Abstract
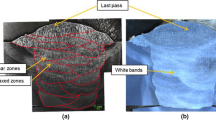
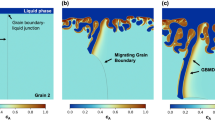
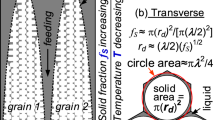
Grain-boundary liquation occurs in the weld heat-affected zone (HAZ) of the Ni-base superalloy 718 at locations where the peak temperatures are greater than about 1200 ‡C. The evolution of the grain structure at these HAZ locations depends upon the interaction between the grains and the grain-boundary liquid. The evolution of grain structure in the presence of grain-boundary liquid was simulated by subjecting samples to controlled thermal cycles using resistance heating. A measurement of grain size as a function of isothermal hold at two peak temperatures of 1200 ‡C and 1227 ‡C indicated that in alloy 718, the kinetics of grain growth depended upon the prior thermal history of the alloy. In the solution-treated alloy, the presence of grain-boundary liquid did not arrest grain growth at either peak temperature. In the homogenized and aged alloy, a grain refinement was observed at the peak temperature of 1227 ‡C, while an arrest of grain growth was observed at a peak temperature of 1200‡C. Liquid film migration (LFM) and subgrain coalescence, either acting alone or simultaneously, are shown to explain most of the observed microstructural phenomena and the kinetics of grain growth in the alloy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.J. Pepe and W.F. Savage:Welding Journal, 1967, vol. 46, pp. 411~s-422~s.
W.A. Owczarski, D.S. Duvall, and C.P. Sullivan:Welding Journal, 1967, vol. 46, pp. 423~s-432~s.
B. Weiss, G.E. Grotke, and R. Stickler:Welding Journal, 1970, vol. 49, pp. 471~s-487~s.
J.A. Brooks:Welding Journal, 1974, vol. 53, pp. 517~s-523~s.
W.A. Baeslack III, S.J. Savage, and F. Froes:Journal of Materials Science Letters, 1986, pp. 935–39.
A.D. Romig, Jr., J.C. Lippold, and M.J. Cieslak:Metall. Trans. A, 1988, vol. 19A, pp. 35–50.
J.J. Pepe and W.F. Savage:Welding Journal, 1970, vol. 49, pp. 545~s-553~s.
B. Radhakrishnan and R.G. Thompson:Metall. Trans. A, 1992, vol. 23A, pp. 1783–99.
I.A. Aksay, C.E. Hoge, and J.A. Pask:J. Phys. Chem., 1974, vol. 78, pp. 1178–83.
T.P. Isaac, M. Dollar, and T.B. Massalski:Metall. Trans. A, 1988, pp. 675–86.
D. McLean:Grain Boundaries in Metals, Oxford University Press, London, 1957.
E.D. Hondros and M.P. Seah:Intl. Metals Rev., 1977, vol. 22, pp. 262–301.
J.C. Lippold:Welding Journal, Jan. 1983, vol. 62, pp. ls-lls.
D.N. Yoon:Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci., vol. 19, 1989, pp. 43–58.
C.A. Handwerker: inDiffusion Phenomena in Thin Films and Microelectronic Materials, D. Gupta and P.S. Ho, eds., Noyes Publications, New Jersey, U.S.A.
M. Hillert:Scripta Metall., 1983, vol. 17, pp. 237–40.
R.G. Thompson and S. Genculu:Welding Journal, Dec. 1983, vol. 62 (12), pp. 337s-345s.
W.A. Baeslack III and D.E. Nelson:Metallography, 1986, vol. 19, pp. 371–79.
P.J. Valdez and J.B. Steinman:Effect of Minor Elements on the Weldability of High-nickel Alloys, Welding Research Council, New York, 1969, pp. 93–120.
E.G. Thompson:Welding Journal, Feb. 1969, vol. 48 (2), pp. 70s-79s.
T.J. Kelly: Trends in Welding Research, ASM, 1986.
B. Radhakrishnan and R.G. Thompson:Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 887–902.
B. Radhakrishnan and R.G. Thompson:Metall. Trans. A, 1993, vol. 24A, pp. 1409–22.
B. Radhakrishnan and R.G. Thompson:Scripta Metall. 1990, vol. 24, pp. 537–42.
J.G. Byrne:Recovery, Recrystallization and Grain Growth, Macmillan Co., New York, 1965.
G. Muralidharan: Masters Thesis, University of Alabama at Birmingham, 1988.
D.J. Srolovitz, G.S. Grest, and M.P. Anderson:Acta Metall., 1985, vol. 33, pp. 2233–47.
N.A. Wilkinson: inSuperalloy 718: Metallurgy and Applications, E.A. Loria, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1989, pp. 119–33.
J.L. Burger, R.R. Biederman, and W.H. Couts: inSuperalloy 718: Metallurgy and Applications, E.A. Loria, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1989, pp. 207–17.
J.C.M. Li:J. Appl. Phys., 1962, vol. 33, p. 2958.
R.M. German:Liquid Phase Sintering, Plenum Press, New York, 1985, pp. 133–43.
C. Boucher, D. Varela, M. Dadian, and H. Granjon:Revue de Metallurgie, Dec. 1976, pp. 817-31.
T. Muschik, W.A. Kaysser, and T. Hehenkamp:Acta Metall., 1989, vol. 37, pp. 603–13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Formerly Research Associate, with the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Radhakrishnan, B., Thompson, R.G. Kinetics of grain growth in the weld heat-affected zone of alloy 718. Metall Trans A 24, 2773–2785 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02659501
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02659501