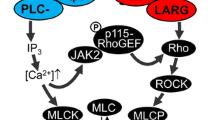
Summary
Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), an ubiquitous regulatory peptide, has diverse effects on the differentiation and behavior of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC). However, the molecular mechanism through which TGF-α exerts its effects remains obscure. We investigated the phosphoinositide/protein kinase C [PKC] signaling pathway in the action of TGF-β on cultured embryonic avian VSMC of differing lineage: a) thoracic aorta, derived from the neural crest; and b) abdominal aorta, derived from mesenchyme. The second messenger responsible for activation of PKC is sn-1,2-diacylglycerol [DAG]; TGF-β increased the mass amounts of DAG in the membranes of neural crest-derived VSMC concurrent with translocation of PKC from the soluble to the membrane fraction, but TGF-β had no effect on the DAG or PKC of mesenchyme-derived VSMC. TGF-β potentiated the growth of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-treated, neural crest-derived VSMC; but abolished PDGF-induced growth of mesenchymal cells. It is concluded that molecular and functional responses of VSMC to TGF-β are heterogeneous and are functions of the embryonic lineage of the VSMC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Latif, A. A.; Akhtar, R. A.; Hawthorne, J. N. Acetylcholine increases the breakdown of triphosphoinositide of rabbit iris muscle prelabelled with (32P) phosphate. Biochem. J. 162:61–73; 1977.
Ames, B.; Dubin, D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 235:769–775; 1960.
Beall, A. C.; Rosenquist, T. H. Smooth muscle cells of neural crest origin form the aorticopulmonary septum in the avian embryo. Anat. Rec. 226:360–366; 1990.
Bradford, M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248–254; 1976.
Bell, L.; Madri, J. A. Effect of platelet factors on migration of cultured bovine aortic endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Circ. Res. 65:1057–1065; 1989.
Castellot, J. J., Jr.; Pukac, L. A.; Caleb, B. L., et al. Heparin selectively inhibits a protein kinase C-dependent mechanism of cell cycle progression in calf aortic smooth muscle cells. J. Cell Biol. 109:3147–3155; 1989.
Chambard, J.-C.; Pouyssegur, J. TGF-β inhibits growth factor-induced DNA synthesis in hamster fibroblasts without affecting the early mitogenic events. J. Cell. Physiol. 135:101–107; 1988.
Chen, J-K.; Hoshi, H.; McKeehan, W. L. Transforming growth factor type β specifically stimulates synthesis of proteoglycan in human adult arterial smooth muscle cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:5287–5291; 1987.
Cotran, R. S.; Kumar, V.; Robbins, S. L. In: Robbins’ Pathologic Basis of Disease, 4th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1989:553–597.
Foster, J. A. Synthesis of soluble and insoluble elastins in cultures of chick aortic cells. Lab. Invest. 58:667–673; 1988.
Goodman, L. V.; Majack, R. A. Vascular smooth muscle cells express distinct TGF-beta receptor phenotypes as a function of cell density in culture. J. Biol. Chem. 264:5241–5244; 1989.
Griendling, K. K.; Rittenhouse, S. E.; Brock, T. A., et al. Sustained diacylglycerol formation from inositol phospholipids in angiotensin II-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 261:5901–5906; 1986.
Guerrin, M.; Darbon, J. M.; Guilbaud, N., et al. Transforming growth factor beta reverses phorbol diester resistance of a breast adenocarcinoma (MCF-7) subline. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 166:687–694; 1990.
Haller, H.; Smallwood, J.; Rasmussen, H. Protein kinase C translocation in intact vascular smooth muscle strips. Biochem. J. 270:375–381; 1990.
Hedin, U.; Bottger, B. A.; Forsberg, E., et al. Diverse effects of fibronectin and laminin on phenotypic properties of cultured arterial smooth muscle cells. J. Cell Biol. 107:307–320; 1988.
Heine, U. L.; Munoz, E. F.; Flanders, K. C., et al. Role of transforming growth factor-beta in the development of the mouse embryo. J. Cell Biol. 105:2861–2826; 1987.
Hill, D. J.; Strain, A. J.; Elstow, S. F., et al. Bi-functional action of transforming growth factor-beta on DNA synthesis in early passage human fetal fibroblasts. J. Cell. Physiol. 128:322–328; 1986.
Kawahara, Y.; Kariya, K.; Fukumoto, Y., et al. Protein kinase C as both positive and negative regulator for proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. IARC (Int. Agency Res. Cancer) Sci. Publ. 92:102–117; 1988.
