Abstract
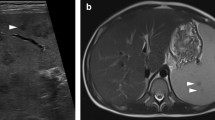
Neutropenic typhlitis is a frequently fatal disease most commonly reported in leukemics. The authors have treated eight such patients over the last 18 months. All patients had abdominal pain and sepsis during chemotherapy-induced neutropenia. CT scanning was diagnostic in six patients thought to have typhlitis. Two patients were not diagnosed before exploratory laparotomy. The authors have found nonoperative treatment highly effective in patients who do not manifest signs of peritonitis, perforation, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, or clinical deterioration. Recurrent typhlitis was frequent after conservative therapy (recurrence rate, 67 percent), however. One patient underwent an elective right hemicolectomy after a second episode, and typhlitis did not recur despite neutropenia associated with a subsequent course of chemotherapy. It is concluded that successful treatment of this disease hinges on: 1) early diagnosis provided by a high index of suspicion and the use of CT scanning, 2) nonoperative treatment for uncomplicated cases, and 3) elective right hemicolectomy to prevent recurrence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dosik GM, Luna M, Valdivieso M, et al. Necrotizing colitis in patients with cancer. Am J Med 1979;67:646–56.
Slavin RE, Dias MA, Saral R. Cytosine arabinoside induced gastrointestinal toxic alterations in sequential chemotherapeutic protocols. Cancer 1978;42:1747–59.
Steinberg D, Gold J, Brodin A. Necrotizing enterocolitis in leukemia. Arch Intern Med 1973;131:538–44.
Mower WJ, Hawkins JA, Nelson EW. Neutropenic enterocolitis in adults with acute leukemia. Arch Surg 1986;121:571–3.
Shaked A, Shinar E, Freund H. Neutropenic typhlitis: a plea for conservatism. Dis Colon Rectum 1983;26:351–2.
Shamberger RC, Weinstein HJ, Delorey MJ, et al. The medical and surgical management of typhlitis in children with acute nonlymphocytic (myelogenous) leukemia. Cancer 1986;57:603–9.
Moir CR, Scudamore CH, Benny WB. Typhlitis: selective surgical management. Am J Surg 1986;151:563–6.
Varki AP, Armitage JO, Feagler JR. Typhlitis in acute leukemia. Cancer 1979;43:695–7.
Kingry RL, Hobson RW, Muir RW. Cecal necrosis and perforation with systemic chemotherapy. Am Surg 1973;39:129–33.
Kies MS, Luedke DW, Boyd JF, McCue MJ. Neutropenic enterocolitis: two case reports of long-term survival following surgery. Cancer 1979;43:730–4.
Gandy W, Greenberg BR. Successful medical management of neutropenic enterocolitis. Cancer 1983;51:1551–5.
Alt B, Glass NR, Sollinger H. Neutropenic enterocolitis in adults: review of the literature and assessment of surgical intervention. Am J Surg 1985;149:405–8.
Lea JW, Masys DR, Shackford SR. Typhlitis: a treatable complication of acute leukemia therapy. Cancer Clin Trials 1980;3:355–62.
Kunkel JM, Rosenthal D. Management of the ileocecal syndrome: neutropenic enterocolitis. Dis Colon Rectum 1986;29:196–9.
Wagner ML, Rosenberg HS, Fernbach DJ, Singleton EB. Typhlitis: a complication of leukemia in childhood. AJR 1970;109:341–50.
Ryan ME, Morrissey JF. Typhlitis complicating methimazole-induced agranulocytosis. Gastrointestinal Endosc 1983;29:299–302.
Geelhoed GW, Kane MA, Dale DC, Wells SA. Colon ulceration and perforation in cyclic neutropenia. J Pediatr Surg 1973;8:379–82.
Bingold LP, Harvey HP. Necrotizing enterocolitis associated with invasion by clostridium septicum complicating cyclic neutropenia. Aust NZ J Med 1979;9:426–9.
Pokorney BH, Jones JM, Shaikh BS, Aber RC. Typhlitis: a treatable cause of recurrent septicemia. JAMA 1980;243:682–3.
Hopkins DG, Kushner JP. Clostridial species in the pathogenesis of necrotizing enterocolitis in patients with neutropenia. Am J Hematol 1983;14:289–95.
Ikard RW. Neutropenic typhilitis in adults. Arch Surg 1981;116:943–5.
Prolla JC, Kirsner JB. The gastrointestinal lesions and complications of the leukemias. Ann Intern Med 1964;61:1084.
Boley SJ. Vascular disorders of the intestine. New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts, 1971.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Keidan, R.D., Fanning, J., Gatenby, R.A. et al. Recurrent typhlitis. Dis Colon Rectum 32, 206–209 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02554529
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02554529