Abstract
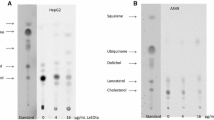
Exposure of primary rat hepatocytes and human HepG2 cells to water-soluble garlic extracts resulted in the concentration-dependent inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis at several different enzymatic steps. At low concentrations, sterol biosynthesis from [14C]acetate was decreased in rat hepatocytes by 23% with an IC50 (half-maximal inhibition) value of 90μg/mL and in HepG2 cells by 28% with an IC50 value of 35 μg/mL. This inhibition was exerted at the level of hydroxymethylglutaryl-COA reductase (MHG-CoA reductase) as indicated by direct enzymatic measurements and the absence of inhibition if [14C]mevalonate was used as a precursor. At high concentrations (above 0.5 mg/mL), inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis was not only seen at an early step where it increased considerably with dose, but also at later steps resulting in the accumulation of the precursors lanosterol and 7-dehydrocholesterol. No desmosterol was formed which, however, was a major precursor accumulating in the presence of triparanol. Thus, the accumulation of sterol precursors seem to be of less therapeutic significance during consumption of garlic, because it requires concentrations one or two orders of magnitude above those affecting HMG-CoA reductase. Alliin, the main sulfur-containing compound of garlic, was without effect itself. If converted to allicin, it resulted in similar changes of the sterol pattern. This suggested that the latter compound might contribute to the inhibition at the late steps. In contrast, nicotinic acid and particularly adenosine caused moderate inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase activity and of cholesterol biosynthesis suggesting that these compounds participate, at least in part, in the early inhibition of sterol synthesis by garlic extracts.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HMG-CoA reductase:
-
hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase (EC 1.1.1.34)
- IC50 :
-
the concentration for half-maximal inhibition
- LDH:
-
lactate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.27)
- SI-TLC:
-
silverion thin-layer chromatography
References
Augusti, K.T., and Mathew, P.T. (1973)Ind. J. Exp. Biol. 11, 239–241.
Jain, R.C. (1975)Artery 1, 115–125.
Jain, R.C., and Vyas, C.R. (1975)Artery 1, 363–364.
Reuter, H.D. (1988) inArzneimitteltherapie heute (Berufsverband Deutscher Internisten, ed.) Vol. 1, pp. 13–64, Aesopus Verlag, Zug.
Mader, F.H. (1990)Arzneim-Forsch/Drug. Res. 40, 1111–1116.
Vorberg, G., and Schneider, B. (1990)Br. J. Clin. Practice 44 (Suppl. 69, 7–11.
Davis, R.A., Engelhorn, S.C., Pangburn, S.H., Weinstein, D.B., and Steinberg, D. (1979)J. Biol. Chem. 254, 2010–2016.
Havel, C., Hansbury, E., Scallen, T.J., and Watson, J.A. (1979)J. Biol. Chem. 254, 9573–9582.
Bell-Quint, J., and Forte, T. (1981)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 663, 83–98.
Aufenanger, J., Pill, J., Schmidt, F.H., and Stegmeier, K. (1986)Biochem. Pharmacol. 35, 911–916.
Gebhardt, R. (1986) inResearch in Isolated and Cultured Hepatocytes (Guguen-Guillouzo, C., and Guillouzo, A., eds.) pp. 353–375, John Libbey Eurotex, London, INSERM, Paris.
De La Vaga, F.M., and Mendoza-Figueroa, T. (1991)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1081, 293–300.
Ugele, B., Kempen, H.J.M., Gebhardt, R., Meijer, P., Burger, H.-J., and Princen, H.M.G. (1991)Biochem. J. 276, 73–77.
Kempen, H.J., Van Son, K., Cohen, L.H., Griffioen, M., Verboom, H., and Havekes, L. (1987)Biochem. Pharmacol. 36, 1245–1249.
Boogaard, A., Griffioen, M., and Cohen, L.H. (1987)Biochem. J. 241, 345–351.
Ranganathan, S., and Kottke, B.A. (1989)Hepatology 9, 547–551.
Gebhardt, R. (1991)Arzneim-Forsch/Drug Res. 41, 800–804.
Müller, B. (1989)Dtsch. Apoth. Ztg. 46, 2500–2504.
Iberl, B., Winkler, G., Müller, B., and Knobloch, K. (1990)Planta Med. 56, 320–326.
Gebhardt, R., Fitzke, H., Fausel, M., Eisenmann-Tappe, I., and Mecke, D. (1990)Cell Biol. Toxicol. 6, 365–378.
Gebhardt, R., and Jung, W. (1982)J. Cell Sci. 56, 233–244.
Fahrner, J., Labruyere, W.T., Gaunitz, C., Moorman, A.F.M., Gebhardt, R., and Lamers, W.H. (1993)Eur. J. Biochem. 213, 1067–1073.
Pill, J., Aufenanger, J., Stegmeier, K., Schmidt, F.H., and Müller, D. (1987)Fresenius Z. Anal. Chem. 327, 558–560.
Shapiro, D.J., Nordstrom, J.L., Mitchelen, J.J., Rodwell, J.W., and Schimke, R.T. (1974)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 370, 369–377.
Nepokroeff, C.M., Lakshmanan, M.R., and Porter, J.W. (1975)Methods Enzymol. 35, 37–44.
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., and Randall, R.J. (1951)J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275.
Gebhardt, R. (1991)Medwelt 42 (Suppl. 7a), 12–13.
Qureshi, A.A., Abuirmeileh, N., Din, Z.Z., Elson, C.E., and Burger, W.C. (1983)Lipids 18, 343–348.
Koch, H.P., and Hahn, G. (1988)Knoblauch, pp. 42–72, Urban & Schwarzenberg München.
Glover, J., and Green, C. (1957)Biochem. J. 67, 308–316.
Van-den-Bossche, H., Willemsens, G., Cools, W., Cornelissen, F., Lauwers, W.F., and Van-Cutsem, J.M. (1980)Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 17, 922–928.
Horton, B.J., Horton, J.D., and Sabine, J.R. (1971)Biochim Biophys. Acta 239, 475–481.
Avigan, J., Steinberg, D., Vroman, H.E., Thompson, M.J., and Mosettig, E. (1960)J. Biol. Chem. 235, 3123–3126.
Goh, E.H., Colles, S.M., and Otte, K.D. (1989)Lipids 24, 652–655.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedication: This article is dedicated to Prof. Dr. D. Mecke on the occasion of his 60th birthday.
About this article
Cite this article
Gebhardt, R. Multiple inhibitory effects of garlic extracts on cholesterol biosynthesis in hepatocytes. Lipids 28, 613–619 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02536055
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02536055