Kojima, I.; Kojima, K.; Rasmussen, H. Role of calcium and cAMP in the action of adrenocorticotropin on aldosterone secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 260:4248–4256; 1985.
Kojima, S.; Harpel, P. C.; Rifkin, D. B. Lipoprotein (a) inhibits the generation of transforming growth factor beta: an endogenous inhibitor of smooth muscle cell migration. J. Cell Biol. 113:1439–1445; 1991.
LiLievre, C. S.; LeDouarin, N. M. Mesenchymal derivatives of the neural crest: analysis of chimeric quail and chick embryos. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 34:125–154; 1975.
Libby, J.; Martinez, R.; Weber, M. J. Tyrosine phosphorylation in cells treated with transforming growth factor-β. J. Cell. Physiol. 129:159–166; 1986.
Madri, J. A.; Kocher, O.; Merwin, J. R., et al. Interactions of vascular cells with transforming growth factors-β. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 593:243–258; 1990.
Majack, R. A. Beta-type transforming growth factor specifies organizational behavior in vascular smooth muscle cell cultures. J. Cell. Biol. 105:465–471; 1987.
Massague, J.; Cheifetz, S.; Boyd, F. T., et al. TGF-β receptors and TGF-β binding proteioglycans: recent progress in identifying their functional properties. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 593:59–72; 1990.
Nishizuka, Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature 308:693–698; 1984a.
Nishizuka, Y. Turnover of inositol phospholipids and signal transduction. Science 225:1365–1370; 1984b.
Potts, J. D.; Runyan, R. B. Epithelial-mesenchymal cell transformation in the embryonic heart can be mediated, in part, by transforming growth factor-beta. Dev. Biol. 134:392–401; 1989.
Preiss, J.; Loomis, C. R.; Bishop, W. R., et al. Quantitative measurement of sn-1,2-diacylglycerols present in platelets, hepatocytes and ras- and sis-transformed normal rat kidney cells. J. Biol. Chem. 261:8597–8600; 1986.
Roberts, A. B.; Anzano, M. A.; Lamb, L. C., et al. New class of transforming growth factors potentiated by epidermal growth factor: isolation from non-neoplastic tissue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:119–123; 1981.
Robertson, P. L.; Markovac, J.; Datta, S. C., et al. Transforming growth factor beta stimulates phosphoinositol metabolism and translocation of protein kinase C in cultured astrocytes. Neurosci. Lett. 93:107–113; 1988.
Rosenquist, T. H.; Beall, A. C. Elastogenic cells in the developing cardiovascular system: smooth muscle, nonmuscle, and cardiac neural crest. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 588:106–119; 1990.
Rosenquist, T. H.; Fray-Gavalas, C. A.; Waldo, K., et al. Development of the musculoelastic septation complex in the avian truncus arteriosus. Am. J. Anat. 180:339–356; 1990.
Ross, R. Endothelial injury and atherosclerosis. In: Simionescu, N.; Simionescu, M., eds. Endothelial cell biology in health and disease. New York: Plenum Press; 1988:371–384.
Russell, S. B.; Trupin, K. M.; Rodriguez-Eaton, S., et al. Reduced growth-factor requirement of keloid-derived fibroblasts may account for tumor growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:587–591; 1988.
Sporn, M. B.; Roberts, A. B. Peptide growth factors are multifunctional. Nature 332:217–219; 1988.
Sunako, M.; Kawahara, Y.; Hirata, K., et al. Mass analysis of 1,2-diacylglycerol in cultured rabbit vascular smooth muscle cells. Hypertension 15:84–88; 1990.
Wakefield, L. M.; Smith, D. M.; Masui, T., et al. Distribution and modulation of the cellular receptor for transforming growth factor beta. J. Cell Biol. 105:965–975; 1987.
Wooten, M. W.; Wrenn, R. W. Redistribution of phospholipid/calcium-dependent protein kinase and altered phosphorylation of its soluble and particulate substrate proteins in phorbol ester-treated rat pancreatic acini. Cancer Res. 45:3912–3917; 1985.
Wrenn, R. W.; Barrow, M. A.; Redmond, M. E. Protein kinase C in developing chick heart: selective localization to atrium versus ventricle and changes in activity levels during cardiogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 972:110–112; 1988.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wrenn, R.W., Raeuber, C.L., Herman, L.E. et al. Transforming growth factor-beta: Signal transduction via protein kinase C in cultured embryonic vascular smooth muscle cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol - Animal 29, 73–78 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02634374
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02634374