and their significance. In: Bell K (ed) Carbonatites genesis and evolution. Unwin Hyman, London, pp 70–87
Kjarsgaard BA, Hamilton DL (1989) The genesis of carbonatites by immiscibility. In: Bell K (ed) Carbonatites genesis and evolution. Unwin Hyman, London, pp 388–404
Kogarko LN (1993) Geochemical characteristics of oceanic carbonatites from the Cape Verde Islands. S Afr J Geol 96:119–125
Kogarko LN, Plant DA, Henderson CMB, Kjarsgaard BA (1991) Na-rich carbonate inclusions in perovskite and calzirtite from the Guli intrusive Ca-carbonatite, polar Siberia. Contrib Mineral Petrol 109:124–129
Kogarko LN, Kononova VA, Orlova MP, Woolley AR (1995) Alkaline rocks and carbonatites of the world. 2. Former USSR. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 226
Koster van Groos AF (1975) The effect of high CO2 pressure on alkalic rocks and its bearing on the formation of alkalic ultrabasic rocks and the associated carbonatites. Am J Sci 275:163–185
Le Bas MJ (1984) Oceanic carbonatites. In: Kornprobst J (ed) Kimberlites I. Kimberlites and Related Rocks. (Development in Petrology, Vol IIA). Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 169–178
Lorand JP, Conquéré F (1983) Contribution a l'etude des sulfures dans les enclaves de lherzolite a spinelle des basaltes alcalins (Massif Central et Languedoc, France). Bull Mineral 106: 585–605
Maclean WH (1969) Liquidus phase relations in the FeS FeO Fe3O4−SiO2 system and their application in geology. Econ Geol 64:865–884
Mariano AN, Roeder PL (1983) Kerimasi: a neglected carbonatite volcano. J Geol 91:449–455
McGetchin TR, Besancon JR (1973) Carbonate inclusions in mantle derived pyropes. Earth Planet Sci Lett 18:408–410
Ngwenya BT, Bailey DK (1990) Kaluwe carbonatite, Zambia; an alternative to natrocarbonatite. J Geol Soc 147:213–216
Prins P (1981) The geochemical evolution of the alkaline and carbonatite complexes of the Damaraland Igneous Province, S.W. Africa Ann Univ Stellenbosch Ser Al Geol 3:145–278
Puustinen K (1969) The carbonatite of Siilinjarvi in the Precambrian of eastern Finland: a preliminary report. Lithos 3:89–92
Pyle JM, Haggerty SE (1994) Silicate-carbonate liquid immiscibility in upper-mantle eclogites: implications for natrosilicic and carbonatitic conjugate melts. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 58:2997–3011
Reid AM, Donaldson CH, Dawson BJ, Brown RW, Ridley WI (1975) The Igwisi Hills extrusive “kimberlite”. Phys Chem Earth 9:199–218
Robins B (1971) Syenite-carbonatite relationships in the Seiland Gabbro Province, Finnmark, northern Norway. Nor Geol Unders 272:43–58.
Rudnick RL, McDonough WF, Chappell BW (1993) Carbonatite metasomatism in the northern Tanzanian mantle: petrographic and geochemical characteristics. Earth Planet Sci Lett 114:463–475
Ryabchikov ID, Brey G, Kogarko LN, Bulatov VK (1989) Partial melting of carbonated peridotite at 50 kbar. Geokhimia 1:3–9
Schiano P, Clocchiatti R, Joron JL (1992) Melt and fluid inclusions in basalts and xenoliths from Tahaa Island, Society Archipelago: evidence for a metasomatised upper mantle. Earth Planet Sci Lett 111:69–82
Smith D (1987) Genesis of carbonate in pyrope from ultramafic diatremes on the Colorado Plateau, Southwestern United States. Contrib Mineral Petrol 97:389–396
Sweeney RJ, Green DH, Sie SH (1992) Trace and minor element partitioning between garnet and amphibole and carbonatitic melt. Earth Planet Sci Lett 113:1–14
Thibault Y, Edgar AD, Lloyd FE (1992) Experimental investigation on melts from a carbonated phlogopite lherzolite: implications from metasomatism in the continental lithospheric mantle. Am Mineral 77:784–794
Tredoux M, de Wit MJ, Hart RJ, Armstrong RA, Lindsay NNM, Sellschop JPF (1989) Platinum group elements in a 3.5 Ga mickel-iron occurrence: possible evidence of deep mantle origin. J Geophys Res 94B:795–813
Wallace ME, Green DH (1988) An experimental determination of primary carbonatite magma composition. Nature 335: 343–346
Wood BJ, Bryndzya LT, Johnsen KE (1990) Mantle oxidation state and its relationship to tectonic environment and fluid speciation. Science 248:337–345
Wyllie PJ (1978) Mantle fluid composition buffered in peridotite-CO2−H2O by carbonates, amphibole, and phlogopite. J Geol 86:687–713
Wyllie PJ (1989) Origin of carbonatites: evidence from phase equilibrium studies. In: Bell K (ed) Carbonatites genesis and evolution. Unwin Hyman, London, pp 500–540
Wyllie PJ, Huang WL (1976) Carbonation and melting reaction in the system CaO MgO−SiO2−CO2 at mantle pressure with geophysical and petrological application. Contrib Mineral Petrol 54:79–107
Yaxley GM, Crawford AJ, Green DH (1991) Evidence for carbonatite metasomatism in spinel peridotite xenoliths from Western Victoria, Australia. Earth Planet Sci Lett 107:305–317
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: I. Parsons
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kogarko, L.N., Henderson, C.M.B. & Pacheco, H. Primary Ca-rich carbonatite magma and carbonate-silicate-sulphide liquid immiscibility in the upper mantle. Contr. Mineral. and Petrol. 121, 267–274 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02688242
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02688242