Abstract
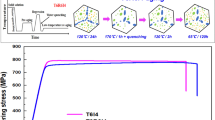
A study has been made of the effect of Ti additions on the microstructure in two stage and single stage aging of an Al-5 Zn-2 Mg alloy. The influence of aging treatment was examined for alloys with and without Ti addition. The alloys were solution heat treated at 510°C, air cooled then aged at various temperatures below the GP zone solvus for short times before aging above the GP zone solvus at 200°C. The Ti addition alloy yields a small precipitate free zone (PFZ ∼ 0.3 μ) and a higher density of precipitate near the edge of the PFZ than in the midgrain region. The ternary alloy without Ti addition produces a wide range of PFZ sizes (0.4 to 4 μ) depending upon the aging temperature below the GP zone solvus. Significant changes in the morphology of the matrix precipitate, the amount of grain boundary precipitate, and the width of the PFZ, were observed in single stage aging at 200°C as a result of the Ti addition. These results could be explained in terms of Ti interacting with vacancies or solute atoms, causing the changes in the vacancy and/or solute concentration profiles. A model based upon solute and vacancy concentrations coupled with a time at temperature effect has been developed to allow the interpretation of the observed two-stage aging results in an Al-Zn-Mg alloy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Thomas and J. Nutting:J. Inst. Metals, 1959-60, vol. 88, p. 81.
J. L. Taylor:J. Inst. Metals, 1963-64, vol. 92, p. 301.
J. D. Ebury and R. B. Nicholson:Acta Met., 1965, vol. 13, p. 403.
P. N. T. Unwin, G. W. Lorimer, and R. B. Nicholson:Acta Met, 1969, vol. 17, p. 1363.
D. W. Pashley, M. H. Jacobs, and J. T. Vietz:Phil. Mag., 1967, vol. 16, p. 51.
G. W. Lorimer and R. B. Nicholson:Acta Met., 1966, vol. 14, p. 1009.
C. A. Gove and G. Judd:Met. Trans., 1973, vol. 4, p. 1023.
J. J. Polmear:J. Inst. Metals, 1958-59, vol. 87, p. 24.
C. R. Shastry and G. Judd:Met.Trans., 1971, vol. 2, p. 3283.
M. H. Jacobs and D. W. Pashley:The Mechanism of Phase Transformations in Crystalline Solids, pp. 43–48, The Institute of Metals, London, 1969.
W. F. Smith and N. J. Grant:Trans. ASM, 1969, vol. 62, p. 724.
M. Doyama:Phys. Lett., 1966, vol. 21, no. 4, p. 395.
P. Doig and J. W. Edington:Met. Trans. A, 1975, vol. 6A, no. 4, p. 943.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Formerly Graduate Research Assistant, Materials Engineering, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, New York.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Judd, G. Microstructure study on the effect of titanium in the aging treatment of an Al-Zn-Mg alloy. Metall Trans A 9, 553–559 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02646412
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02646412