Abstract
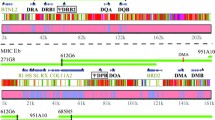
Evolutionary studies of complement factor B (Bf) and C2 in lower vertebrates have revealed the presence of the Bf/C2 common ancestor-like molecule in lamprey (cyclostome) and the Bf molecule encoded by the duplicated genes closely linked to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) inXenopus (amphibian). To further define whenBf/C2 gene duplication occurred and when linkage between theBf/C2 gene and theMHC was established, we amplified theBf/C2 sequences in teleost, the Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes), by reverse transcription—polymerase chain reaction with primers corresponding to the common amino acid sequences shared by mammalian Bf and C2. Only a single molecular species has been amplified, and the corresponding cDNA clones were isolated from the liver cDNA library. The longest insert contained 2384 nucleotides with an open reading frame of 754 residues. The deduced amino acid sequence showed 33.6% and 34.1% overall identity with the human Bf and C2 sequences, respectively, hence this clone was named medakaBf/C2. The single-copy medakaBf/C2 gene had exactly the same exon-intron organization as the mammalianBf andC2 genes, and spanned about 8 kilobases. TheBf/C2 locus was mapped to the close proximity (2.9cM) of the superoxide dismutase locus on the linkage group XX by the use of a restriction site polymorphism between two inbred strains of the medaka.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aviv, H. and Leder, P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acidcellulose.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 69: 1408–1412, 1972
Bartl, S. and Weissman, I. L. Isolation and characterization of major histocompatibility complex class II B genes from the nurse shark.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 262–266, 1994
Bentley, D. R. Primary structure of human complement component C2. Homology to two unrelated protein families.Biochem J 239: 339–345, 1986
Carroll, M. C., Campbell, R. D., Bentley, D. R., and Porter, R. R. A molecular map of the human major histocompatibility complex class III region linking complement genes C4, C2 and factor B.Nature 307: 237–241, 1984
Chaplin, D. D., Woods, D. E., Whitehead, A. S., Goldberger, G., Colten, H. R., and Seidman, J. G. Molecular map of the murineS region.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80: 6947–6951, 1983
Davis, B. J. Dis electrophoresis-II. Method and application to human serum proteins.Ann N Y Acad Sci 121: 404–427, 1964
Dodds, A. W. and Day, A. J. The phylogeny and evolution of the complement system.In K. Whaley, M. Loos, and J. M. Weiler (eds.):Immunology and Medicine, pp. 39–88, Kluwer Academic Publishers, London, 1993
Flajnik, M. F., Canel, C., Kramer, J., and Kasahara, M. Evolution of the major histocompatibility complex: molecular cloning of major histocompatibility complex class I from the amphibianXenopus.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 537–541, 1991
Greenhalgh, P. and Steiner, L. A. Recombination activating gene 1 (Rag 1) in zebrafish and shark.Immunogenetics 41: 54–55, 1995
Grimholt, U., Hordvik, I., Fosse, V. M., Olsaker, I., Endresen, C., and Lie, Ø. Molecular cloning of major histocompatibility complex class I cDNAs from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar).Immungenetics 37: 469–473, 1993
Hashimoto, K., Nakanishi, T., and Kurosawa, Y. Isolation of carp genes encoding major histocompatibility complex antigens.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 6863–6867, 1990
Hashimoto, K., Nakanishi, T., and Kurosawa, Y. Identification of a shark sequence resembling the major histocompatibility complex class I α3 domain.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 2209–2212, 1992
Hinds, K. R., and Litman, G. W. Major reorganization of immunoglobulin VH segmental elements during vertebrate evolution.Nature 320: 546–549, 1986
