Abstract
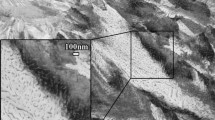
The bainite transformation at 723 K in an Fe-2 pct Si-0.6 pct C alloy (mass pct) was investigated with transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and quantitative metallography to clarify the growth mechanism of the ferritic component of bainite. In early stages of transformation, the bainitic ferrite was carbide free. The laths of bainitic ferrite within a packet were parallel to one another and separated by carbon-enriched retained austenite. The average carbon concentration of the bainitic ferrite was estimated to be 0.19 mass pct at the lowest, indicating that the ferrite was highly supersaturated with respect to carbon. The laths did not thicken during the subsequent isothermal holding, although they were in contact with austenite of which the average carbon concentration was lower than the paraequilibrium value. In the later stage of transformation, large carbide plates formed in the austenite between the laths, resulting in the decrease in the carbon concentration of the austenite. Subsequently, the ferrite with a variant different from the initially formed ferrite in the packet was decomposed for the completion of transformation. The present results indicate that the bainitic ferrite develops by a displacive mechanism rather than a diffusional mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.I. Aaronson:Inst. Met., Monogr., 1969, vol. 33, pp. 270–81.
H.K. Hehemann, K.R. Kinsman, and H.I. Aaronson:Metall. Trans., 1972, vol. 3, pp. 1077–94.
J.W. Christian and D.V. Edmonds: inInt. Conf. on Phase Transformation in Ferrous Alloys, A.R. Marder and J.I. Goldstein, eds., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1984, pp. 293–325.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia and J.W. Christian:Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 767–97.
H.I. Aaronson, W.T. Reynolds,Jr., G.J. Shiflet, and G. Spanos:Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21A, pp. 1343–80.
R.F. Hehemann and A.R. Troiano:Trans. AIME, 1954, vol. 200, pp. 1272–80.
J.M. Oblak and R.F. Hehemann:Transformation and Hardenability in Steels, Climax Molybdenum Co., Ann Arbor, MI, 1967, pp. 15–30.
R. Le Houillier, G. Begin, and A. Dube:Metall. Trans., 1971, vol. 2, pp. 2645–53.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia and D.V. Edmonds:Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 895–907.
B.P.J. Sandvik:Metall. Trans. A, 1982, vol. 13A, pp. 777–87; 789-800.
U.K. Tsuzaki, C. Nakao, and T. Maki:Mater. Trans. JIM, 1991, vol. 32, pp. 658–66.
L. Zwell R.C.:quoted by Ruhl and Morris Cohen:Trans. TMS- AIME, 1969, vol. 245, pp. 241–51.
L. Cheng, A. Bottger, Th.H. de Keijser, and E.J. Mittemeijer:Scripta Metall. Mater., 1990, vol. 24, pp. 509–14.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, S.A. David, J.M. Vitek, and R.W. Reed:Mater. Sci. Technol., 1991, vol. 7, pp. 686–98.
W.T. Reynolds Jr., S.K. Liu, F.Z. Li, S. Hartfield, and H.I. Aaronson:Metall. Trans. A, 1990, vol. 21 A, pp. 1479–91.
M. Hillert and L.I. Staffansson:Acta Chem. Scand., 1970, vol. 24, pp. 3618–26.
B. Uhrenius: in Hardenability Concepts with Applications to Steel, V.D. Doane and J.S. Kirkaldy, eds., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1978, pp. 28-81.
M. Enomoto:Metall. Trans. A, 1989, vol. 20A, pp. 332–33.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia and A.R. Waugh:Acta Metall., 1982, vol. 30, pp. 775–84.
I. Stark, G.D.W. Smith, and H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia:Int. Conf. on Solid-Solid Phase Transformations, Institute of Metals, London, 1988, pp. 211–15.
B. Josefsson and H.-O. Adren:Mater. Sci. Technol., 1991, vol. 7, pp. 849–51.
W.T. Reynolds, Jr., S.S. Brenner, and H.I. Aaronson:Scripta Metall., 1988, vol. 22, pp. 1343–48.
K.W. Andrews:J. Iron Steel Inst., 1965, vol. 203, pp. 721–27.
S.J. Matas and R.F. Hehemann:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1961, vol. 221, pp. 179–85.
J.M. Rigsbee and H.I. Aaronson:Acta Metall., 1979, vol. 27, pp. 365–76.
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia:Scripta Metall., 1983, vol. 17, pp. 1475–79.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Formerly Graduate Student, Kyoto University, Kyoto 606-01, Japan
This article is based on a presentation made at the Pacific Rim Conference on the “Roles of Shear and Diffusion in the Formation of Plate-Shaped Transformation Products,” held December 18-22, 1992, in Kona, Hawaii, under the auspices of ASM INTERNATIONAL’S Phase Transformations Committee.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsuzaki, K., Kodai, A. & Maki, T. Formation mechanism of bainitic ferrite in an Fe-2 Pct Si-0.6 Pct C alloy. Metall Mater Trans A 25, 2009–2016 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02649049
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02649049