Summary
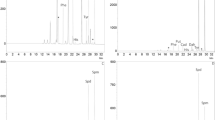
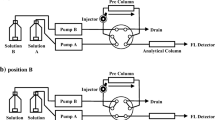
The reagentp-nitrobenzyloxycarbonyl chloride (PNZ-CI) was used for pre-column derivatization of biogenic amines (BAs) at ambient temperature followed by reversed-phase, liquid-chromatographic separation of the derivatives. Optimized derivatization of samples was achieved within 10 min in borate buffer by adding PNZ-Cl in acetonitrile (MeCN). Excess reagent was scavenged by subsequent addition of glycine in water. For LC a Superspher® RP-18e column and gradient elution using a ternary gradient system containing sodium acetabe buffer (pH 6.1), sodium acetate buffer (pH 4.3) and MeCN, were used. The PNZ-derivatives were quantified by their UV-absorption at 265 nm. Detection limits of BAs were approximately 62–1000 μg L−1 (injected amounts: 53–850 pg) at a signal-to-noise ratio of 3:1. The coefficients of determination were 0.9906–0.9992. Diaminohexane was used as internal standard. Recoveries of BAs ranged from 78–93% depending on the food matrix. This method was applied to the quantitative determination of 2-phenylethylamine, tryptamine, serotonin, putrescine, histamine, cadaverine, tyramine, spermidine, and spermine, in beer, wine, vinegars, and lactic fermented cabbage juice.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Cad:
-
cadaverine (1,5-diaminopentane)
- Dhx:
-
1,6-diaminohexane (internal standard)
- Him:
-
histamine
- Ocp:
-
octopamine
- Pea:
-
2-phenylethylamine
- Put:
-
putrescine (1,4-diaminobutane)
- Seo:
-
serotonin
- Spd:
-
spermidine
- Spm:
-
spermine
- Trm:
-
tryptamine
- Tym:
-
tyramine
References
A. Askar, H. Treptow, “Biogene Amine in Lebensmitteln,” Ulmer, 1986, Stuttgart, Germany.
J. A. Maga, CRC Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr.10, 373 (1978).
M. H. Silla Santos, Int. J. Food Microbiol.29, 213 (1996).
E. Karmas, Lebensm. Wiss. Technol.14, 273 (1981).
M. T. Veciana-Nogues, A. Marine-Font, M. C. Vidal-Carou, J. Agric. Food Chem.45, 2036 (1997).
D. M. Beutling (ed), “Biogene Amine in der Ernährung”, Springer, 1996, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, Germany.
N. Seller, L. Demisch, H. Schneider, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.10, 51 (1971).
D. Hornero, A. Garrido, Analyst119, 2037 (1995).
A. Halsáz, A. Baráth, L. Simon-Sarkadi, w. Holzapfel, J. Food Sci. Technol.5, 42 (1994)
A. R. Shalaby, Food Res. Int.29, 675 (1996).
J. P. Gouygou, C. Martin, C. Sinquin, P. Durand, Oceanis15, 599 (1989).
M. Leclerq, L. Gouilloux, Technol. Biol.5, 212 (1989).
C. Beyer, A. Van den Ende, Clin. Chim. Acta129, 211 (1983).
S. Yamamoto, H. Itano, H. Kataoka, M. Makita, J. Agric. Food. Chem.30, 435 (1982).
I. Rodriguez, H. K. Lee, S. F. Y. Li, J. Chromatogr. A745, 255 (1996).
O. Busto, J. Guasch, F. Borrull, J. Chromatogr. A737, 205 (1996).
J. Kirschbaum, B. Luckas, W.-D. Beinert, J. Chromatogr. A661, 193 (1994).
J. Kirschbaum, I. Busch, H. Brückner, Chromatographia45, 263 (1997).
O. Busto, M. Mestres, J. Guasch, F. Borrull, Chromatographia40, 404 (1995).
M. Vallé, P. Malle, S. Bouquelet, J. AOAC Int.80, 49 (1997).
A. Bockhardt, I. Krause, H. Klostermeyer, Z. Lebensm. Unters. Forsch.203, 65 (1996).
H. Brückner, M. Lüpke, J. Chromatogr. A697, 295 (1995).
M. Izquierdo-Pulido, A. Mariné-Font, M. C. Vidal-Carou, J. Food Sci.59, 1104 (1994).
M. Izqierdo-Pulido, J. Font-Fábregas, J. M. Carceller-Rosa, A. mariné-Font, M. C. Vidal-Carou, J. Food Prot.60, 831 (1997).
M. Izqierdo-Pulido, J. Font-Fábregas, M. C. Vidal-Carou, Food Chem.54, 51 (1995).
M. Jackson, “Michael Jackson's Beer Companion”, 1993, Duncan Baird Publishers, London.
T. Bauza, A. Blaise, P. L. Teissedre, J. P. Mestres, F. Daumas, J. C. Cabanis, Sciences des Aliments15, 559 (1995).
J. C. Rivas-Gonzalo, J. F. Santos-Hernandez, A. Marine-Font, J. Food Sci.48, 417 (1983).
B. Blackwell, L. A. Mabbitt, E. Marley, J. Food Sci.34, 47 (1969).
O. Busto, Y. Valero, J. Guasch, F. Borrull, Chromatographia38, 571 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kirschbaum, J., Meier, A. & Brückner, H. Determination of biogenic amines in fermented beverages and vinegars by pre-column derivatization withpara-nitrobenzyloxycarbonyl chloride (PNZ-Cl) and reversed-phase LC. Chromatographia 49, 117–124 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02575272
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02575272