Hordvik, I., Grimholt, U., Fosse, V. M., Lie, Ø., and Endresen, C. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNAs encoding theMHC class II β chain in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar).Immunogenetics 37: 437–441, 1993
Horiuchi, T., Kim, S., Matsumoto, M., Watanabe, I., Fujita, S., and Volanakis, J. E. Human complement factor B: cDNA cloning, nucleotide sequencing, phenotypic conversion by site-directed mutagenesis and expression.Mol Immunol 30: 1587–1592, 1993
Ishikawa, N., Nonaka, M., Wetsel, R. A., and Colten, H. R. Murine complement C2 and factor B genomic and cDNA cloning reveals different mechanisms for multiple transcripts of C2 and B.J Biol Chem 265: 19040–19046, 1990
Jensen, J. A., Festa, E., Smith, D. S., and Cayer, M. The complement system of the nurse shark: hemolytic and comparative characteristics.Science 214: 566–569, 1981
Kandil, E., Namikawa, C., Nonaka, M., Greenberg, A. S., Flajnik, M. F., Ishibashi, T., and Kasahara, M. Isolation of low molecular mass polypeptide complementary DNA clones from primitive vertebrates: implication for the origin of MHC class I-restricted antigen presentation.J Immunol 156: 4245–4253, 1996
Kasahara, M., Vazquez, M., Sato, K., McKinney, E. C., and Flajnik, M. F. Evolution of the major histocompatibility complex: Isolation of class II A cDNA clines from the cartilaginous fish.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 6688–6692, 1992
Kato, Y., Salter-Cid, L., Flajnik, M. F., Kasahara, M., Namikawa, C., Sasaki, M., and Nonaka, M. Isolation of theXenopus complement factor B complementary DNA and linkage of the gene to the frog MHC.J Immunol 153: 4546–4554, 1994
Kato, Y., Salter-Cid, L., Flajnik, M. F., Namikawa, C., Sasaki, M., and Nonaka, M. Duplication of the MHC-linkedXenopus complement factorB gene.Immunogenetics 42: 196–203, 1995
Krumdieck, R. and Volanakis, J. E. Construction and expression of complement factor B/C2 chimeras of the region encoded by exon 15.Abstract book, The 9th International Congress of Immunology, p. 102, 1995
Kubota, Y., Shimada, A., and Shima, A. DNA alterations detected in the progeny of paternally irradiated Japanese medaka fish (Oryzias latipes).Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 330–334, 1995
Lambris, J. D., Lao, Z., Pang, J., and Alsenz, J. Third component of trout complement. cDNA cloning and conservation of functional sites.J Immunol 151: 6123–6134, 1993
Lambris, J. D., Pappas, J., Mavroidis, M., Wang, Y., Manzone, H., Swager, J., Pasquier, L. D., and Silibovsky, R. The third component ofXenopus complement: cDNA cloning, structural and functional analysis, and evidence for an alternate C3 transcript.Eur J Immunol 25: 572–578, 1995
Mo, R., Kato, Y., Nonaka, M., Nakayama, K., and Takahashi, M. Fourth component ofXenopus laevis complement: cDNA cloning and linkage analysis of the frogMHC.Immunogenetics 43: 360–369, 1996
Namikawa, C., Salter-Cid, L., Flajnik, M. F., Kato, Y., Nonaka, M., and Sasaki, M. Isolation ofXenopus LMP-7 homologues. Striking allelic diversity and linkage to MHC.J Immunol 155: 1964–1971, 1995
Nonaka, M., Yamaguchi, N., Natsuume-Sakai, S., and Takahashi, M. The complement system of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). I. Identification of the serum lytic system homologous to mammalian complement.J Immunol 126: 1489–1494, 1981
Nonaka, M., Fujii, T., Kaidoh, T., Natsuume-Sakai, S., Nonaka, M., Yamaguchi, N., and Takahashi, M. Purification of a lamprey complement protein homologous to the third component of the mammalian complement system.J Immunol 133: 3242–3249, 1984
Nonaka, M. and Takahashi, M. Complete complementary DNA sequence of the third component of complement of lamprey. Implication for the evolution of thioester containing proteins.J Immunol 148: 3290–3295, 1992
Nonaka, M., Takahashi, M., and Sasaki, M. Molecular cloning of a lamprey homologue of the mammalian MHC class III gene, complement factor B.J Immunol 152: 2263–2269, 1994
