Abstract
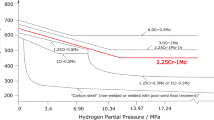
Four normalized carbon steels made in different ways (Si-killed, Al-killed, REM-treated, and electroslag refined) were studied to determine the role of differing fine inclusions on the early stages of hydrogen attack (HA). Hydrogen exposures were made at 450°C (6.5 MPa) and 375°C (7.6 MPa). The first stage of HA is shown to be the development of a closely spaced (1 to 2 µm) array of small bubbles over the ferrite/pearlite, or occasionally the ferrite/ferrite boundaries. These bubbles grew together to form tears, primarily in the rolling plane, leading to more rapid expansion normal to this plane than parallel to it. Fracture planes followed high solute layers in banded steel but only rarely if ever did the fine bubbles form on inclusions. At 450°C REM-treated steel was attacked the fastest and Al-killed steel required exposures two to four times as long for attack.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. G. Shewmon:Met. Trans. A, 1976, vol. 7A, pp. 279–86.
R. E. Allen, R. J. Jansen, P. C. Rosenthal, and F. H. Vitovec:Proc. API, 1962, vol. 42, pp. 452–62.
H. M. Shih and H. H. Johnson:Scripta Met., 1977, vol. II, pp. 151–54.
Steels for Hydrogen Service at Elevated Temperatures and Pressures in Petroleum Refineries and Petrochemical Plants, API Publ. 941, 2nd ed., June 1977.
H. G. Nelson and R. D. Moorhead: ASTM STP 600, pp. 88–96, ASTM Publication, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, 1976.
C. R. Levart:Popular Electronics, Aug. 1976, vol. 10, pp. 46–7.
L. C. Weiner:Corrosion, 1961, vol. 17, pp. 137–43.
R. T. Ratcliffe:Brit J. Appl. Phys., 1965, vol. 16, pp. 1193–96.
A. A. Sagües, B. Okray Hall and H. Wiedersich: Scripta Met. 1978, vol. 12, pp. 319–326.
H. A. Wriedt and Hsun Hu:Met Trans. A, 1976, vol. 7A, pp. 711–18.
J. W. Flowers and S. P. Karas:J. Appl. Phys., 1967, vol. 38, pp. 1085–86.
R. Kiessling:Nonmetallic Inclusions in Steel, 2nd ed., Part III, pp. 4–7, The Metals Soc, London, 1978.
D. A. Westphal and F. J. Worzala inHydrogen in Metals, ASM, 1974, pp. 78–89.
M. Hasegawa and S. Nomura: J. Iron Steel Inst. Jap., vol. 17, 1977, pp. 187–93.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
formerly Graduate Student at Ohio State University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pishko, R., McKimpson, M. & Shewmon, P.G. The effect of steelmaking on the hydrogen attack of carbon steel. Metall Trans A 10, 887–894 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02658308
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02658308