Abstract
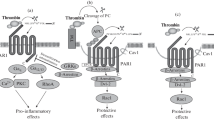
Aquaporin 4 (AQP4) is a key molecule for maintaining water balance in the central nervous system, and its dysfunction might cause brain edema. However, little is known about the regulation of AQP4 expression. Because thrombin has been implicated in brain edema formation, the purpose of this study is to determine whether thrombin affects expression of AQP4 in astrocytes. Here, the effect of thrombin on AQP4 expression in vitro was evaluated using Western blot analysis and RT-PCR. Meanwhile, we investigated whether the effect of thrombin on AQP4 expression was due to protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR-1). In addition, we examined the role of protein kinase C (PKC) in the effect of thrombin on AQP4 expression using Western blot analysis. We found that thrombin did not affect cell viability at concentrations of 0.05, 0.5, 5, or 50 nM but killed astrocytes at concentrations of 500 nM, with approx 72% of astrocytes surviving at 500 nM thrombin. Our data showed that AQP4 protein expression achieved only 28% of controls in 500 nM thrombin treatment, even if astrocytes survived approx 72% of controls at 500 nM thrombin. Thrombin significantly inhibited AQP4 in a time-and dose-dependent manner in vitro (p<0.05). Cathepsin-G, a thrombin PAR-1 inhibitor, reversed significantly (p<0.05) the effect of thrombin on AQP4 mRNA and protein expression in astrocytes. We also observed that PKC inhibitor H-7 or prolonged pretreatment with TPA can rapidly increase AQP4 expression (p<0.05). Thrombin might inhibit AQP4 expression in rat astrocytes, and this effect is possibly mediated by the PKC pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cavanaugh K. P., Gurwitz D., Cunningham D. D., and Bradshaw R. A. (1990) Reciprocal modulation of astrocyte stellation by thrombin and proteasenexin-1. J. Neurochem. 54, 1735–1743.
Coughlin R. S. (2000) Thrombin signalling and proteaseactivated receptors. Nature 407, 258–264.
Grand R. J. A., Tumell A. S., and Grabham P.W. (1996) Cellular consequences of thrombin-receptor activation. Biochem. J. 313, 353–368.
Gurwitz D. and Cunningham D. D. (1988) Thrombin modulates and reverses neuroblastoma neurite out-growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 85, 3440–3444.
Han Z., Wax M. B., and Patil R. V. (1998) Regulation of aquaporin-4 water channels by phorbolester-dependent protein phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 6001–6004.
Jung J. S., Bhat R. V., Preston G. M., Guggino W.B., Baraban J. M., and Agre P. (1994) Molecular characterization of an aquaporin cDNA from brain: candidate osmoreceptor and regulator of water balance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 91, 13,052–13,056.
Kataoka H., Joh T., Kasugai K., Okayama N., Moriyama A., Asai K., and Kato T. (1998) Expression of mRNA for heregulin and its receptor, ErbB-3 and ErbB-4, in human upper gastrointestinal mucosa. Life Sci. 63, 553–564.
Lee K. R., Kawai N., Kim S., Sagher O., and Hoff J. T. (1997) Mechanisms of edema formation after intracerebral hemorrhage: effects of thrombin on cerebral blood flow, blood-brain barrier permeability, and cell survival in a rat model. J. Neurosurg. 86, 272–278.
Manley G. T., Fujimura M., Ma T., Noshita N., Filiz F., Bollen A.W., et al. (2000) Aquaporin-4 deletion in mice reduces brain edema after acute water intoxication and ischemic stroke. Nat. Med. 61, 59–163.
Masada T., Xi G., Hua Y., and Keep R. F. (2000) The effects of thrombin preconditioning on focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 867, 173–179.
Muro H., Waguri-Nagaya Y., Mukofuiiwara Y., Iwahashi T., Otsuka T., Matsui, N., et al. (1999) Autocrine induction of gliostatin/platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor (GLS/PD-ECGF) and GLS-induced expression of matrix metaloproteinases in rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford) 38, 1195–1202.
Nakahama K., Nagano M., Fujioka A., Shinoda K., and Sasaki H. (1999) Effect of TPA on aquaporin 4 mRNA expression in cultured rat astrocytes. Glia 25, 240–246.