Ono, H., Klein, D., Vincek, V., Figueroa, F., O’hUigin, C., Tichy, H., and Klein, J. Major histocompatibility complex class II genes of zebrafish.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 11886–11890, 1992
Ono, H., Figueroa, F., O’hUigin, C., and Klein, J. Cloning of the β2-microglobulin gene in the zebrafish.Immunogenetics 38: 1–10, 1993a
Ono, H., O’hUigin, C., Vincek, V., Stet, R. J. M., Figueroa, F., and Klein, J. New β chain-encodingMhc class II genes in the carp.Immunogenetics 38: 146–149, 1993b
Rast, J. P. and Litman, G. W. T-cell receptor gene homologs are present in the most primitive jawed vertebrates.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 9248–9252, 1994
Saiki, R. K., Gelfand, D. H., Stoffel, S., Scharf, S. J., Higuchi, R., Horn, G. T., Mullis, K. B., and Erlich, H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase.Science 239: 487–491, 1988
Saitou, N. and Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees.Mol Biol Evol 4: 406–425, 1987
Salter-Cid, L., Kasahara, M., and Flajnik, M. F.HSP70 genes are linked to theXenopus major histocompatibility complex.Immunogenetics 39: 1–7, 1994
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S., and Coulson, A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 5463–5467, 1977
Sato, K., Flajnik, M. F., Pasquier, L. D., Katagiri, M., and Kasahara, M. Evolution of the MHC: Isolation of class II β-chain cDNA clones from the amphibianXenopus laevis.J Immunol 150: 2831–2843, 1993
Seeger, A., Mayer, W. E., and Klein, J. A complement factor B like cDNA clone from the zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio).Mol Immunol 32: 511–520, 1996
Shima, A. and Shimada, A. Development of a possible nonmammalian test system for radiation-induced germ-cell mutagenesis using a fish, the Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes).Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 2545–2549, 1991
Shum, B. P., Avila, D., Pasquier, L. D., Kasahara, M., and Flajnik, M. F. Isolation of a classical MHC class I cDNA from an amphibian. Evidence for only one class I locus in theXenopus MHC.J Immunol 151: 5376–5386, 1993
Smith, L. C., Chang, L., Britten, R. J., and Davidson, E. H. Sea urchin genes expressed in activated coelomocytes are identified by expressed sequence tags.J Immunol 156: 593–602, 1996
Stanley, K. K. and Herz, J. Topological mapping of complement component C9 by recombinant DNA techniques suggests a novel mechanism for its insertion into targen membranes.EMBO J 6: 1951–1957, 1987
Tanaka, M., Fukada, S., Matsuyama, M., and Nagahama Y. Structure and promoter analysis of the cytochromeP-450 aromatase gene of the teleost fish, medaka (Oryzias latipes).J Biochem 117: 719–725, 1995
Thomas, P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77: 5201–5205, 1980
Thompson, J. D., Higgins, D. G., and Gibson, T. J. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice.Nucleic Acids Res 22: 4673–4680, 1994
Wada, H., Naruse, K., Shimada, A., and Shima, A. Genetic linkage map of a fish, the Japanese medakaOryzias latipes.Mol Marine Biol Biotech 4: 269–274, 1995
Wu, L., Morley, B. J., and Campbell, R. D. Cell-specific expression of the human complement protein factor B gene: Evidence for the role of two distinct 5′-flanking elements.Cell 48: 331–342, 1987
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The nucleotide sequence data reported in this paper have been submitted to the GenBank, DDBJ, EMBL, and NCB1 nucleotide sequence databases and have been assigned the accession number D84063
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuroda, N., Sasaki, M., Nonaka, M. et al. Molecular cloning and linkage analysis of the Japanese medaka fish complementBf/C2 gene. Immunogenetics 44, 459–467 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02602808
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02602808