Abstract
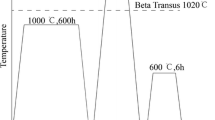
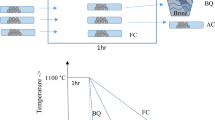
The effect of added oxygen in the range of 1000 to 4000 wt ppm on the microstructures of a Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb alloy has been investigated and compared to the microstructures for a high-purity alloy. For specimens cooled from theα phase, interstitial oxygen stabilizes the lamellar microstructure with respect toγ grains, with higher than equilibrium values for theα 2 volume fraction. For specimens cooled from theα +γ phase field, the lamellar microstructure still tends to be favored by oxygen, but it is found that the phase volume fractions are not significantly different from equilibrium values. This suggests that interstitial O essentially reduces the kinetics of theα toα +γ transformation. Thus, interstitial oxygen will have a strong effect on microstructures obtained by continuous cooling fromα, but significantly less on those, such as the duplex microstructure, obtained by long treatment in theα +γ phase field. In general, increased O content is well correlated with reduced ductility. Finally, the role of interstitial oxygen on this phase transformation is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.M. Dimiduk:Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1999, vol. 263, pp. 281–88.
Y.-W. Kim:Materials Research Society Symp. Proc., Materials Research Society, Pittsburgh, PA, 1991, vol. 213, pp. 777–94.
S.C. Huang and E.L. Hall:Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 2619–27.
D.W. McKee and S.C. Huang:Corr. Sci., 1992, vol. 33, pp. 1899–914.
S.C. Huang: inStructural Intermetallics, R. Darolia, J.J. Lewandowski, C.T. Liu, P.L. Martin, D.B. Miracle, and M.V. Nathal, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1993, pp. 299–307.
J. Beddoes, W. Wallace, and L. Zhao:Int. Mater. Rev., 1995, vol. 40, pp. 197–217.
C. Ouchi, H. Iizumi, and S. Mitao:Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1998, vol. 243, pp. 186–95.
A. Menand, A. Huguet, and A. Nerac-Partaix:Acta Mater., 1996, vol. 12, pp. 4729–37.
A. Menand, H. Zapolsky-Tatarenko, and A. Nerac-Partaix:Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1998, vol. 250, pp. 55–64.
A. Menand, E. Cadel, C. Pareige, and D. Blavette:Ultramicroscopy, 1999, vol. 78, pp. 63–72.
E.L. Hall and S.C. Huang: inMicrostructure/Property Relationships in Titanium Aluminides and Alloys, Y.-W. Kim and R.R. Boyer, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1991, pp. 47–64.
W. Lefebvre, A. Menand, A. Loiseau, and D. Blavette:Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, vol. 327, pp. 40–46.
B.-J. Lee and N. Saunders:Z. Metallkd., 1997, vol. 88, pp. 152–61.
F. Perdrix: Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paris-Sud, France, 2000.
F. Perdrix, M. Cornet, J. Bigot, and J.-P. Chevalier:J. Phys IV France, 2000, vol. 10, Pr6, pp. 15–20.
J. Bigot:C.R. Acad. Sci. Paris, 1974, vol. 279, Ser. C, pp. 67–69.
J. Bigot: Ph.D. Thesis, Faculté des Sciences de Paris, Paris, 1969.
M. Lamirand: Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paris XII, Créteil, 2004.
J.-P. Dallas: CECM-CNRS, Vitry, private communication, 1998.
F. Perdrix, M.F. Trichet, J.L. Bonnentien, M. Cornet, and J. Bigot:Intermetallics, 1999, vol. 7, pp. 1323–28.
N. Saunders: inGamma Titanium Aluminides, Y.-W. Kim, D.M. Dimiduk, and M.H. Loretto, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1999, pp. 183–88.
F.B. Pickering:Physical Metallurgy and the Design of Steels, Applied Science Publishers, London, 1978.
C. Angelier and J. Béchet: InBeta Titanium Alloys, A. Vassel, D. Eylon, and Y. Combres, eds., Revue de Métallurgie, Paris, 1994, no. 8, pp. 127–33.
M. Göken, M. Kempfand, and W.D. Nix:Acta Mater., 2001, vol. 49, pp. 903–11.
P.M. Hazzledine and D.M. Dimiduk: inGamma Titanium Aluminides, Y.-W. Kim, D.M. Dimiduk, and M.H. Loretto, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1999, pp. 481–87.
H. Inui, K. Kishida, M. Misaki, M. Kobayashi, Y. Shirai, and M. Yamagushi:Phil. Mag. A, 1995, vol. 72, pp. 1609–31.
R.C. Pond, P. Shang, T.T. Cheng, and M. Aindow:Acta Mater., 2000, vol. 48, pp. 1047–53.
Y. Mishin and C. Herzig:Acta Mater., 2000, vol. 28, pp. 589–623.
D.E. Larsen: United State Patent no. 5,685,924 (Nov. 11, 1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lamirand, M., Bonnentien, J.L., Guérin, S. et al. Effects of interstitial oxygen on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb with fully lamellar and duplex microstructures. Metall Mater Trans A 37, 2369–2378 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02586211
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02586211