Neveu I., Jehan F., Jandrot-Perrus M., Wion D., and Brachet P (1993) Enhancement of the synthesis and secretion of nerve growth factor in primary cultures of glial cells by proteases: a possible involvement of thrombin. J. Neurochem. 60, 858–867.
Nicole O., Goldshmidt A., Hamill C. E., Sorensen S. D., Sastre A., Lyuboslavsky P., et al. (2005) Activation of protease-activated receptor-1 triggers as trogliosis after brain injury. J. Neurosci. 25, 4319–4329.
Nudel U., Zakut R., Shani M., Neuman S., Levy Z., and Yaffe D. (1983) The nucleotide sequence of the rat cytoplasmic beta-actin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 11, 1759–1771.
Ohyama H., Hosomi N., Takahashi T., Mizushige K., and Kohno M. (2001) Thrombin inhibition attenuates neurodegeneration and cerebral edema formation following transient forebrain ischemia. Brain Res. 902, 264–271.
Papadopoulos M. C., Manley G.T., Krishna S., and Verkman A. S. (2004) Aquaporin-4 facilitates reabsorption of excess fluid in vasogenic brain edema. FASEB J. 18, 1291–1293.
Renesto P., Si-Tahar M., Moniatte M., Balloy V., Van Dorsselaer A., Pidard D., and Chignard M. (1997) Specific inhibition of thrombin-induced cell activation by the neutrophil proteinases elastase, cathepsin G, and proteinase 3: evidence for distinct cleavage sites within the aminoterminal domain of the thrombin receptor. Blood 89, 1944–1953.
Saadoun S., Papadopoulos M. C., Davies D. C., Krishna S., and Bell B. A. (2002) Aquaporin-4 expression is increased in oedematous human brain tumours. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 72, 262–265.
Sun M. C., Honey C. R., Berk C., Wong N. L., and Tsui J. K. (2003) Regulation of aquaporin-4 in a traumatic brain injury model in rats. J. Neurosurg. 98, 565–569.
Tanaka C. and Nishizuka Y. (1994) The protein kinase C family for neuronal signaling. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 17, 551–567.
Tanaka J., Toku K., Zhang B., Ishihara K., Sakanaka, M., and Maeda N. (1999) Astrocytes preventneuronal death induced by reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Glia 28, 85–96.
Vaughan P. J., Pike C. J., Cotman C.W., and Cunningham D. D. (1995) Thrombin receptor activation protects neurons and astrocytes from cell death produced by environmental insults. J. Neurosci. 15, 5389–5401.
Vergnolle N. (2000) Proteinase-activated receptors—novel signals for gastrointestinal pathophysiology (Review). Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 14, 257–266.
Wang H. and Resier G. (2003) The role of the Ca-sensitive tyrosine kinase Pyk2 and Src in thrombin signalling in rat astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 84, 1349–1357.
Wang H., Ubl J. J., and Reiser G. (2002a) The four subtypes of protease-activated receptors, co-expressed in rat astrocytes, evoke different physiological signaling. Glia 37, 53–63.
Wang H., Ubl J. J., Stricker R., and Resier G. (2002b) Thrombin (PAR-1)-induced proliferation in astrocytes via MAPK involves multiple signaling pathways. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 283, 1351–1364.
Yajun J., Jimin W., Ya H., et al. (2002) Thrombin-receptor activation and thrombin-induced brain tolerance. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 22, 404–410.
Yamamoto N., Sobue K., Miyachi T., Inagaki M., Miura Y., Katsuya H., and Asai K. (2001a) Differential regulation of aquaporin expression in astrocytes by protein kinase C. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 95, 110–116.
Yamamoto N., Yoneda K., Asai K., Sobue K., Tada T., Fujita Y., et al. (2001) Alterations in the expression of the AQP family in cultured rat astrocytes during and reoxygenation. Mol. Bran Res. 90, 26–38.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Y., Cai, D. & Chen, Y. Thrombin inhibits aquaporin 4 expression through protein kinase C-dependent pathway in cultured astrocytes. J Mol Neurosci 31, 83–93 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02686120
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02686120